 |
GNP502S - GENERAL PHYSICS 1B - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2025 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAml BIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCEAnDTECHnOLOGY
FacultyofHealth,Natural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoolof NaturalandApplied
Sciences
Departmentof Biology,
Chemistryand Physics
13JacksonKaujeuaStreet T: +264612072012
Private Bag13388
F: +264612079012
Windhoek
E: dbcp@nust.na
NAMIBIA
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
COURSE:GENERAL PHYSICS 18
DATE: JANUARY 2025
DURATION: 3 HOURS
LEVEL:5
COURSECODE: GNP502S
SESSION: 1
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/ SUPPLEMENTARY: EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
INSTRUCTIONS:
PROF SYLVANUS ONJEFU
MR MARKUS HITILA
PROF DIPTI SAHU
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left-side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHMENTS
1. None
This paper consists of 6 pages including the front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A
QUESTION 1
Suggested Question Types: Multiple Choice/Objectives
Each question in this section carries two marks
[40 MARl<S]
1.1 What is the critical angle for light travelling from water to air. Refractive
index of water = 4/3.
(2)
a. 37° 28' b. 28° 15' C. 48° 36' d. 44o 33'
1.2 If Vis the velocity of a wave, il its wavelength and Tits period, the V, il and T
Are related by the expression:
(2)
a. il = VT
c. T2 = ilV d. V = ilT
1.3 If the angle of incidence for light travelling from air to glass is 45° and
the angle of refraction in the glass is 28°, determine the refractive index
of glass with respect to air.
(2)
a. 1.51 b. 0.66 c. 1.62 2.25
1.4 What is the speed of compression waves (sound waves) in water? The bulk
modulus for water is 2.2 X 10 9 N/m 2 .
(2)
a. 1.6 km/s b. 1.5 km/s c. 1.7 km/s d. 1.8 km/s
1.5 All are example of electromagnetic wave except ................ .
(2)
a. visible light b. microwave c. X-rays d. beta
1.6 A normal human ear can respond to ............. frequency range.
(2)
a. 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz b. 20,000 Hz to 20, 000000 Hz c. below 20 Hz
d. above 20,000 Hz
1.7 What is the refractive index of a substance if the real depth is 6 m and its
apparent depth is 4.5 m?
(2)
a. 10.5
b. 1.33 C. 1.50 d. 0.75
General Physics 1B (GNP502S)
2nd Opportunity January 2025
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.8 The direction of light ray changes as it passesfrom one medium to another.
The phenomenon is called
(2)
a. Diffraction b. refraction c. dispersion d. reflection
1.9 An object with a height of 1.00 cm is placed 10.0 cm from a concave mirror
whose radius of curvature is 30.0 cm. Determine the position of the image.
(2)
a. 30 cm b. -30 cm c. 20 cm d. - 20 cm
1.10 In the dispersion of white light into its component colors, ............ ..
is the least bent.
(2)
a. Violet b. blue c. green
d. red
1.11 The mirage is a phenomenon of ................ ..
(2)
a. Interference
d. diffraction
b. total internal reflection c. dispersion
1.12 ............. has the shortest wavelength when a triangular prism spread white
light out into its component colors.
(2)
a. Yellow b. indigo c. orange d. violet
1.13 Wave tend to spread out or bend in when they pass an edge or through
a gap. This bending effect is called what?
(2)
a. dispersion b. diffraction c. superposition d. interference
1.14 The focusing of different colours of light at different distances behind a
lens is known as what?
(2)
a. myopia b. hyperopia c. astigmatism d. chromatic aberration
1.15 In an instance where a wave travel along the same flat plane in which the
vibrating particle that carries the wave oscillate, such waves are called
what?
(2)
a. gamma waves b. longitudinal waves c. transverse waves d. x- rays
General Physics 1B (GNP502S)
2nd Opportunity January 2025
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.16 The whistle of a train emits a tone of frequency 440 Hz as the train
approaches a stationary observer at 30 m/s. What frequency does the
observer hear? [Speed of wave is 331 m/s].
{2)
a. 380 Hz b. 483 Hz c. 485 Hz d. 484 Hz
1.17 ............ is the characteristic of a note which enables us to differentiate
a high note from a low note.
(2)
a. Intensity b. node c. pitch d. loudness
1.18 One cycle of a wave takes 0.1 s to pass a stationary observer. What is the
frequency of the wave?
(2)
a. 0.1 Hz b. 0.2 Hz c. 10 Hz d. 20 Hz
1.19 What is the critical angle for light travelling from water to air?
= -]. ,...,
4
[Take'dnw
(2)
3
a. 0.75°1' b. 48°'36' c. 28°40' d. 25°17'
1.20 A long rope is fixed at one end, and the free end is made to oscillate in one
plane at right angles to the rope with frequency of 4 Hz. The successive
crests are 0.6 m apart. Determine the speed of the waves.
(2)
a. 6.7 mis b. 0.15 mis c. 2.4 mis d. 4.6 mis
SECTION B
[60 MARKS]
QUESTION2
[16 MARKS]
2.1 A concave mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm produces an inverted image
3 times the size of an object placed perpendicular to the axis. Calculate
the positions of the object and the image.
(8)
2.2 State the two condition that must be fulfilled for total internal reflection to
occur.
(4)
2.3 A thin glass lens (n = 1.5) has a focal length of+ 10 cm in air. Compute its focal
length in water (n = 1.33).
(4)
General Physics 1B (GNP502S)
2nd opportunity January 2025
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 3
[15 MARKS]
3.1 Differentiate between chromatic aberration and spherical aberration
and give one example for each of their correction.
(6)
3.2 If tension is maintained on a stretched string of length 0.6 m, such that its
fundamental frequency of 220Hz is excited, determine the velocity of the
transverse wave in the string.
(4)
3.3 Light of wavelength 750 nm passes through a slit 1.0 X 1o-3 mm wide. How
wide is the central maximum on a screen 20 cm away?
(5)
QUESTION4
4.1 State doppler effect in sound.
[14 MARKS]
(2)
4.2 An automobile moving at 30.0 mis is approaching a factory whistle that has
a frequency of 500 Hz.
4.2.1 If the speed of sound in air is 340 mis, what is the apparent frequency of the
whistle as heard by the driver?
(3)
4.2.2 Repeat for the case of a car leaving the factory at the same speed.
(3)
4.3 When two tuning forks are sounded simultaneously, they produce one beat
every 0.30 seconds.
4.3.1 By how much their frequency differ if the number of beats per second
equal the frequency difference.
(3)
4.3.2 A tiny piece of chewing gum is placed on a prong of one fork. Now there is
one beat every 0.40 seconds. Was this turning fork lower- or the higher
frequency fork?
(3)
QUESTIONS
[15 MARKS]
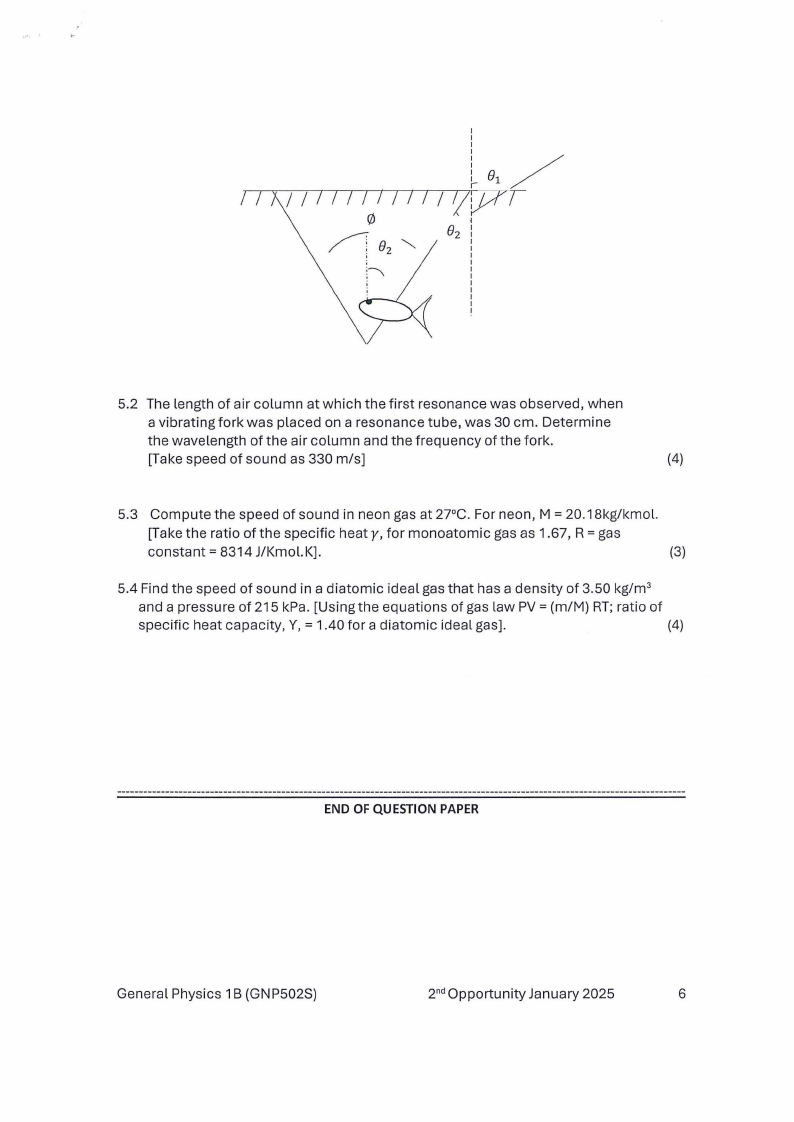
5.1 When a fish looks up at the surface of a perfectly smooth lake, the surface
Appears dark except inside a circular area directly above it. Calculate the
angle(/) that this illuminated region subtends. (The index of refraction of water
n 2 = 1.333 and of air is n 1 = 1).
(4)
General Physics 1B (GNP502S)
2nd Opportunity January 2025
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
II
I
(/J
/[
02"'
:~
5.2 The length of air column at which the first resonance was observed, when
a vibrating fork was placed on a resonance tube, was 30 cm. Determine
the wavelength of the air column and the frequency of the fork.
[Take speed of sound as 330 mis]
(4)
5.3 Compute the speed of sound in neon gas at 27°C. For neon, M = 20.1 Skg/kmol.
[Take the ratio of the specific heat y, for monoatomic gas as 1.67, R = gas
constant= 8314 J/Kmol.K].
(3)
5.4 Find the speed of sound in a diatomic ideal gas that has a density of 3.50 kg/m 3
and a pressure of 215 kPa. [Using the equations of gas law PV = (m/M) RT; ratio of
specific heat capacity, Y, = 1.40 for a diatomic ideal gas].
(4)
END OF QUESTION PAPER
General Physics 1B (GNP502S)
2nd Opportunity January 2025
6





