 |
IEC820S- INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS- 2ND OPP- NOV 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OFSCIEnCEAno TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCES& EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE
BACHELOR OF ECONOMICS HONOURS
(0SBECH)
DATE:
DURATION:
MARKS:
INDUSTRIAL ECONOMICS (IEC820S)
January 2024
3 Hours
100
EXAMINER
MODERATOR
SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
Prof. T. KAULIHOWA (Namibia University of Science and Technology}
Dr. E. TINGUM
(University of Namibia}
INSTRUCTIONS
1. This paper is made up of two {2} sections (A &B}
2. Answer ALL questions
3. Show all your workings & and round off only the final answers to 2 decimal places
4. Calculators are allowed.
This paper consists of 5 pages including this cover page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SectionA: Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following is a key emphasis of Industrial economics?
a. Monopoly Firms
b. Imperfectly competitive markets
c. Perfectly competitive market
d. Free entry and exit conditions.
20 Marks
2. Which of the following is NOT true about Schumpeter's theory of creative destruction?
a. Competition is driven by innovation.
b. Abnormal profit and market power are bad.
c. Innovators destroy old products and processes.
d. Innovators earn profit at a decreasing rate.
3. Which of the following is not an attribute of firm conduct?
a. Price controls
b. Collusion
C. Predatory pricing
d. Vertical Integration
4. Which of the following is true about the New Industrial Economics Theory
a. Causality runs from Structure to Conduct to Performance
b. Conduct determines both Structure and Performance
c. Causality is bidirectional.
d. Causality runs from Performance to Conduct to Structure
5. Which of the following increases concentration and market power the most?
a. No entry barriers
b. Differentiated products.
c. Prohibitive entry barriers
d. Brand differentiation
6. The less elastic the demand for monopolist's producer, the degree of monopoly power will be...
a. More
b. Less
c. Same
d. Zero
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

7. In Porter's "five forces model", what is the key type of competitive activity that exists between
firms/organizations?
a. The potential for entry into the industry
b. The threat to substitute
c. The power of customers
d. The level of rivalry
8. Which of the following is NOT a measure of market concentration?
a. Concentration ratio
b. Lerner Index
c. Hirschman -Herfindahl Index
d. Entropy Index
9. Which of the following is a form of non price competition?
a. Advertising
b. Quality of service
C. Product quality
d. All of the above
10. One of the reasons that most economists do not support government industrial and trade
policies is that the outcome of these policies cannot;
a. Have a positive effect on a country's industries.
b. Be accurately predicted.
c. Help countries to overcome comparative disadvantage.
d. Prevent countries from losing a comparative advantage
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Section B
80 Marks
1. Which model (Cournot, Bertrand) would you think provides a better approximation to each
of the following industries: Oil refining and insurance? Motivate your answer.
[4)
2. Assume that Namibia's telecommunication Industry is represented by the following cost
function. C (q1, q2) = 40 + 10q 1+ 15q2- {3q1q2/2). Where q1 denotes MTC output and q2
represents Telecom Namibia output. Further to this, assume that Ray's average costs (RAC)
adopt A1 = 0.8, A2 = 0.2 production ratio. Use Ray's average cost of multi-product firms to
determine if the telecommunication industry exhibits a global economy or diseconomies of
scale, where . Show all your steps.
[8]
3. Assume an oligopolistic industry with two identical firms (MTC-Namibia & Paratus) with
inverse demand function P = 62 - 2Q and total cost functions , . Where q1 & Cl are the
quantity and cost for MTC-Namibia and q2 & C2 represent quantity & cost for Paratus
respectively. Answer the following questions.
a. Use a Cournot model to determine the equilibrium values of profit and quantities for
each firm.
[10
b. Assume MTC has a first-mover advantage to set prices and Paratus follows. What
are the equilibrium values of profit and quantities for each firm in this case? [8]
c. Use the Lerner index to measure the level of market power in each model. [S]
d. Use answers in a), b), c) and d) to discuss the economic welfare implications of this
duopoly market.
[S]
4. Suppose a local roofing company has market power and faces the following inverse demand
curve. and a marginal cost curve . Where Q is the quantity of roofing jobs and P is the price
in N$. With the use of the diagram, show the dead weight loss from market power at the
firm's profit-maximising level of output.
[10)
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
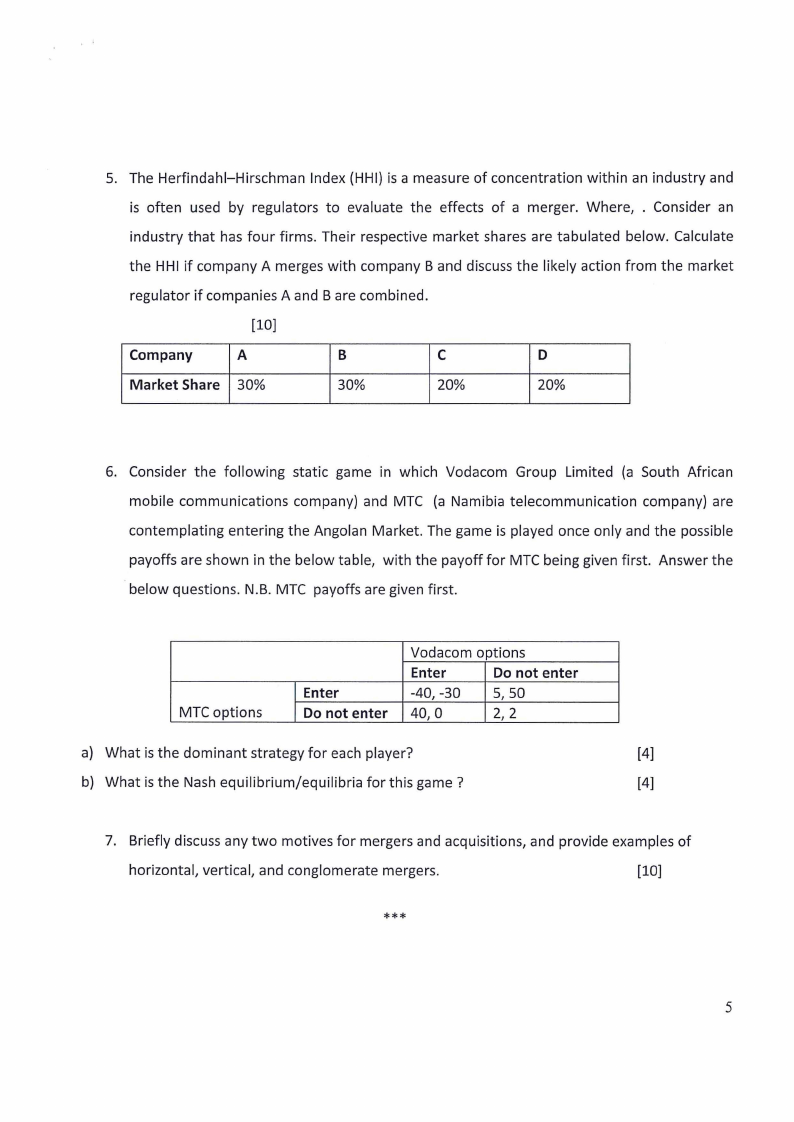
5. The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index {HHI} is a measure of concentration within an industry and
is often used by regulators to evaluate the effects of a merger. Where, . Consider an
industry that has four firms. Their respective market shares are tabulated below. Calculate
the HHI if company A merges with company Band discuss the likely action from the market
regulator if companies A and Bare combined.
[10]
Company
A
B
C
D
Market Share 30%
30%
20%
20%
6. Consider the following static game in which Vodacom Group Limited (a South African
mobile communications company) and MTC (a Namibia telecommunication company) are
contemplating entering the Angolan Market. The game is played once only and the possible
payoffs are shown in the below table, with the payoff for MTC being given first. Answer the
below questions. N.B. MTC payoffs are given first.
MTC options
Enter
Do not enter
Vodacom options
Enter
Do not enter
-40, -30 5,50
40,0
2, 2
a) What is the dominant strategy for each player?
[4]
b) What is the Nash equilibrium/equilibria for this game?
[4]
7. Briefly discuss any two motives for mergers and acquisitions, and provide examples of
horizontal, vertical, and conglomerate mergers.
[10]
***
5





