 |
GEP521S - GASTROINTESTINAL AND ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2025 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

f
IU..-HnAmI BIA univERS ITY
'7 OF SCIEnCE AnDTECHnOLOGY
FacultyofHealthN, atural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoool f HealthSciences
Departmentof Preventative
HealthSciences
13JacksonKaujeuaStreet T: +264612072970
PrivateBag13388
F: +264612079970
Windhoek
E: dphs@nust.na
NAMIBIA
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR OF HUMAN NUTRITION
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BOHN
LEVEL:5
COURSE:GASTROINTESTINAL AND ENDOCRINE
PHYSIOLOGY
COURSECODE: GEP521S
DATE: JANUARY 2025
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION: QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
DR. PENEHAFO HAITAMBA-SHINDUME
MR. GEORGE WALIOMUZIBU MUKISA
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. No Permissible material
This question paper consists of 7 pages including this front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

20MARKS j
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
[10 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements/questions in each numbered section and select the most
appropriate answer or phrase from the given possibilities. Fill in the appropriate letter next
to the number of the correct statement/phrase on your ANSWERSHEET.
[10]
1.1 Which of these glands does not secrete saliva into the oral cavity?
A) Submandibular glands
B) Goblet glands
C) Sublingual glands
D) Parotid glands
1.2 HCL.
A) Is an enzyme.
B) Creates the acid conditions necessary for pepsin to work.
C) Is secreted by the small intestine
D) Activates salivary amylase.
E) All the above.
1.3 Which of these hormones stimulate stomach secretions?
A) Cholecystokinin
B) Gastric inhibitory peptide
C) Gastrin
D) Secretin
1.4 Given these ducts:
1. Common bile duct
2. Common hepatic duct
3. Cystic duct
4. Hepatic ducts
Choose the arrangement that lists the ducts in the order that bile passes through them
when moving from the bile canaliculi of the liver to the small intestine.
A) 3,4,2
B) 3,2,1
C) 3,4,1
D) 4,1,2
E) 4,2,1
Gastrointestinaland Endocrine Physiology(GEP5215)
2
2nd Opportunity-JAN2025
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.5 Which of these is not a function of the large intestine?
A) Absorption of fats
B) Absorption of certain vitamins
C) Absorption of water and salts
D) Production of mucus
E)All of the above.
1.6 Hormones secreted from the posterior pituitary
A) Are produced in the anterior pituitary
B) Are transported to the posterior pituitary within axons
C) Include GH and TSH
D) Are steroids
E)All of the above
1.7 Growth hormone
A) Increases the usage of glucose.
B) Increases the breakdown of lipids.
C) Decreases the synthesis of proteins.
D) Decreases the synthesis of glycogen.
E) All of the above.
1.8 Within the pancreas, the pancreatic islets produce
A) Insulin
B) Glucagon
C) Digestive enzymes
D) Both a and b
E) All of the above.
1.9 If Aldosterone secretions increase
A) Blood potassium levels increase
B) Blood hydrogen levels increase
C) Acidosis results
D) Blood sodium levels decrease
E) Blood volume increases
1.10 If a person who has diabetes mellitus forgot to take an insulin injection, symptoms
that may soon appear include?
A) Acidosis
B) Hyperglycaemia
C) Increased urine production
D) Lethargy and Fatigue
Gastrointestinal and Endocrine Physiology (GEP5215)
3
2nd Opportunity-JAN2025
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
E)All of the above
QUESTION 2: MATCH EACH ANSWER
[10 MARKS]
2.1 Match the following endocrine glands with their origins and the type of hormones they
produce {Steroid, Peptide, or Amine) {One mark for a full correct answer)
(5)
Endocrine Gland
1. Adrenal medulla
2. Adrenal cortex
3. Thyroid gland
4. Gonads
5. Pancreas
Germ Layer Origin
a) Endoderm
b) Mesoderm
c) Ectoderm neural cells
Hormone Type
Steroid
Peptide
Amine
2.2 Match each GIT condition (Column A) with its correct effect on digestion and absorption
(Column B). Each correct match is worth 1 mark.
(5)
GIT Pathology
1. Celiac disease
2. Lactose intolerance
3. Gastroesophageal reflux
(GERO)
4. Crohn's disease
5. Peptic ulcers
disease
Effects on Digestion and Absorption
A-Inflammation of any part of the GIT, often
causing malabsorption of nutrients and
chronic diarrhea.
B- Sores in the stomach or duodenum that
can impair digestion and lead to pain,
bleeding, or blockages.
C-lnflammation and damage to the small
intestine, leading to poor nutrient
absorption, especially of fats and fat-soluble
vitamins.
D-Difficulty digesting milk sugar (lactose),
causing bloating, diarrhea, and discomfort
when consuming dairy products.
E-Acid from the stomach backs up into the
esophagus, causing heartburn and potential
damage to the esophageal lining.
=SECTION B: SHORT/LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Pleaseanswer ALLthe questions in this section.
QUESTION 3:
3.1 List and explain 4 functions of Bile Acids.
Gastrointestinal and Endocrine Physiology (GEP5215)
4
[80 MARKS]
[20 MARKS]
(4)
2nd Opportunity-JAN2025
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

3.2 Describe the following reactions that take place during the phase 2 detoxification
pathway in the liver:
i) Glutathione Conjugation
(2)
ii) Methylation
(2)
3.3 Elaborate the 3 primary ways the ENSinteracts with the CNS.
(3)
3.4 Discussthe process of how protein is digested.
(6)
3.5 Propose the meaning of Steatorrhea and state its symptoms?
(3)
QUESTION 4:
[20 MARKS]
4.1 Differetiate between an endocrine and an exocrine gland. Give two
examples of each.
(4)
4.2 Describe what a steroid hormone is and give an example a one.
(2)
4.3 Suggest the three different regions within the adrenal cortex and the hormones they
produce.
(6)
4.4 Propose two disorders involving the Adrenal glands.
(2)
4.5 Identify six symptoms that may indicate a person is experiencing an underactive
thyroid (hypothyroidism).
(6)
QUESTION 5:
[10 MARKS]
Describe the process of carbohydrate digestion in each of the following parts of the
gastrointestinal tract (You can consider a flow chart for illustration purposes):
Mouth
(1)
i. Stomach
(1)
ii. Small intestines
(1)
iii. Pancreatic enzymes
(2)
iv. Intestinal enzymes
(3)
V. End product
(2)
Gastrointestinal and Endocrine Physiology (GEP5215)
5
2nd Opportunity-JAN2025
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
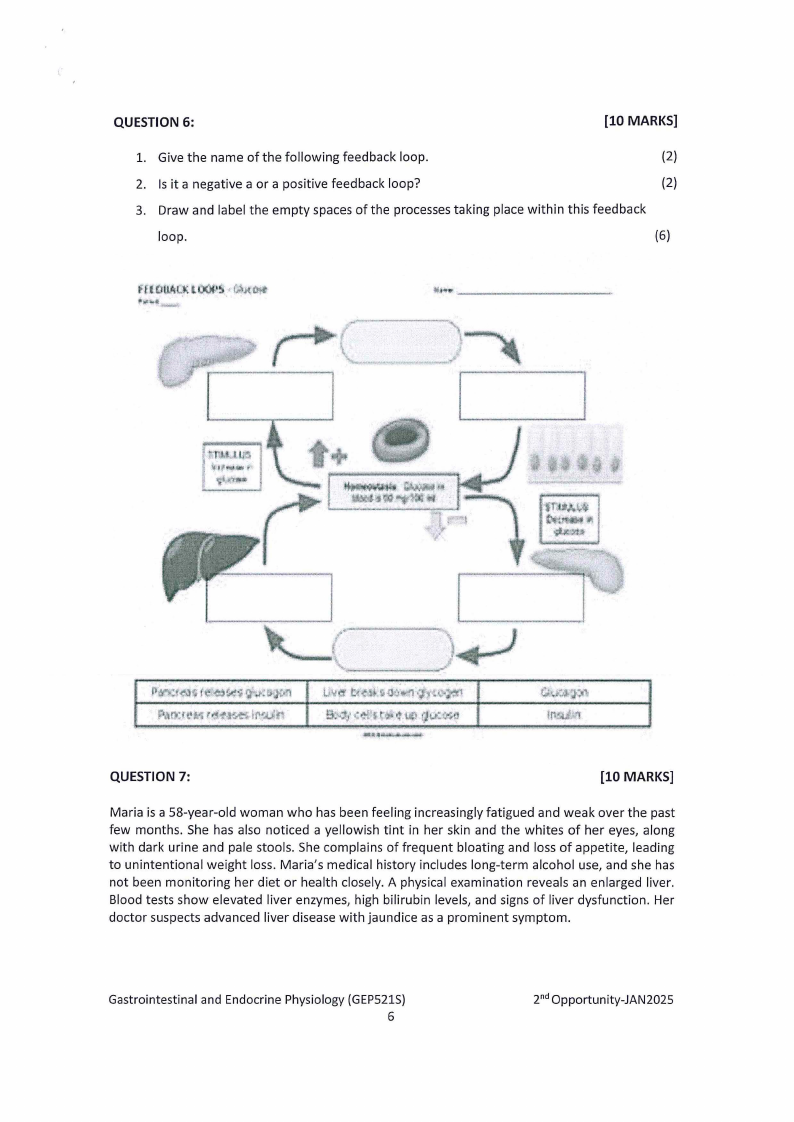
QUESTION 6:
[10 MARKS]
1. Give the name of the following feedback loop.
(2)
2. Is it a negative a or a positive feedback loop?
(2)
3. Draw and label the empty spaces of the processes taking place within this feedback
loop.
(6)
....-. ,fft0(1Jittt¢(HJ~ ,{,.)~~
--·\\"_~"·-'-'·-
I
QUESTION 7:
[10 MARKS]
Maria is a 58-year-old woman who has been feeling increasingly fatigued and weak over the past
few months. She has also noticed a yellowish tint in her skin and the whites of her eyes, along
with dark urine and pale stools. She complains of frequent bloating and loss of appetite, leading
to unintentional weight loss. Maria's medical history includes long-term alcohol use, and she has
not been monitoring her diet or health closely. A physical examination reveals an enlarged liver.
Blood tests show elevated liver enzymes, high bilirubin levels, and signs of liver dysfunction. Her
doctor suspects advanced liver disease with jaundice as a prominent symptom.
Gastrointestinal and Endocrine Physiology (GEP521S)
6
2nd Opportunity-JAN2025
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

7.1 What is jaundice, and why is it a common symptom of advanced liver disease?
(2)
7.2 How does liver dysfunction contribute to Maria's symptoms, such as yellowing of the skin
and eyes, dark urine, and pale stools?
(2)
7.3 Discussthe role of bilirubin in the development of jaundice in patients with liver disease. (2)
7.4 Mention lifestyle factors, including Maria's history of alcohol use, may have contributed to
her liver disease?
(2)
7.5 Suggest potential treatment options and lifestyle changes that could help manage Maria's
condition and slow the progression of liver disease.
(2)
QUESTION 8:
[10 MARKS]
Jacob is a 52-year-old man who has been feeling unusually tired and thirsty for the past few
months. He has also been experiencing frequent urination, especially during the night. Jacob
mentions that he has gained weight over the years and has a sedentary lifestyle due to his desk
job. His diet consists mostly of fast food and sugary snacks. He also has a family history of
diabetes. A recent blood test revealed that Jacob has elevated blood glucose levels, and his
doctor diagnosed him with type 2 diabetes.
Jacob is concerned about his condition and wants to know how he can manage it.
8.1 Explain type 2 diabetes, and how does it affect blood sugar regulation in the body?
(2)
8.2 Propose how Jacob's lifestyle and diet might have contributed to the development of
type 2 diabetes.
(2)
8.3 State symptoms of diabetes is Jacob experiencing, and how are they related to
high blood glucose levels?
(2)
8.4 Suggest lifestyle changes that Jacob could implement to help manage his diabetes and
improve his health.
(2)
8.5 Why is it important for Jacob to monitor his blood sugar levels regularly, and how
can this help in managing his condition?
(2)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Gastrointestinal and Endocrine Physiology (GEP521S)
7
2nd Opportunity-JAN2025





