 |
ZLY520S - ZOOLOGY 1 - 2ND OPP - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA un IVERS ITV
OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF AGRICULTUREAND NATURALRESOURCESSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF NATURALRESOURCESMANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BNRS
LEVEL: 7
COURSECODE: ZLY520S
COURSENAME: ZOOLOGY1
DATE:JANUARY 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 150
SECONDOPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S} Mrs. L. Theron
MODERATOR: Mr. Helmuth Tjikurunda
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examination question paper
2. Answering book
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 4 PAGES(Excluding this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A
QUESTION 1
Provide the correct term for each of the following.
[10]
1.1 Animals where the blastopore develops into the mouth.
1.2 The respiratory pigment found in the blood of Gastropods.
1.3 Common name for the parasitic flatworms belonging to the classTrematoda.
1.4 Asexual reproduction in which a small part of the parent's body separates from
the rest and develops into a new individual.
1.5 Away from, or opposite to, the mouth.
1.6 Jaw-like ossicles found in starfish and used to keep the body surface clean.
1.7 A rasp-like structure in the alimentary tract of chitons and snails.
1.8 Jointly beneficial association between individuals of two different species.
1.9 Distinct difference between the males and females of a species, as in lions
(2 words)
1.10 An animal with a true coelom.
QUESTION 2
One word in each of the following lists does not belong with the rest of the words in
that list. Write down the number (only) and the word/term that doesn't fit.
[10]
2.1 Mandibles; maxillae; antennae; Limu/us; crab
2.2 Lepidoptera; antennae; proboscis; halters; membranous wings
2.3 Bivalvia; radula; head reduces; shipworm; siphon
2.4 Ophiuroidea; flexible arms; ossicles; ambulacral groove; tube feet
2.5 Pycnogonida; crab; chelicerae; ovigerous legs.
2.6 Oligochaeta; clitellum; peristomium; nephridia
2.7 Radial symmetry; head; water vascular system; tube feet; madreporite
2.8 Antennae; ants; thorax; ticks; mandible
2.9 Tube feet; pedicellariae; starfish; diploblastic; radial symmetry
2.10 Protrusible tongue; Salamander; internal fertilisation; toad
QUESTION 3
Eachof the following sets of characteristics describes a Class. Write down the number
(only) and the Classthat particular set refers to.
[10]
3.1 Head and trunk; diplosegments; cylindrical bodies; antennae
3.2 Undivided heart; spiral valve; placoid scales
3.3 Cold blooded; webbed feet; breath with lungs and gills
3.4 Head reduced; radula; shell opened at both ends
3.5 Limpets; torsion; well-developed head; muscular foot
3.6 Sea horse; bony skeleton; operculum
3.7 Arms not sharply set off from disc; tube feet; madreporite
3.8 Long movable spines; tube feet; no arms
3.9 Polyp stage dominates; budding; solitary of colonial forms
3.10 Head reduced; no radula; foot blade-like; laterally compressed
SUB-TOTAL [30]
1
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B
QUESTION 4 (Cell division)
Match the terms below to the descriptions. Note that terms can be used more than
once! You can only use the corresponding LETTER
A= Ana phase I - lnterphase M = Metaphase P = Prophase T = Telophase
(9)
4.1 The sister chromatids are moving apart.
4.2 The nuclear membrane fades from view
4.3 A new nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes
4.4 The cytoplasm of the cell is being divided
4.5 The chromatin is found in the nucleus
4.6 Animal cells begin to pinch in
4.7 The spindle is formed
4.8 Chromatids line up along the equator
4.9 Chromosomes are not visible
Provide the correct term for each of the following description.
(3)
4.10 Chromosomal material found in the nucleolus - before cell division begins.
4.11 Matching genes on a chromosome -for a specific trait.
4.12 A group of 2 homologous chromosomes that come together to undergo
crossing over.
[12]
QUESTION 5 (Genetics)
5.1 Distinguish between general properties and specific properties relevant to
genetics. Make use of examples.
(4)
5.2 What is the difference between somatic mutations and germ-line mutations?
(4)
5.3 Give the "name" of Mendel's second Law; state the law, AND explain what it
means.
(4)
[12]
QUESTION 6
Explain locomotion in each of the following groups:
6.1 Earthworms
(6)
6.2 Molusca
(6)
6.3 Echinodermata
(6)
[18]
QUESTION 7
7.1 Explain the difference between hermaphroditic and dioecious animals. Provide
one example for each term -from the phylum Annelida.
(4)
7.2 Why is it of advantage for slow moving animals to be hermaphrodites?
(2)
7.3 Write a report on the ecological importance of earthworms. Make use of full
sentences!
(6)
[12]
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 8
8.1 Explain the difference between complete and incomplete metamorphosis in
insects. Give TWO insect orders as example for each type.
(6)
8.2 In tabular form, provide 4 differences between the Araneae and the Solpugida. (5)
Also give the common name of each Order.
8.3 What is unique about the Diptera? (How do they differ from most other
insects)?
(2)
[13]
QUESTION 9
9.1 List the 4 adaptive groups of bivalves found in the ocean and provide a specific
characteristic for each group that suits that particular lifestyle.
(8)
9.2 Two distinctive characteristics of molluscs are the presence of a shell and a
radula. Explain how these two features are modified in the following molluscs
groups:
(6)
9.2.1 Gastropoda
9.2.2 Bivalvia
9.2.3 Cephalopoda
[14]
QUESTION 10
10.1 In tabular form, provide 4 differences between sea urchins and sand dollars.
(4)
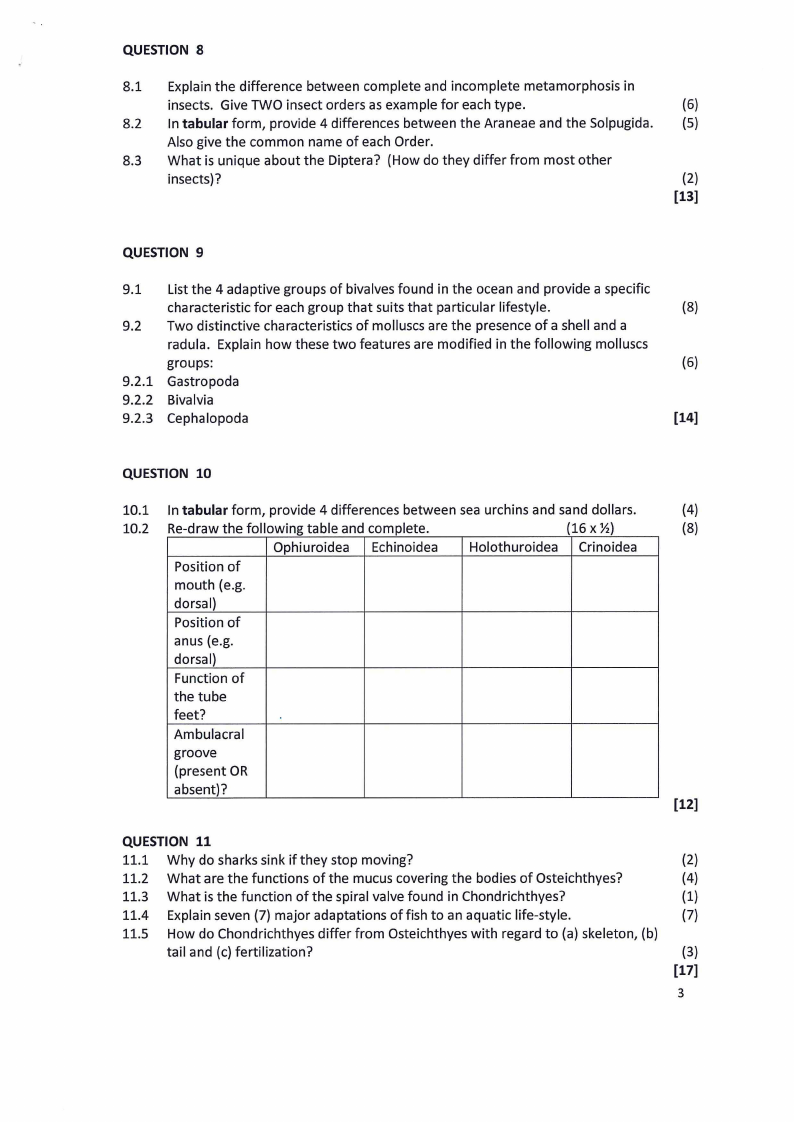
10.2 Re-draw the following table and complete.
(16 x ½}
(8)
Ophiuroidea Echinoidea Holothuroidea Crinoidea
Position of
mouth (e.g.
dorsal)
Position of
anus (e.g.
dorsal)
Function of
the tube
feet?
Ambulacral
groove
(present OR
absent)?
[12]
QUESTION 11
11.1 Why do sharks sink if they stop moving?
(2)
11.2 What are the functions of the mucus covering the bodies of Osteichthyes?
(4)
11.3 What is the function of the spiral valve found in Chondrichthyes?
(1)
11.4 Explain seven (7) major adaptations of fish to an aquatic life-style.
(7)
11.5 How do Chondrichthyes differ from Osteichthyes with regard to (a) skeleton, (b)
tail and (c) fertilization?
(3)
[17]
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 12
12.1 Explain the difference between the feet of frogs and toads and provide a reason
for the difference.
(2)
12.2 Explain how the hind legs of a frog are specialized for jumping.
(3)
12.3 Amphibians are ectothermic animals. What are the advantages of this?
(4)
12.4 Why are there no ovoviviparous frogs?
(1)
[10]
SUB-TOTAL [120]
TOTAL [150]
4





