 |
MMB711S - MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 3 - 1ST OPP - JUNE 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORYSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: MMB711S
COURSE NAME: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 3
SESSION:
JUNE 2022
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION:
3 HOURS
MARKS:
115
FIRSTOPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Ms. V Tjijenda
Dr Markus Schuppler
MODERATOR: Prof RT Mavenyengwa
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
None
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A (15)
QUESTION 1
[10]
State the mode of action for each of the following antimicrobials.
1.1
Zidovudine
(1)
1.2
lsoniazid
(1)
1.3
Amphotericin B
(1)
1.4
Caspofungin
(1)
1.5
Saquinavir
(1)
1.6
MMR vaccine
(1)
1.7
Amantadine
(1)
1.8
Flucytosine
(1)
1.9
Linezolid
(1)
1.10 Rifampicin
(1)
QUESTION 2
[S]
Choose the correct answer and report only the suitable letter next to the
relevant question. One (1) mark for each correct answer.
2.1
With increased levels of oxidizable organic materials in wastewater,
the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) will:
A. increase
B. decrease
C. remain the same
D. increase or decrease depending on the nature of the materials involved
2.2 Microbes are involved in which step(s) of wastewater treatment?
A. primary and secondary
B. primary and tertiary
C. secondary and tertiary
D. secondary only
2.3
Which is an important product of anoxic sewage treatment that is used
further in the wastewater treatment plant?
A.CO2
B. H2
C. H20
D.CH4
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

2.4 Which bacterium is used as an "indicator organism" in drinking water
analysis?
A. Staphylococcus aureus
B. Legione/la pneumophila
C. Enterococcus faecal is
D. Rhone/la aquatilis
2.5 Which enzyme is specific for E. coli and used for their identification as
"Indicator organism" in drinking water analysis?
A. ~-Galactosidase
B. ~-Glucuronidase
C. ~-Glucosidase
D. ~-Amylase
SECTION B (85)
QUESTION 3
[20]
3.1
In 2019, Namibia had 22 cases of leprosy, which was an increase from
the 17 reported in 2018 and 11 in 2017. Name the method used in the
laboratory to diagnose leprosy, the principle and mention the expected
result if positive.
(7)
3.2
What is the function of malachite green in a TB medium
(1)
3.3
Why is it important to identify and treat MOTT infection
(3)
3.4
Explain what is meant by "extensively drug resistant TB".
(3)
3.5
Give the principle of Mycobacterial Growth Indicator Tube automated
System that is widely used for culturing Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
(3)
3.6
Identify the laboratory level suitable for Mycobacteria analysis and
provide any two (2) mechanical engineering requirements.
(3)
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 4
[20]
4.1
Differentiate between thermally monomorphic and dimorphic fungi.
(2)
4.2
4.2.1
4.2.2
4.2.3
The clinical infections caused by dermatophytes are generally referred
to as Ringworm or Tinea. Name the body part affected by the following: (3)
One (1) mark for each correct answer.
Tinea pedis
Tinea unguium
Tinea barbae
4.3
Mention the use of cornmeal agar and the expected results.
(2)
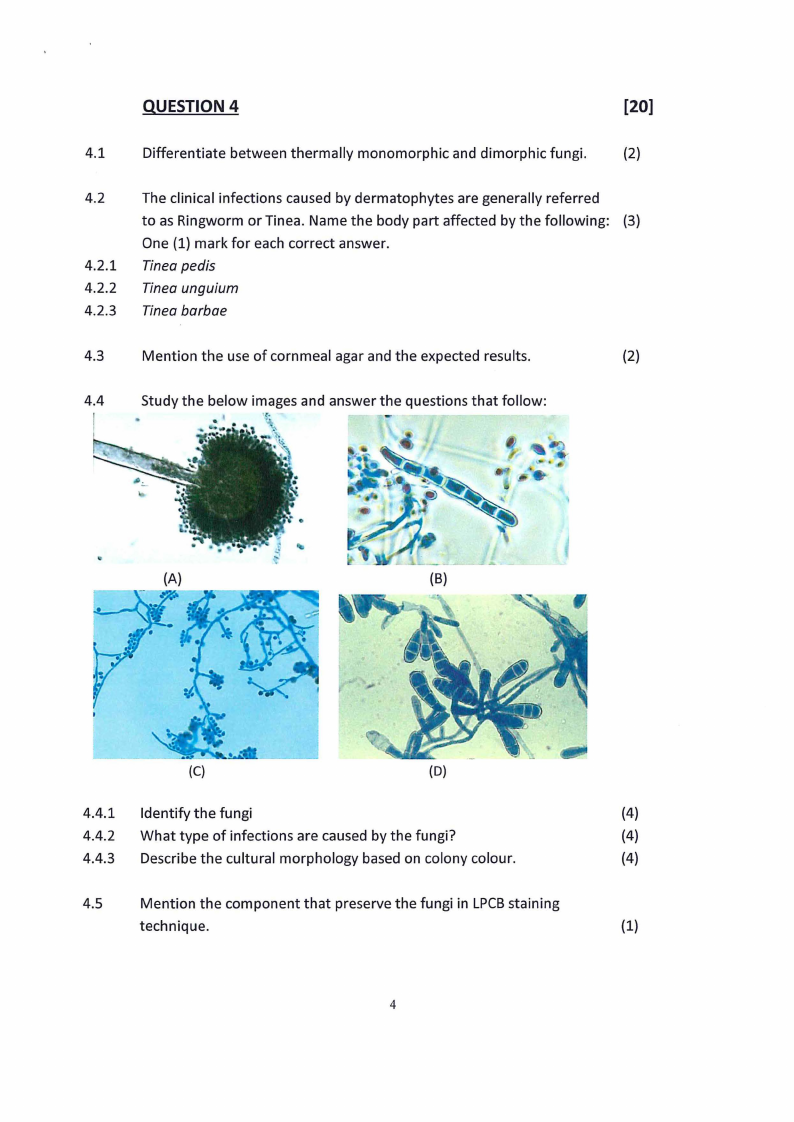
Study the below images and answer the questions that follow:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
4.4.1 Identify the fungi
(4)
4.4.2 What type of infections are caused by the fungi?
(4)
4.4.3 Describe the cultural morphology based on colony colour.
(4)
4.5
Mention the component that preserve the fungi in LPCBstaining
technique.
(1)
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION5
[21]
5.1
Complete the table below. Where there is no intermediate write 'none'.
Copy the table into your answer book.
(16)
Parasite
Echinococuss
granulosus
Toxop/asma
gondii
Schistosoma
spp.
Taenia saginata
Intermediate
host
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
Definitive host Infective stage Diagnostic stage
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
5.2.1 Identify the organism to specie level.
(1)
5.2.2 Summarize the life cycle of this pathogen.
(4)
QUESTION6
[24]
6.1
6.1.1
6.1.2
6.1.3
Differentiate between Marburg virus, Dengue fever and MERS-COVbased
on the following: (Three (3) marks for each correct answer.)
(9)
Virus genome
Type of infection caused
Animal reservoir
6.2
6.2.2
An infant with a loud barking cough presents at the Emergency Room
with laryngotracheobronchitis during a winter outbreak. A viral infection
is suspected.
Provide the most probable clinical diagnosis for this patient. Justify your
answer.
(2)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

6.2.3 Which other virus can be confused with the clinical presentation
of the patient.
(2)
6.2.4 Using the information provided in the case scenario, how did you
differentiate this infection with the infection mentioned in 5.2.3.
(1)
6.3
Describe the pathogenesis of HIV-1 virus.
{8)
6.4
Explain the use of qPCRin HIV diagnosis other than HIV detection.
{2)
SECTION C {15)
QUESTION 7
[15]
7.1 For the statement provided below, decide whether the statement is
True or False. Write only the number and "True" for a true statement
and "False" for a false statement. One (1) mark for each correct answer. (5)
7.1.1
7.1.2
7.1.3
7.1.4
7.1.5
The heat-stable emetic-type enterotoxin Cereulide is formed during
growth of Bacillus cereus in food.
The diarrhea-type enterotoxins of Bacillus cereus are heat-stable and
formed during growth of the bacteria in the small intestine of host.
The food most likely to be contaminated with botulism neurotoxins
are improperly processed home-canned foods?
Difficulty in swallowing, double vision and diarrhea are typical symptoms
of food borne botulism.
Botulin um neurotoxins {BoNTs) prevent the release of acetylcholine from
the nerve end by the cleavage of SNAREproteins
7.2 Listeria monocytogenes is an intracellular pathogen.
7.2.1 Name the steps and the required pathogenicity factors {proteins
or structures) produced by Listeria monocytogenes as displayed in 1.
in the order they are required along the different steps of the infection. (5)
(See figure on next page)
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
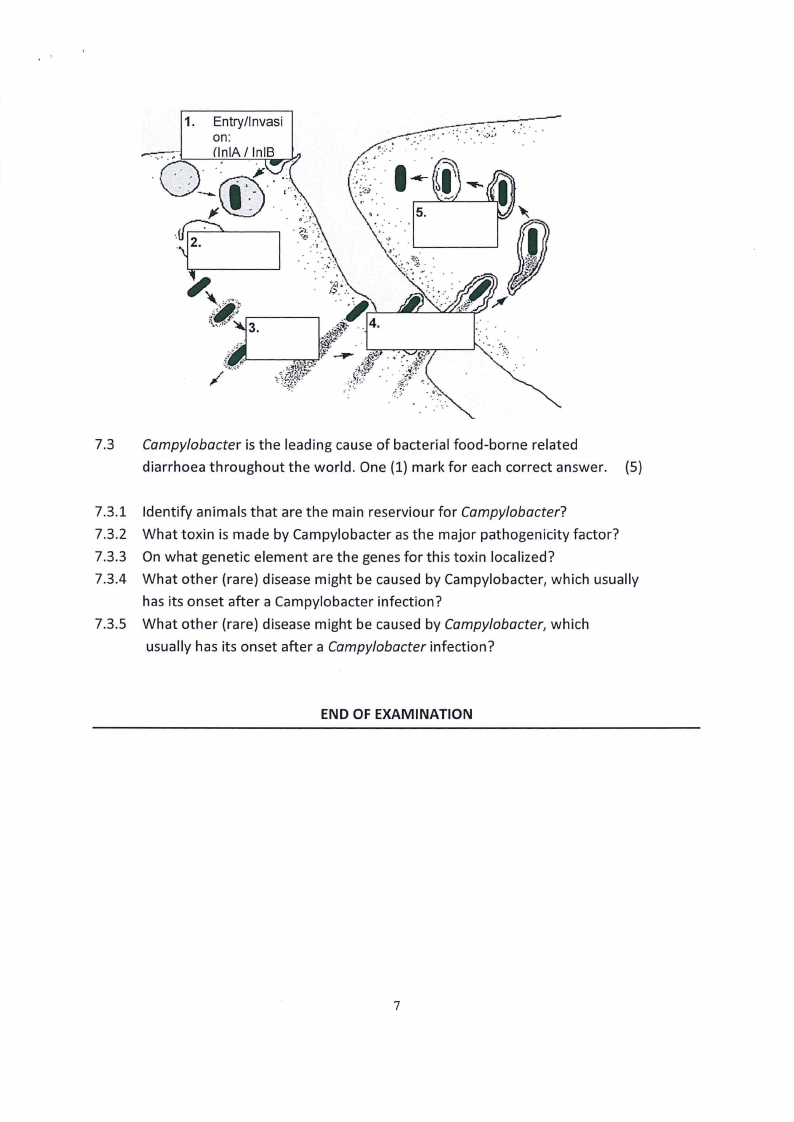
1. Entry/lnvasi
7.3 Campy!obacter is the leading cause of bacterial food-borne related
diarrhoea throughout the world. One (1) mark for each correct answer. (5)
7.3.1
7.3.2
7.3.3
7.3.4
7.3.5
Identify animals that are the main reserviour for Campylobacter?
What toxin is made by Campylobacter as the major pathogenicity factor?
On what genetic element are the genes for this toxin localized?
What other (rare) disease might be caused by Campylobacter, which usually
has its onset after a Campylobacter infection?
What other (rare) disease might be caused by Campy!obacter, which
usually has its onset after a Campylobacter infection?
END OF EXAMINATION
7





