 |
SMK611S - SERVICES MARKETING - 2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE AnD TECHn OLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCEAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF MARKETING & LOGISTICS
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MARKETING
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07MARB
LEVEL: 6
COURSE CODE: SMK611S
COURSE NAME: SERVICESMARKETING
SESSION: JULY2022
PAPER: (PAPER1)
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Mr. C. KAZONDOVI
MODERATOR: Mr. J. NDUNGAUA
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions and Number the answers clearly.
2. This paper consists of two (2) sections (A & B).
3. Use the tables provided on [page 7] to answer Section A, Question
One (1) AND Question Two (2) on [page 8] respectively: Detach and
insert it into your answer booklet.
4. Write as legible and as precise as possible.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF~ PAGES (Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A
Question 1
Multiple choice questions
Choose the correct answer and use the table provided on [page 8] to answer these questions, detach
and insert it into your answer booklet. 1.5 marks will be awarded for each correct answer.
[20 x 1.5 = 30 Marks]
1.1) Services Marketing is most likely geared towards:
A) employee satisfaction.
B) customer satisfaction.
C) green marketing.
D) advertising effectiveness.
E) market reach.
1.2) All of the following are benefits of customer satisfaction except:
A) the firm is more insulated from price competition.
B) the firm provides a positive work environment for its employees.
C) positive word-of-mouth communications is generated from satisfied customers.
D) satisfied customers make purchases more frequently.
E) none of these are exceptions.
1.3) Customer satisfaction can be defined by comparing:
A) predicted service and perceived service.
B) predicted service and desired service.
C) desired service and perceived service.
D) adequate service and perceived service.
E) expected service and desired service.
1.4) ______
is the level of service the customer actually wants to receive.
A) Desired service
B) Predicted service
C) Perceived service
D) Adequate service
E) Derived expectations
1.5) The zone of tolerance is defined as the difference between:
A) predicted service and perceived service.
B) predicted service and desired service.
C) desired service and adequate service.
D) adequate service and perceived service.
E) expected service and desired service
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.6) The firm's increased research orientation and enhanced upward communication will assist the
firm in decreasing which one of the following gaps?
A) knowledge gap
B) standards gap
C) delivery gap
D) communications gap
E) confirmation gap
1.7) Understanding the customer is a critical step toward minimizing or completely eliminating the
_____
gap.
A) knowledge
B) standards
C) delivery
D) communications
E) confirmation
1.8) A hotel may feel that its customers prefer comfortable rooms, when, in fact, the majority of the
hotel's customers spend little time in their rooms and are more interested in on-site amenities such as
the pool, spa, and restaurants. This hotel is suffering from a __ gap.
A) knowledge
B) standards
C) delivery
D) communications
E) confirmation
. 1.9) Employee willingness to perform and employee-job fit are directly related to which of the following
service quality gaps?
A) knowledge gap
B) standards gap
C) delivery gap
D) communications gap
E) service gap
1.10) The ____
gap is the difference between the service the firm promises to deliver through
its external communications and the service it actually delivers to its customers.
A) knowledge
B) standards
C) delivery
D) communications
E) service
1.11) The _____
service performance
A) Empathy.
B) Responsiveness.
C) Assurance
D) Reliability.
E) None of these
dimension is an assessment of the firm's consistency and dependability in
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.12) Which of the following would not be considered a tangible clue?
A) The appearance of employees
B) The appearance of the firm's physical facilities
C) The smile on an employee's face
D) The quality of instruction in an educational setting.
E) All of these
1.13) Minimizing the amount of role conflict and role ambiguity experienced by employees will help
reduce the size of this gap is known as ____
_
A) Knowledge gap.
B) Standards gap
C) Delivery gap.
D) Communications gap
E) None of these
1.14) Fixing a right price for services offered is difficult because of _____
_
A) perishability.
B) heterogeneity.
C) inseparability.
D) accessibility
E) intangibility.
1.15) Service consumers tend to be more brand loyal than goods consumers because
A) More choices are available
B) Brand loyalty lowers the amount of perceived risk
C) Each service provider provides many brands
D) Location of the provider is the major driver in the consumer selection process
E) All of these
1.16) Customers ultimately determine the services by_____
_
A) The type of competitors.
8) The levels of marketing effectiveness and operational efficiency
C) The cycle of fluctuations
D) The price of the competitors.
E) None of these
1.17) A buyers' perception of value is considered a trade-off between
A) Product value and psychic cost
8) Total customer value and total customer cost.
C) Image value and energy cost
D) Personnel value and buyer cost
E) Service value and monetary cost.
1.18) Total customer value consists of all of the following components except
A) Product value.
B) Service value.
C) Image value
D) Personnel value.
E) None of these
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

1.19) Which of the following statements about the pricing of services (compared to the pricing of
goods) is false?
A) The demand for services tends to be more elastic than the demand for goods
B) Cost-oriented pricing is more difficult for services
C) Comparing prices of competitors is more difficult for service consumers.
D) Self-service is a viable competitive alternative.
E) None of these
1.20) Word-of-Mouth communication networks are particularly important for service firms because
A) Service customers tend to rely more on personal than non-personal source of information.
B) Service firms do not believe in promotional efforts.
C) Service firms can seldom afford to pay for promotional expenditures.
D) Service customers tend to rely more on non-personal than personal sources of information.
E) None of these
Question Two
True or False Questions
Use the table provided on [page 8] to answer these questions, detach and insert it into your answer
booklet. 1 mark will be awarded for each correct answer.
[20 x 1 = 20 Marks]
2.1) Complainers about your service are more likely to do business with you again than non-
complainers.
2.2) CRM is limited by its focus on past purchase patterns.
2.3) Most economies are dominated by the service sector
2.4) With pure tangible goods, the offer consists primarily of a tangible good such as books, shoes -
however, prominent services accompany this offer.
2.5) Due to the fact that employees are already part of the service delivery process, internal marketing
is a less vital aspect of services marketing.
2.6) An external marketing program flows out of a service culture. A service marketing program is
doomed to failure if its organizational culture does not support serving the customer
2.7) If management expects employee's attitudes to be positive toward the customer, management
must have a positive attitude toward the customer and the employees
2.8) A Service Culture is a culture that supports customer service through policies, procedures, reward
system and actions.
2.9) A service culture requires turning the organisational structure upside down.
2.10) Service organisations need to "hire for skills and train for attitude". .
2.11) In services organisations, more emphasis is placed on personality, energy and attitude when
recruiting selecting and training prospective/current employees.
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

2.12) Uniforms are important because employee's dress contributes greatly to the customer's
encounter with the employee.
2.13) In order to best manage emotional labour, managers must hire employees who can cope with
the stress caused by dealing with customers face-to-face.
2.14) CRM platforms should be geared towards all customers and not require that customers be
categorised and that each category receives a special treatment
2.15) Financial bonds are the final parts in terms of building customer relationships.
2.16) The Servuction model is used to illustrate the factors that influence the service experience;
including those that are visible and those that are not.
2.17) The Service gap is the gap between customer expectations of the service and their perception
of the service actually delivered.
2.18) The service quality process can be examined in terms of gaps between expectations and
perceptions on the part of management, employees, and customers.
2.19) Customisation Bonds means that companies seek to build more intimate relationships through
interpersonal bonds.
2.20) Social bonds often occur where the services offered by the service provider are designed into
the systems or processes of the client company.
SECTION B
[Total 50 Marks]
Question 3
Three levels of services are involved in any purchase. Describe with an example of a service-oriented
scenario how the service levels are inter-connected.
(10 marks)
Question 4
Consider all Five (5) of the Service Quality (ServQual) dimensions and discuss, with relevant examples
how each dimension can be used to evaluate overall company performance with regard to service
quality.
(20 marks)
Questions 5
The Four (4) integral Characteristics of Services Marketing causes numerous challenges for service
providers. Discuss with relevant service-oriented examples how the service provider can try and
overcome these challenges.
(20 marks)
Total 100 marks
(END)
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
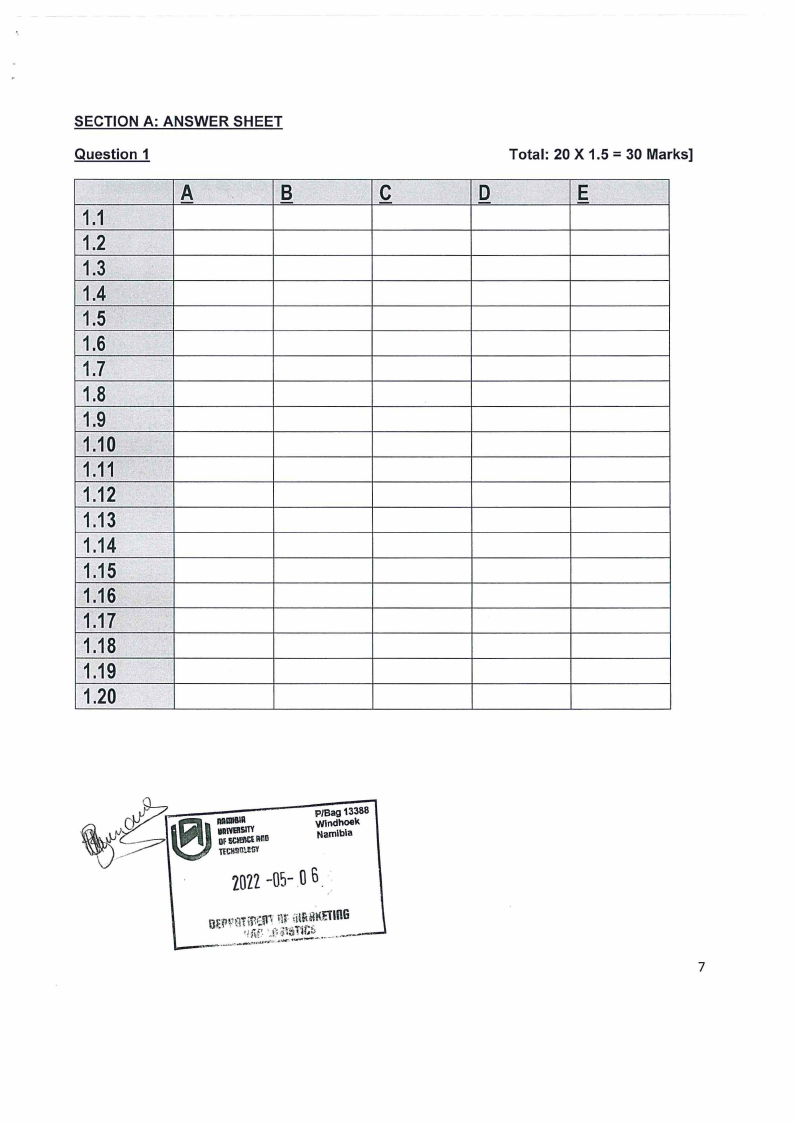
SECTION A: ANSWER SHEET
Question 1
Total: 20 X 1.5 = 30 Marks]
A
B
C
D
E
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9 ,_
1.10
1.11
1.12
1.13
1.14
1.15
1.16
1.17
1.18
1.19
1.20
7
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

Question 2
2.1
2.2
2.3
2.4
2.5
2.6
2.7
2.8
2.9
2.10
2.11
2.12
2.13
2.14
2.15
2.16
2.17
2.18
2.19
2.20
True
False
STUDENT NAME& STUDENT NO:
[Total: 20 X 1 = 20 Marks]
8





