 |
ALM811S- ADVANCED LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT- 2ND OPP- JULY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF MARKETING, LOGISTICS AND SPORT MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF LOGISTICSAND SUPPLYCHAIN MANAGEMENT HONOURS
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08LSCH
LEVEL: 8
COURSE NAME: ADVANCE LOGISTICS
COURSE CODE: ALM811S
MANAGEMENT
SESSION: JULY 2024
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S)
SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
MS. E ELAGO
MODERATOR: MR B CHICKEN
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Read all the questions carefully before answering.
3. Number the answers clearly.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 4 PAGES {Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
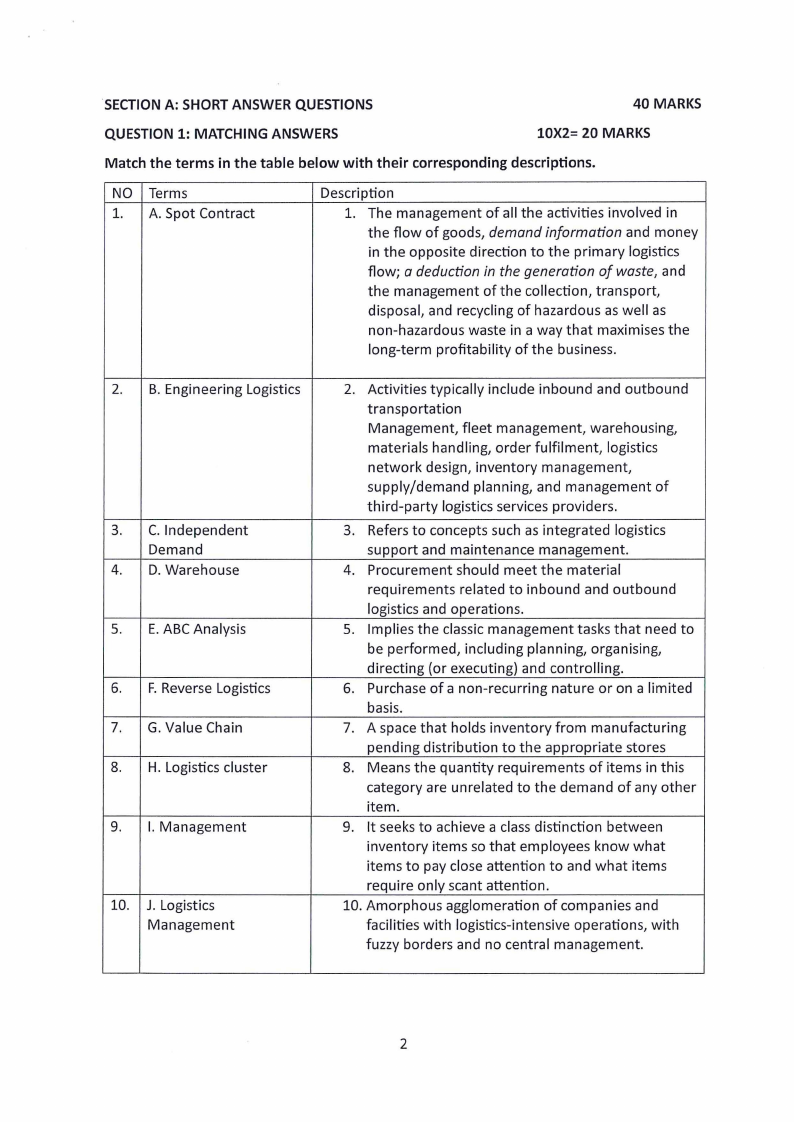
SECTION A: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
40 MARKS
QUESTION 1: MATCHING ANSWERS
10X2= 20 MARKS
Match the terms in the table below with their corresponding descriptions.
NO Terms
1. A. Spot Contract
Description
1. The management of all the activities involved in
the flow of goods, demand information and money
in the opposite direction to the primary logistics
flow; a deduction in the generation of waste, and
the management of the collection, transport,
disposal, and recycling of hazardous as well as
non-hazardous waste in a way that maximises the
long-term profitability of the business.
2. B. Engineering Logistics
3. C. Independent
Demand
4. D. Warehouse
5. E. ABC Analysis
6. F. Reverse Logistics
7. G. Value Chain
8. H. Logistics cluster
9. I. Management
10. J. Logistics
Management
2. Activities typically include inbound and outbound
transportation
Management, fleet management, warehousing,
materials handling, order fulfilment, logistics
network design, inventory management,
supply/demand planning, and management of
third-party logistics services providers.
3. Refers to concepts such as integrated logistics
support and maintenance management.
4. Procurement should meet the material
requirements related to inbound and outbound
logistics and operations.
5. Implies the classic management tasks that need to
be performed, including planning, organising,
directing (or executing) and controlling.
6. Purchase of a non-recurring nature or on a limited
basis.
7. A space that holds inventory from manufacturing
pending distribution to the appropriate stores
8. Means the quantity requirements of items in this
category are unrelated to the demand of any other
item.
9. It seeks to achieve a class distinction between
inventory items so that employees know what
items to pay close attention to and what items
require only scant attention.
10. Amorphous agglomeration of companies and
facilities with logistics-intensive operations, with
fuzzy borders and no central management.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2: TRUE/FALSE
2X10= 20 MARKS
State whether the following statements are true or false.
2.1. In Namibia, air cargo faces challenges in accessibility and distribution, with uneven
handling procedures and limited availability across the country's airports.
2.2. Contrary to widespread belief, the Trans-Cunene Corridor does not constitute a
tripartite transboundary passage spanning a vast 1,900-kilometer route connecting Walvis
Bay, Windhoek, Gaborone, and Johannesburg.
2.3. Through the strategic integration of information technology, significant opportunities
have been unlocked, paving the way for substantial enhancements in distribution
efficiency on a large scale.
2.4. Outbound transport pertains to the logistical movement of finalized merchandise,
meticulously arranged on pallets within containers or tautliner trucks, destined for either
distribution centers or direct store deliveries, particularly in scenarios involving full truck
or container loads.
2.5. Implementing the just-in-time methodology within organizations serves as a strategic
measure to mitigate extensive holding costs, whereby inventory items are meticulously
scheduled to arrive precisely when needed, thereby minimizing excess stock accumulation
and ensuring timely consumption.
2.6. After a collaborative meeting convened by the Ministry of Work and Transport, the
Road Authority, and various other stakeholders in June 2019, there was a collective
consensus to prohibit freight transport via the road network. Subsequently, this purported
decision was purportedly put into effect in its entirety.
2.7. Contrary to popular misconception, human resources management and operations
are erroneously perceived as integral components within the support activities segment
of Porter's Value Chain framework.
2.8. Logistics intricately encompasses a spectrum of activities, meticulously designed
processes, and adept management strategies aimed at orchestrating the seamless flow of
materials within the confines of a particular organisation.
2.9. Business logistics embodies a multifaceted concept, encompassing its practical
application within the commercial landscape alongside the intricate interplay of supply
and demand dynamics concerning both raw materials and finished goods.
2.10. The provision of warehouse facilities, capital expenditure allocations, execution of
construction projects, and transportation services are all subject to contractual
agreements, reflecting the intricate legal frameworks and negotiations that underpin
these essential business activities.
SUB-TOTAL: 40 MARKS
SECTION B: STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
60 MARKS
QUESTION 3
3x10 = 30 Marks
Namibian Logistics Ltd. is a leading logistics company operating in Namibia, specialising in
freight transportation services. The company is currently evaluating the advantages of road
transport as a preferred mode of shipment delivery. As part of this assessment, Namibian
Logistics Ltd. is considering various factors contributing to the effectiveness and efficiency of
road transport.
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

3.1.
Discuss the significance of door-to-door delivery in road transport and its
impact on enhancing efficiency in logistics operations.
{5 marks)
3.2.
Evaluate the accessibility advantage of road transport compared to other
modes of transportation. How does this feature contribute to the globalisation of
supply chains?
(5 marks)
3.3.
Analyse the relationship between road transport's freight security feature and
its ability to minimise theft during shipment delivery. How does this aspect enhance
customer trust and satisfaction?
(5 marks)
3.4.
Assess the role of speed in road transport and its implications for the
transportation of goods over short distances. How does road transport's flexibility in
route selection contribute to maintaining delivery schedules in the• face of traffic
congestion?
{5 marks)
3.5.
Examine the capacity advantage of road transport and its adaptability to meet
increasing demand for freight transportation. How can companies leverage this
feature to optimise their logistics operations and expand their market reach?
{5 marks)
3.6.
Assess the importance of maintaining a high frequency of service in road
transport and its impact on ensuring consistent delivery schedules. How does this
aspect contribute to customer satisfaction and loyalty in the logistics industry?
(5 marks)
QUESTION 4:
30 MARKS
4.1. Procurement staff have steps in the procurement process. In no particular order,
discuss the eight steps involved in the purchasing cycle.
8x2= 16 Marks
4.2. Assess seven reasons why contracts are used in the Supply Chain Management and
Procurement process.
7x2= 14 Marks
SUB-TOTAL: 30 MARKS
SECTION B TOTAL: 60 MARKS
TOTAL MARKS: 100
THE END
4





