 |
EPD611S - EPIDEMIOLOGY 2A -1ST OPP - JUNE 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF HEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION:BACHELOROF ENVIRONMENTALHEALTHSCIENCESH, UMAN NUTRITIONAND
HEALTH!FORMATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 08BOHS
LEVEL:6
COURSE: EPIDEMIOLOGY2A
COURSECODE: EPD6115
DATE:JUNE2022
SESSION:SEMESTEORNE,2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S): MRJOSHUAHIDINWA
MODERATOR: DR ROSWITHA MAHALIE
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
NONE
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 6 PAGES{Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A [30 MARKS]
QUESTION 1
[10 MARKS]
Select the most appropriate answer from the options provided.
Example: 1.35 A
1.1 Many individuals may not realize that they use epidemiologic information
to make daily decisions affecting their health by doing what:
[1]
A. How these patterns relate to the level and distribution of public health
services available
B. Use a condom
C. Disease investigation
D. Outbreak investigation
E. Visiting hospital
1.2 When investigating a disease outbreak, epidemiologists rely on health-care providers
and labolatorians to establish the proper diagnosis
of individual patients on:
[1]
A. How and who
B. Who and what
C. What and where
D. Completing the clinical picture
E. Where and when
1.3 What type of study is used to determine the exposure status for each individual
(clinical trial) or community (community trial):
[1]
A. Observational Study
B. time, place, and person
C. Experimental study
D. Mechanical vector-borne transmission
E. Biological vector-borne transmission
1.4 Simply observing the exposure and outcome status of each study
participant is called:
[1]
A. Applying the knowledge gained by the studies to
community-based practice
B. Observational Study
C. Experimental Study
D. Laboratory result
E. Epidemiology study
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.5 An outbreak in which a group of persons are all exposed to an infectious
agent or a toxin from the same source is called:
[1]
A. For disease diagnosis and treatment in health care facilities
B. For Screening of patients in the community
C. Common Source
D. For the wide range of health-related states and events that are studied
E. Chemical infestation
1.6 The reservoir for diseases which are transmitted from person to person without
intermediaries include the sexually transmitted diseases, measles, mumps,
streptococcal infection, most respiratory pathogens, and many others they
are found in:
[1]
A. Human reservoirs
B. Suspect or probable
C. Confirmed or suspect
D. Not a case
E. Not a case or confirmed
1.7 An outbreak that does not have a common source, but instead spreads
gradually from person to person is called:
[1]
A. Common Source
B. Point Source
C. Propagated
D. Outbreak
E. Epidemic
1.8 The presence of an infectious agent on a body surface, on or in clothes, bedding, toys
surgical instruments or dressings or other inanimate articles or substances including
water, milk and food is called:
[1]
A. Canta mination
B. Infestation
C. Not a case
D. Investigation
E. Disease
1.9 For person or animals the lodgment, development and reproduction
of arthropods on the surface of the body or in the clothes is called:
[1]
A. Common Source
B. Infestation
C. Propagated
D. Infectious
E. Disease
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

10. A person or other animal, including birds and arthropods, that affords
subsistence or lodgements to an infectious agent under natural conditions
is called:'
[1]
A. Contagious disease
B. Infestation
C. Host
D. Bacteria
E. Viruses
QUESTION 2
Indicate which of the following statements is True or False
2.1 If the disease agent acquires drug resistance, it will further
facilitate its spread.
[10 MARKS]
[1]
2.1 An essential requirement for indirect transmission is that the infectious agent must
be capable of surviving outside the human host in the external environment and
retain its basic properties of pathogenesis and virulence till it finds a new host.
[1]
2.2 Transmission of the infectious agent through the agency of water, food does not
including raw vegetables, fruits, milk and milk products.
[1]
2.3 Water and food is not the most frequent vehicle of transmission, because they
are used by everyone.
[1]
2.4 Active immunity depends upon the humoral and cellular responses
of the host.
[1]
2.5 Passiveimmunity it refers to when antibodies produced in one body
human or animal are transferred to another to induce protection against disease. [1]
2.6 When a body is unable to produce its own antibodies it
is called hyper-immunity.
[1]
2.7 Herd immunity does not provide an immunological barrier to the spread of
disease in the human herd.
[1]
2.8 If the herd immunity drops it could result in the occurrence of an
epidemic in the population.
[1]
2.10 The purpose of immunization is to develop immunological memory.
[1]
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
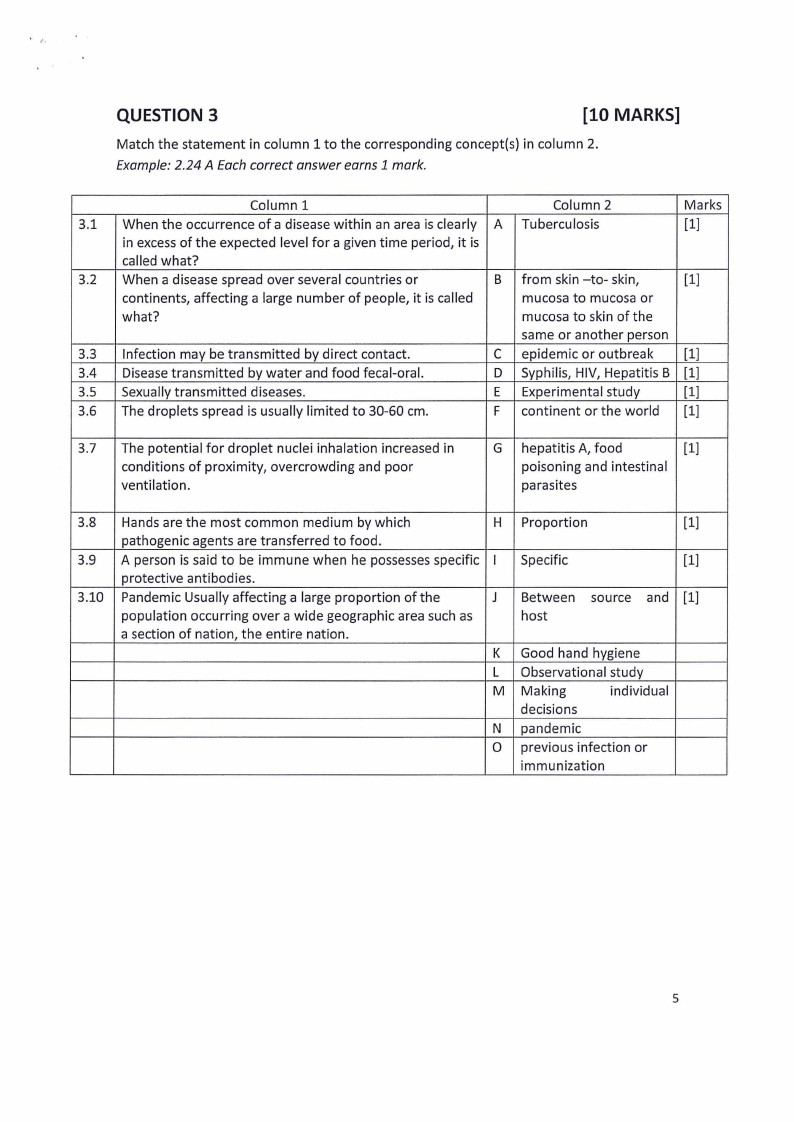
QUESTION 3
[10 MARKS]
Match the statement in column 1 to the corresponding concept(s) in column 2.
Example: 2.24 A Each correct answer earns 1 mark.
Column 1
Column 2
Marks
3.1 When the occurrence of a disease within an area is clearly A Tubercu Iasis
[1]
in excess of the expected level for a given time period, it is
called what?
3.2 When a disease spread over several countries or
B from skin -to- skin,
[1]
continents, affecting a large number of people, it is called
mucosa to mucosa or
what?
mucosa to skin of the
same or another person
3.3 Infection may be transmitted by direct contact.
C epidemic or outbreak
[1]
3.4 Disease transmitted by water and food fecal-oral.
D Syphilis, HIV, Hepatitis B [1]
3.5 Sexually transmitted diseases.
E Experimental study
[1]
3.6 The droplets spread is usually limited to 30-60 cm.
F continent or the world [1]
3.7 The potential for droplet nuclei inhalation increased in
conditions of proximity, overcrowding and poor
ventilation.
G hepatitis A, food
[1]
poisoning and intestinal
parasites
3.8 Hands are the most common medium by which
H Proportion
[1]
pathogenic agents are transferred to food.
3.9 A person is said to be immune when he possessesspecific I Specific
[1]
protective antibodies.
3.10 Pandemic Usually affecting a large proportion of the
J Between source and [1]
population occurring over a wide geographic area such as
host
a section of nation, the entire nation.
K Good hand hygiene
L Observational study
M Making
individual
decisions
N pandemic
0 previous infection or
immunization
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B [18 MARKS]
Question 4:
4.1 Discussthe peculiarity of Non-Communicable diseases
4.2 Outline the core functions Epidemiology.
SECTION C [52 MARKS]
[18 Marks]
[8]
[10]
QUESTION 5:
[34 MARKS]
5.1 Elaborate Prevention of Road Traffic Accidents.
[10]
5.2 Discussthe activities which you need to carry out under primary, secondary,
and tertiary prevention of non-communicable disease.
[12]
5.3 Mention some of the Intermediate risk factors of non-communicable disease.
[4]
5.4 Explain the chain of infection.
[8]
QUESTION 6
6.1 Discussthe steps in an outbreak investigation.
6.2 Explain in detail the principles of epidemiology.
[18 MARKS]
[10]
[8]
Good luck!
TOTAL: 100 MARKS
6





