 |
AGE811S - ADVANCED GEOPHYSICS - 1ST OPP - JUNE 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

r
n Am I 8 I A Un IVERS I TY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnDLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH NATURAL RESOURCESAND APPLIED SCIENCES
SCHOOL OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY, CHEMISTRY AND PHYSICS
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BOSC
LEVEL: 8
COURSE CODE: AGE811S
COURSE NAME: ADVANCEDGEOPHYSICS
SESSION: JUNE 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S)
MODERATOR:
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION
Prof Benjamin MAPANI
MR. Robert MWANACILENGA
ANSWER QUESTION ONE (1) AND ANY OTHER THREE (3)
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES (Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1: Compulsory
1. Indicate the primary geophysical (potential field) method/s that can be used in the
following applications: give a brief explanation why that is the most suitable (the use
of diagrams appropriately will attract marks):
(a) Looking for a for copper sulphide mineralisation in a banded gneiss (5)
(b) Reconnaissance exploration of iron ore deposits on in a large area of 100 km x
100 km (Magnetite and hematite combined).
(5)
(c) Imaging of salt dome
(5)
(d) Investigating pollution of fresh ground water on a municipal landfill or waste
disposal site such as the Kupferberg in Windhoek.
(5)
(e) Examining a mining area for acid mine drainage solutions from the oxidation
of pyrite from their tailings dam.
(5)
QUESTION 2.
(a) Why is the fall off rate on a magnetic anomaly faster than on gravity anomaly? Write
the general formula which expresses the form and amplitude of a
gravity (or magnetic) anomaly. Briefly explain the effect on an anomaly
of each of the parameters in the formula and outline possible ambiguities.
[3, 2]
(b) Show, with the aid of a sketch, the effect on a magnetic anomaly of taking
readings at too coarse a spacing. Discuss how this will affect interpretation?[3]
(c) State the two effects on a magnetic (or gravity) anomaly of burying its
source at progressively deeper depths?
[4]
(d) The laws of gravity allowed physicists and astrophysicists to measure the masses
of planets and stars. The remarkable accuracy of Newton's laws is that they were
able to be used to find the planet Neptune. Answer the following questions:
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

(i) A planet Q, which is the size of Earth, orbits its star 0.8 AU in 0.65 Earth year orbit.
Find the mass of the parent star to the planet Q.
[SJ
(ii) A star with twice the mass of our Sun has an earth like planet that takes 2 years to
orbit the star. What will be the distance between the star and the planet in km?
[6]
(iii) The force of gravity on Earth is given as 9.81 m/s 2• If the Earth was twice its current
mass, and the volume doubled, what would be the acceleration due to gravity on such
a planet?
[5]
QUESTION 3
(a) Discussthe corrections applied to gravity data in order to produce a Bouguer anomaly
map.
[4]
(b) The magnetic data is normaly produced in Total Magnetic intensity anomalies. From
this is calculated the First Vertical Derivative and Analytical Signal. List the benefits,
and drawbacks, of doing so in each case.
[9]
(c) What is the function of a base station in magnetics and gravity surveys? How would
Sunspot activity affect your surveys and what time of the day would be best suited to
carry a magnetic survey
[2, 2, 2]
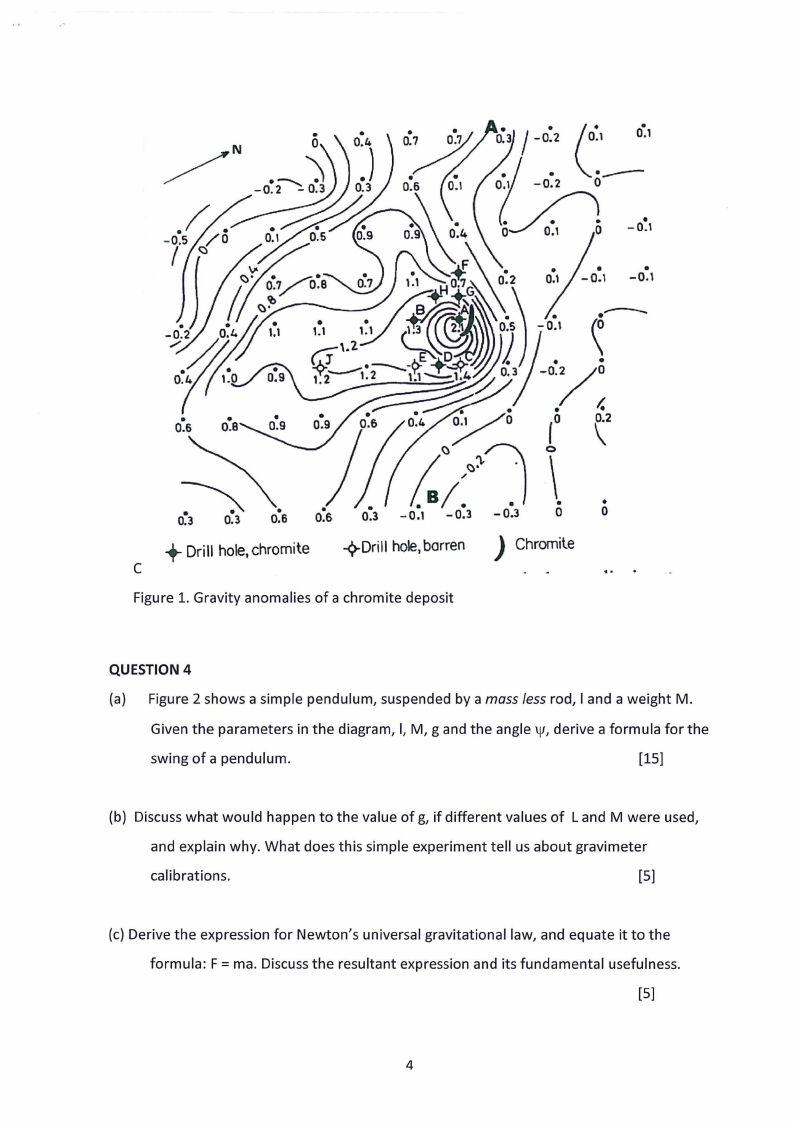
(d) Sketch a gravity anomaly across the chromite ore body in Figure 1 below. Give a brief
explanation outlining why the anomaly shapes differ.
[3]
(e) Suppose the chromite deposit was replaced by a coal deposit, sketch how the new
magnetic anomaly would look like.
[3]
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
0·1 ./o/y
0•.6
0•.1
-0.\\•
0•
C
Figure 1. Gravity anomalies of a chromite deposit
QUESTION 4
(a) Figure 2 shows a simple pendulum, suspended by a mass less rod, I and a weight M.
Given the parameters in the diagram, I, M, g and the angle\\\\', derive a formula for the
swing of a pendulum.
[15]
(b) Discuss what would happen to the value of g, if different values of Land M were used,
and explain why. What does this simple experiment tell us about gravimeter
calibrations.
[S]
(c) Derive the expression for Newton's universal gravitational law, and equate it to the
formula: F = ma. Discuss the resultant expression and its fundamental usefulness.
[S]
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

."
Figure 2.
QUESTION 5
(a) IP and resitivity are useful in the vertical sounding and profiling methodology. To do this
we need to assessthe resistivity or conductiveness of the given area. State three areas
where we can use this methodology, in each case state the relative
conductivity/resistivity of the sought after material compared to the host rock/soil.
[6]
(b) Draw a configuration of the Wenner and Schluberger array. State the differences
between the two and give any advantages if any of one array over the other. [2, 4)
(c) If we need to see or go much deeper in our investigations, which set of electrodes
(voltage or current) do we need to shift and in which fashion relative to the current or
voltage electrodes?
[4)
(d) Discussthe usefulness of radiometries in the exploration of mineral deposits and give an
example of one such mineral/element/material.
[SJ
(b) Distinguish between gamma spectrometers and scintillometers.
[4)
END OF EXAMINATION
5





