 |
RES511S - REMOTE SENSING 1 - 2ND OPP - JULY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENTOF LANDAND SPATIALSCIENCES
QUALIFICATIONS:
DIPLOMA IN GEOMATICS, BACHELOR OF GEOMATICS, BACHELOR OF GEOINFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY
QUALIFICATIONCODES:
LEVEL:5
06DGEO, 07BGEO, 07BGEI
COURSECODE:RES511S
SESSION:JULY 2024
COURSENAME: REMOTE SENSING 1
PAPER:THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
Ms Roxanne Murangi
MODERATOR: Ms Celeste Espach
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Write your student number on each answer sheet used.
2. Answer ALL the questions.
3. Read each question carefully before attempting to answer.
4. Write clearly and neatly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Non-Programmable Calculator.
2. Pen.
3. Pencil.
4. Eraser and ruler.
This paper consists of three (3) pages (including this cover page).
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Remote Sensing 1
Question 1
RESSllS
Answer the multiple-choice questions listed below. Please select the ONE most relevant
response to the following questions. Indicate the correct answer on the answer sheet.
1.1. The principle that is utilised in obtaining Multispectral Images.
(2)
A. Rainbow Principle
B. Spectral Band
C. Dispersion of Light
D. Spectral Band
1.2. When was the term Remote Sensing used for the first time?
(2)
A. Early 1980s
B. Early 1950s
C. Early 1970s
D. Early 1960s
1.3. In an EM field, which field is placed horizontally?
(2)
A. Gamma rays
B. Sonar field
C. Magnetic field
D. Electric field
1.4. What is the mode of collection of images by scanners called?
(2)
A. Satellite images
B. Electromagnetic images
C. Bit-by-bit
D. Sensing
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 2 of 6
July 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Remote Sensing 1
RESSllS
1.5. There is an artificially generated colour image in which blue, green and red colours are
assigned to the wavelength regions to which they do not belong in nature. It is called. (2)
A. Sensor
B. Electro Magnetic Spectrum
C. FalseColour Composite
D. Spectral Band
(10]
Question 2
Which of the following statements about Remote sensing is true or false? Indicate True or
Falseon the answer sheet. If the answer is false provide the correct answer.
2.1. Pixels with weak spectral responses receive high digital numbers (ON).
(2)
2.2. Minimum Mapping Unit (MMU) refers to the smallest area or unit that can be
accurately mapped in a particular mapping project or context.
(2)
2.3. EM radiation travelling through the atmosphere is subjected to absorption and
scattering.
(2)
2.4. Multispectral imaging captures images in hundreds or even thousands of narrow
contiguous spectral bands
(2)
2.5. Random or spike noise is very easy to identify and correct.
(2)
[10]
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page3 of 6
July 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
Remote Sensing 1
Question 3
RESSllS
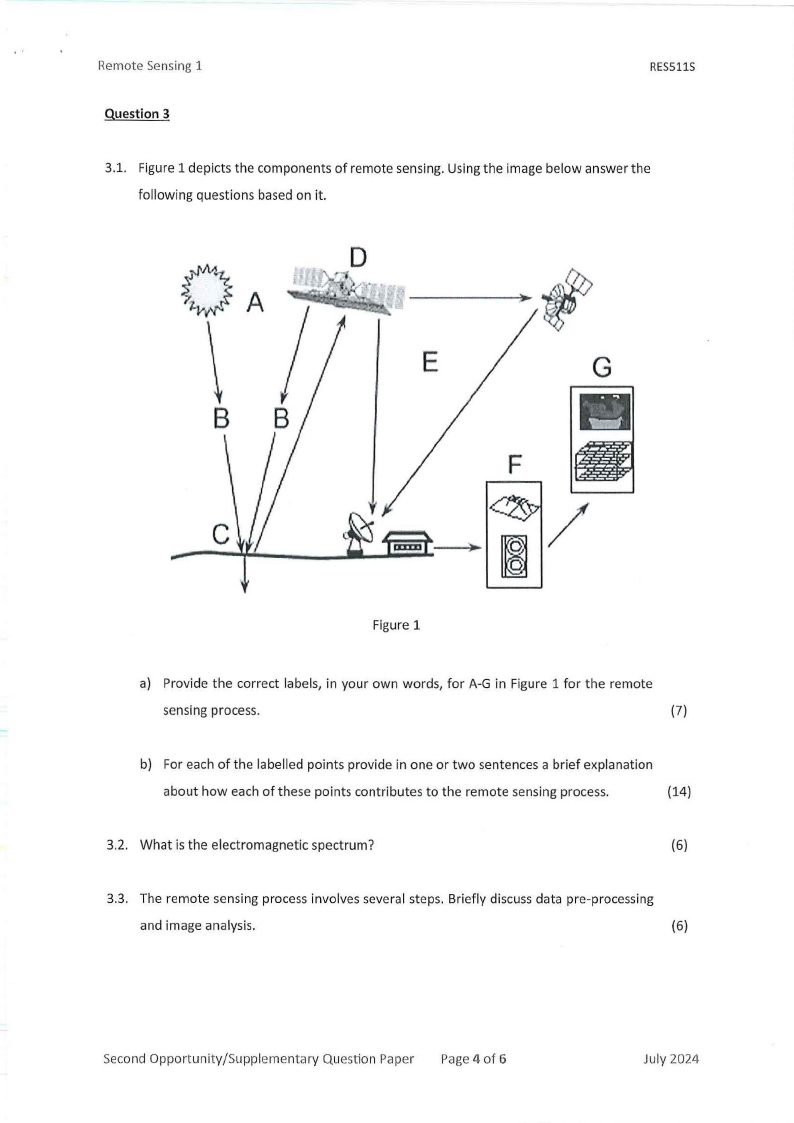
3.1. Figure 1 depicts the components of remote sensing. Using the image below answer the
following questions based on it.
if
G
B
I
I
C
Figure 1
a) Provide the correct labels, in your own words, for A-G in Figure 1 for the remote
sensing process.
(7)
b) For each of the labelled points provide in one or two sentences a brief explanation
about how each of these points contributes to the remote sensing process.
(14)
3.2. What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
(6)
3.3. The remote sensing process involves several steps. Briefly discuss data pre-processing
and image analysis.
{6)
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 4 of 6
July 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
Remote Sensing 1
RESSllS
3.4. There are several advantages and disadvantages of Remote sensing. Discuss the
advantages of versatility and the disadvantages of limited spatial resolution,
respectively.
(4)
3.5. Provide three common phenomena studied at the surface of the sea.
(3)
[40)
Question 4
4.1. Discussthe characteristics of Mie scattering.
(5)
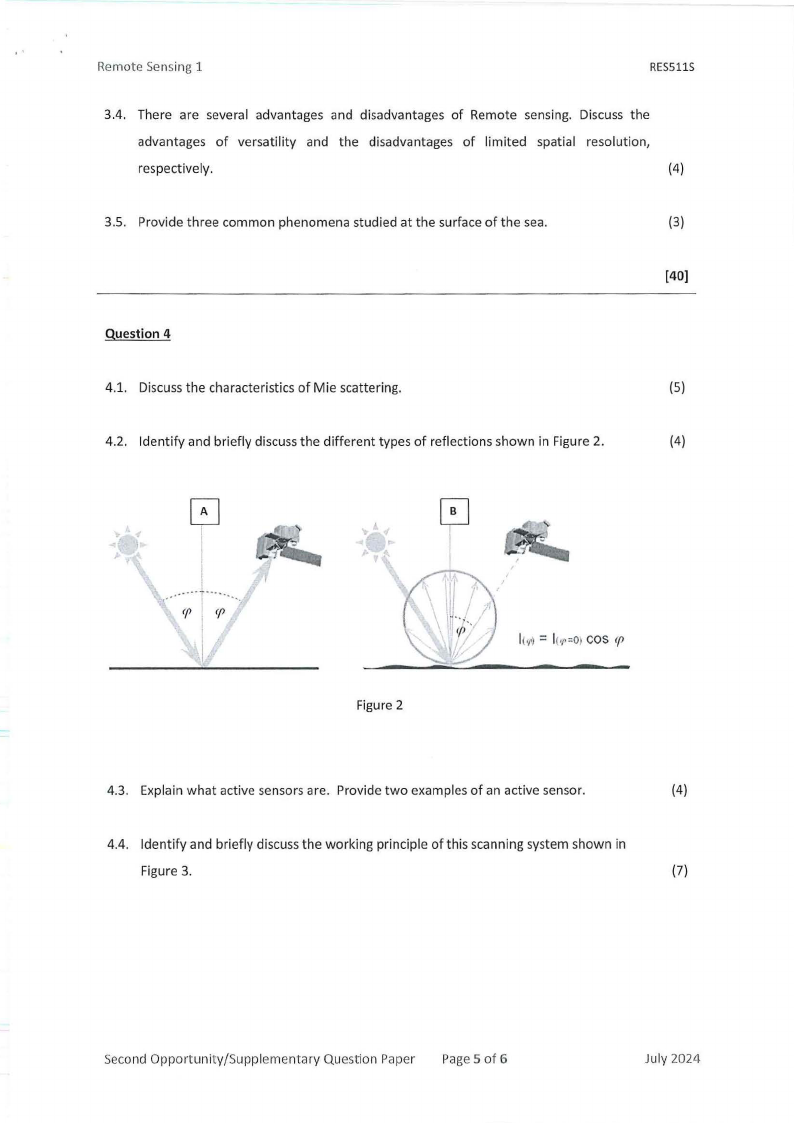
4.2. Identify and briefly discuss the different types of reflections shown in Figure 2.
(4)
Figure 2
l(,rl= lc,r=Oc>os (f>
4.3. Explain what active sensors are. Provide two examples of an active sensor.
(4)
4.4. Identify and briefly discuss the working principle of this scanning system shown in
Figure 3.
(7)
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 5 of 6
July 2024
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
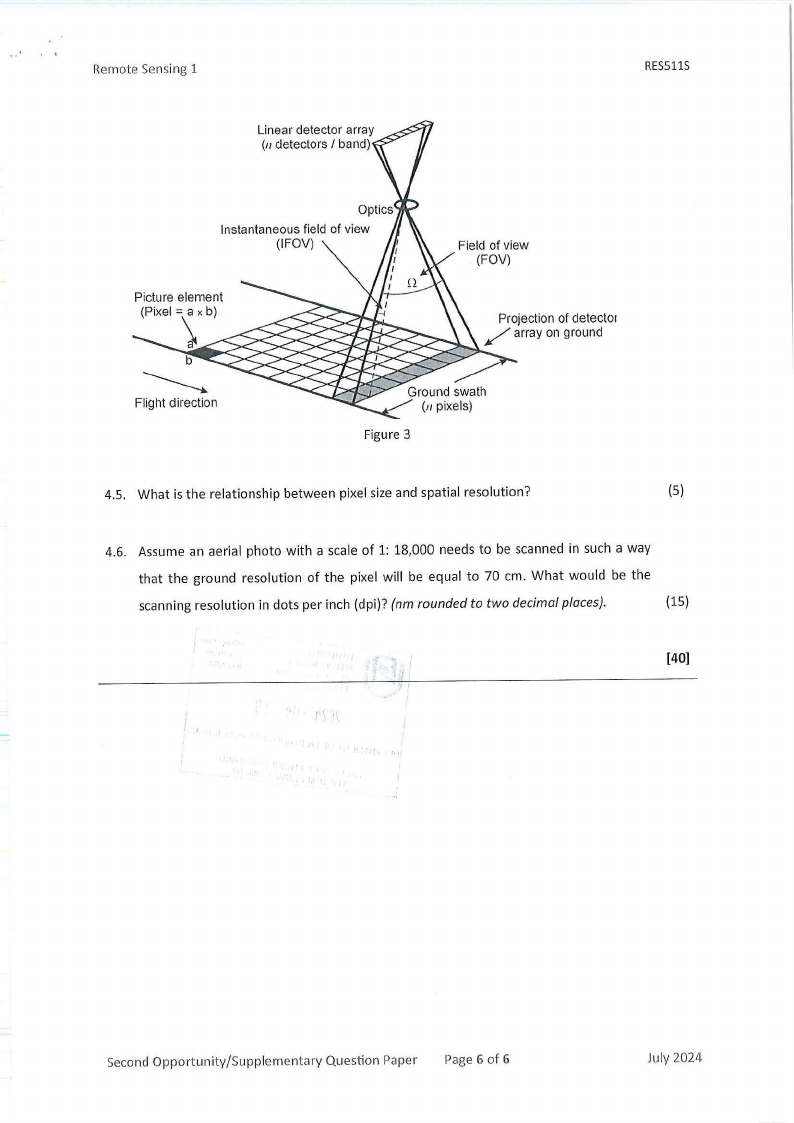
Remote Sensing 1
Linear detector array
(11detectors I band)
RESSllS
Instantaneous field of view
(IFOV)
Picture element
(Pixel = a x b)
Field of view
(FOV)
Projection of cletecto1
/ array on ground
Flight direction
Figure 3
4.5. What is the relationship between pixel size and spatial resolution?
(5)
4.6. Assume an aerial photo with a scale of 1: 18,000 needs to be scanned in such a way
that the ground resolution of the pixel will be equal to 70 cm. What would be the
scanning resolution in dots per inch (dpi)? (nm rounded to two decimal places).
(15)
[40]
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 6 of 6
July 2024





