 |
HMT710S - Hydrometallurgy 314 - 1st Opp - June 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND SPATIAL SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF MINING AND PROCESSENGNEERING
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING IN METALLURGY
QUALIFICATION CODE: 0SBEMT
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: HMT 710S
COURSE NAME: HYDROMETALLURGY 314
SESSION: JUNE 2022
DURATION: 2 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 60
FIRST OPPORTUNITY QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Mr. Bernard Sililo
MODERATOR: Dr. Theresa Coetsee
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions.
2. Read all the questions carefully before answering.
3. Marks for each question are indicated at the end of each question.
4. Please ensure that your writing is legible, neat and presentable.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. Examination paper.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 4 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Question 1
The typical way of operating a solvent extraction process is to run a continuous counter-
current multi-stage system. In these operations, organic substances such as Kerosine are
used.
1.1 Why does copper sulphate dissolve in water and kerosene does not?
(2)
1.2 Where and how is this difference in 1.1 best utilised in hydrometallurgical processes?
(3)
1.3 Instead of precipitation, it is proposed that solvent extraction can be used in the
purification of the solution. If given the general formula of the extractant to be RH:
a) Write down the reaction that represents the loading of copper on the solvent. (1)
b) Explain the importance of pH in the solvent extraction process.
(2)
1.4 The concept of solvent extraction has become an integral part of copper recovery.
Briefly explain why solvent extraction as a way of purifying solution has an advantage
over precipitation in this process.
(5)
Question 2
[15]
2.1 In a traditional Roast - Leach - Electrowin (RLE) process, iron is the main impurity.
Goethite process is one way of removing iron from leach solution. The process is
conducted at elevated temperatures and in solutions with fairly dilute concentrations
of iron.
a) Why would you say goethite process is better compared to jarosite and hematite
processes?
(2)
b) Explain the importance of elevated temperatures and dilute solutions.
(4)
c) Given that oxygen forms the supporting cathodic reaction, give your opinion on the
effect of operating conditions on this process.
(2)
2.2 You are given a process stream from the zinc sulphate leach system that contains 20g/l
Fe that has to be precipitated as goethite and the solution flowrate is 1.5 m3 per hour.
If 90% of iron is precipitated, calculate the mass of goethite produced per hour. Molar
masses: Fe = 56; 0 = 16; H = 1.
(7)
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Question 3
[10]
Gold may be recovered from cyanide solutions by use of the zinc-cementation process.
3.1 Make use of the Eh-pH diagram below for drawing a suitable sketch to explain the
electrochemical principles of the process.
(5)
3.2 Explain what would happen should the concentration of cyanide ions increase and
decrease respectively.
(5)
1.0
- 1.0
OS.28>
--Au.._
Zn(CN)i-
Zn
- 2.0-~~..__...__.____,__.__.__.___.___.___.___.......J
0
4
6
8 10 12 14
pH
Figure 15.2.Potential-pHequilibriumdiagramillustratingfeaturesof theAu-CN-H,O and Zn-CN-H20systems
at 2S'C. (CN"llllal= 10-3 mol 1·1, [Au(CN=J2to]-4mol 1·1, (Zn2·J3.,1 = 10-3 mol 1·1.
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
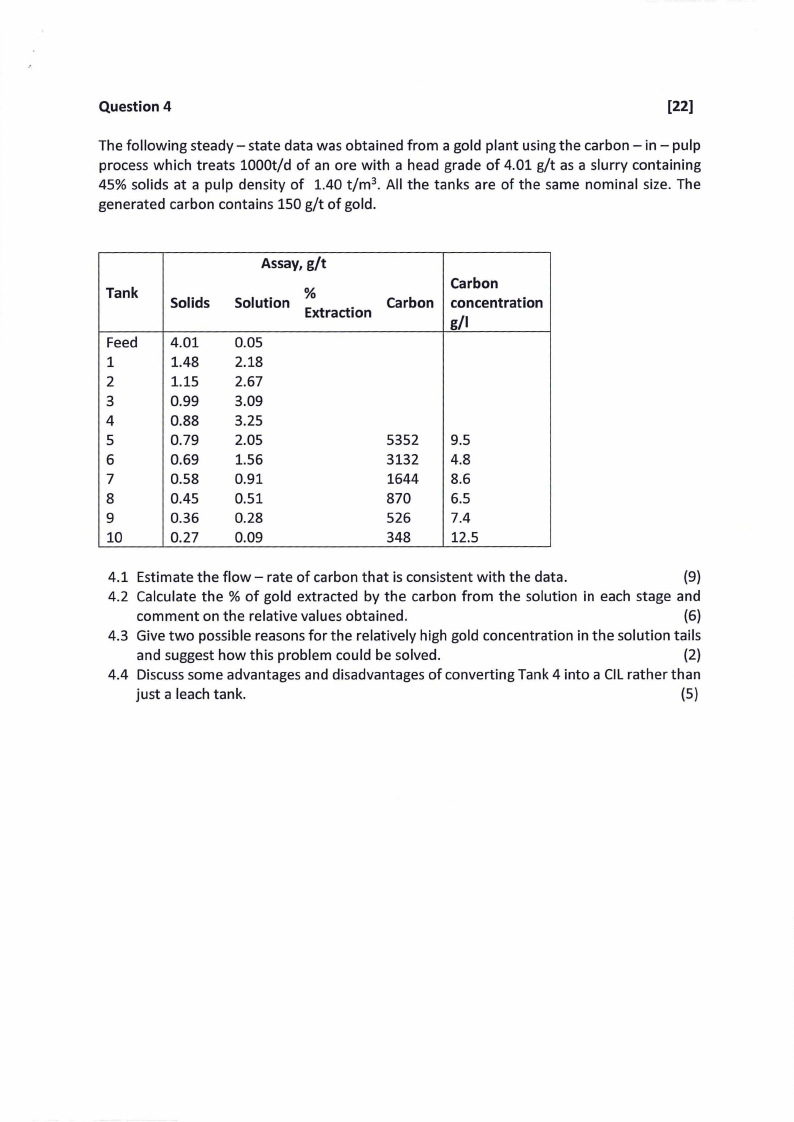
Question 4
[22]
The following steady- state data was obtained from a gold plant using the carbon - in - pulp
process which treats 1000t/d of an ore with a head grade of 4.01 g/t as a slurry containing
45% solids at a pulp density of 1.40 t/m 3• All the tanks are of the same nominal size. The
generated carbon contains 150 g/t of gold.
Tank
Feed
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Solids
4.01
1.48
1.15
0.99
0.88
0.79
0.69
0.58
0.45
0.36
0.27
Assay, g/t
Solution
%
Extraction
0.05
2.18
2.67
3.09
3.25
2.05
1.56
0.91
0.51
0.28
0.09
Carbon
5352
3132
1644
870
526
348
Carbon
concentration
g/1
9.5
4.8
8.6
6.5
7.4
12.5
4.1 Estimate the flow - rate of carbon that is consistent with the data.
(9)
4.2 Calculate the % of gold extracted by the carbon from the solution in each stage and
comment on the relative values obtained.
(6)
4.3 Give two possible reasons for the relatively high gold concentration in the solution tails
and suggest how this problem could be solved.
(2)
4.4 Discuss some advantages and disadvantages of converting Tank 4 into a CILrather than
just a leach tank.
(5)
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |






