 |
NWS620S - NETWORK SECURITY - 1ST OPP - NOV 2020 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
A)
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMPUTING AND INFORMATICS
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BACS
LEVEL: 6
COURSE: NETWORK SECURITY
COURSE CODE: NWS620S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2019
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 2 HOURS
MARKS: 70
EXAMINER(S)
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
MRS. MERCY CHITAURO
MODERATOR:
DR ATTLEE GAMUNDANI
THIS EXAMINATION PAPER CONSISTS OF 2 PAGES
(Excluding this front page)
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions.
2. When writing take the following into account: The style should inform than impress, it should be
formal, in third person, paragraphs set out according to ideas or issues and the paragraphs flowing
in a logical order. Information provided should be brief and accurate.
Please, ensure that your writing is legible, neat and presentable.
4. When answering questions you should be led by the allocation of marks. Do not give too few or
too many facts in your answers.
Number your answers clearly according to the question paper numbering.
6. Clearly mark rough work as such or cross it out unambiguously in ink.
Calculator.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

1. Public key encryption schemes can be used for conventional encryption and digital
certificates.
a. What else can public key encryption schemes be used for?
[1]
b. Suppose that Romanus wants to send a message to Tjitjiri. Describe how a public
key encryption scheme can enable Romanus to send a digitally signed message to
Tjitjiri.
[4]
c. What is the drawback to the digital signature method described in (1b)?
[1]
d. What could be a more efficient way of obtaining a digital signature?
[2]
e. Give a practical example of the solution you mentioned in (1d)
[1]
f. Explain how the solution in (1d) can provide a digital signature
[3]
2. The point of public-key encryption is that the public key is public. Thus, if there is some
broadly accepted public-key algorithm, such as RSA, any participant can send his or her
public key to any other participant or broadcast the key to the community at large.
a. What is the problem to this approach for distributing public keys?
[2]
b. What is the solution to the problem identified in (2a)?
[1]
c. Explain how a user obtains a public-key certificate.
[3]
d. What are the contents of a public-key certificate?
[3]
e. Explain how Tuyapeni can verify Wesley’s public-key certificate.
[3]
f. Name a standard scheme that is universally accepted for formatting public-key
certificates.
[1]
3.
a. Howcan you protect your network from passive attacks?
[2]
b. How many keys are required for two people to communicate via an asymmetric
cipher?
[1]
c. Explain how public key encryption schemes can be used to distribute session keys
for symmetric encryption algorithms.
[6]
4. The SSL Record Protocol provides confidentiality and message integrity security services
for SSL connections.
a. Which 2 services does the SSL Record Protocol provides for SSL connections? [2]
b. Which method does SSL use to get message integrity?
[1]
c. Using your knowledge of SSL. Explain how SSL circumvents the attack given.
i. Brute-force cryptanalytic attack: An exhaustive search of the key space for
a conventional encryption algorithm.
[2]
ii. Man-in-the-middle attack: An attacker interposes during key exchange,
acting as the client to the server and as the server to the client.
[2]
iii. Password sniffing: Passwords in HTTP or other application traffic are
eavesdropped.
[2]
d. When Change Cipher spec protocol value is set to one; what happens?
[2]
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
e. One stage of SSL operation involves the use MAC. What is different at this stage
compared with TLS?
[2]
Cryptolocker is a malware released in September 2013, CryptoLocker spread through
email attachments and encrypted the user’s files so that they couldn’t access them. The
hackers then sent a decryption key in return for a sum of money, usually somewhere from
a few hundred pounds up to a couple of grand (Norton.com, 2017).
a. Viruses typically have 3 components. State and explain the three components of a
virus
[6]
b. Give an example of each virus component in the context of Cryptolocker virus.
[3]
+
BRAWCH2
INTERNET
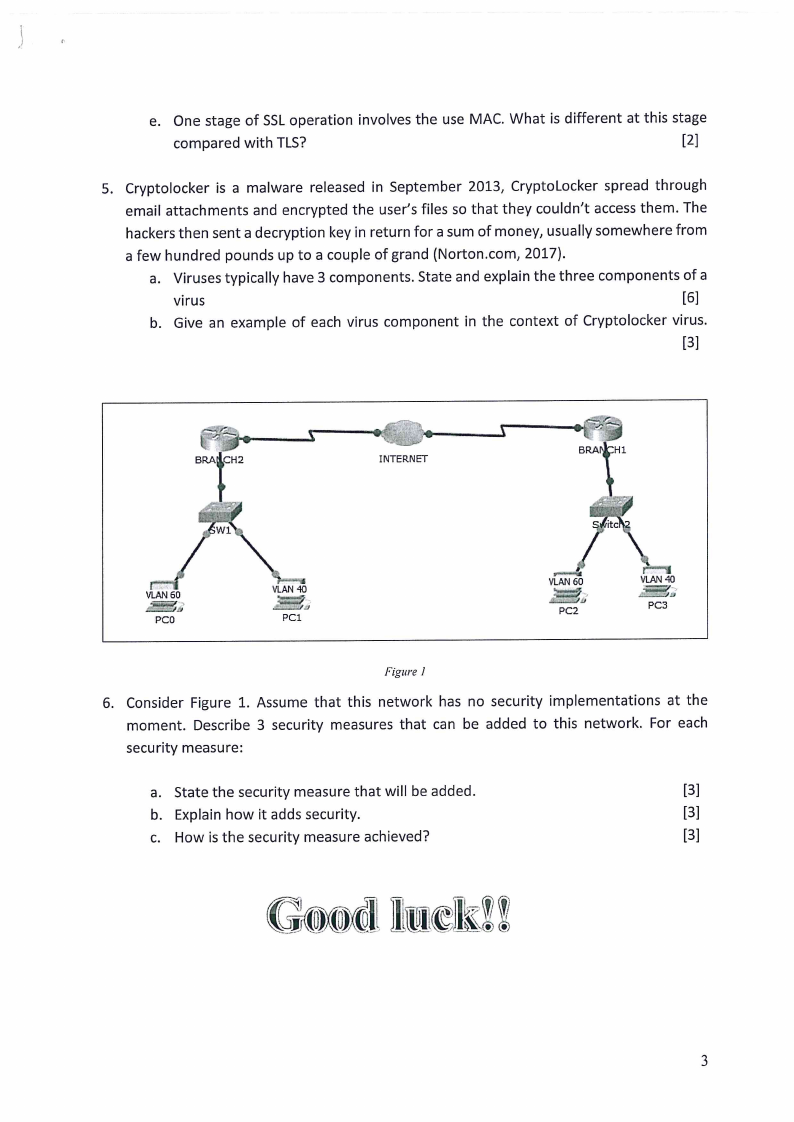
Figure 1
Consider Figure 1. Assume that this network has no security implementations at the
moment. Describe 3 security measures that can be added to this network. For each
security measure:
a. State the security measure that will be added.
[3]
b. Explain how it adds security.
[3]
c. How is the security measure achieved?
[3]
Ick "o@





