 |
ECM712S-ECONOMETRICS-1ST OPP- JUNE 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA un IVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OFCOMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCE AND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ECONOMICS
QUALIFICATION CODE:
07BECO
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: ECM712S
COURSE NAME: ECONOMETRICS
SESSION: JUNE 2024
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) MR. PINEHAS NANGULA
MODERATOR: Dr R. KAMATI
INSTRUCTIONS
I. Answer ALL the questions in section A and B
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
I. Scientific calculator
2. Pen and Pencil
3. Ruler
This question paper consists of _8_ pages (including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A
[20MARKS]
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. After estimating by OLS a two regression model, the resulting residuals:
a) Add up to zero if a constant term was included in the model.
b) Are orthogonal to the model regressors only if a constant term was included in the
model.
c) Have constant variances and null covariances whenever the model errors have these
properties.
d) None of the above
2. What is the difference between R2 and the adjusted R2?
a) the adjusted R2 always increases as more independent variables are added to the
model
b) the adjusted R2 is smaller in this case because the constant term is negative
c) the adjusted R2 adjusts explanatory power by the degrees of freedom
d) None of the above
Use the following to answer questions 3-5:
Eight students are selected randomly and their present graduate GPA is compared to
their undergraduate GPA and scores on standardized tests.
The data are shown below:
Present Undergraduate Standard
GPA GPA
Scores
3.89 3.77
700
3.03 2.75
460
3.34 3.11
550
3.85 3.75
690
3.93 4
720
3.06 2.92
420
3.69 3.7
670
3.91 3.88
670
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
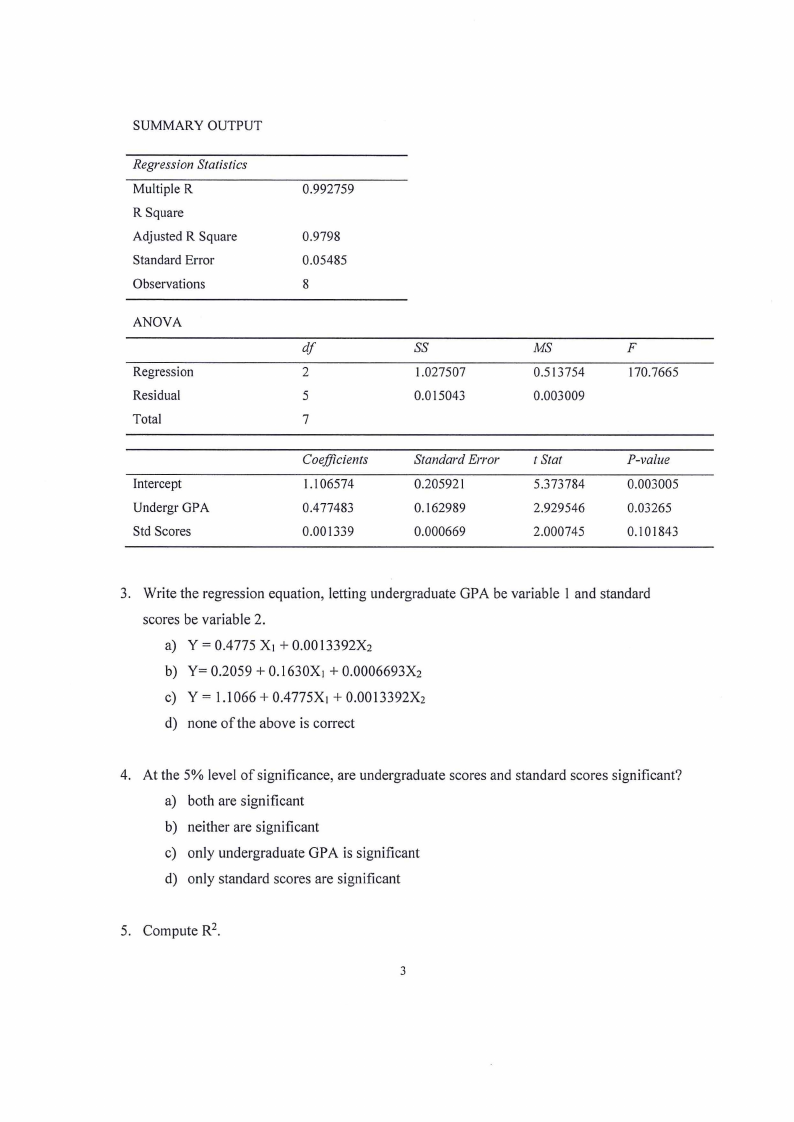
SUMMARY OUTPUT
Regression Statistics
Multiple R
R Square
Adjusted R Square
Standard Error
Observations
ANOVA
Regression
Residual
Total
Intercept
Undergr GPA
Std Scores
0.992759
0.9798
0.05485
8
df
2
5
7
Coefficients
1.106574
0.4 77483
0.001339
ss
1.027507
0.015043
MS
0.513754
0.003009
F
170.7665
Standard Error
0.205921
0.162989
0.000669
t Stat
5.373784
2.929546
2.000745
P-value
0.003005
0.03265
0.101843
3. Write the regression equation, letting undergraduate GPA be variable I and standard
scores be variable 2.
a) Y = 0.4775 X1 + 0.0013392X2
b) Y= 0.2059 + 0.1630X1 + 0.0006693X2
c) Y= l.1066+0.4775X1 +0.0013392X2
d) none of the above is correct
4. At the 5% level of significance, are undergraduate scores and standard scores significant?
a) both are significant
b) neither are significant
c) only undergraduate GPA is significant
d) only standard scores are significant
5. Compute R2.
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

a) 99.4%
b) 98.6%
c) 20.8%
d) very close to 100%
6. Dummy variables are used when:
a) qualitative variables are involved in the model
b) quantitative variables are involved in the model
c) doing residual analysis
d) making transformations of quantitative variables
7. Suppose you obtain the following fitted model: bwght =/Jo+/J1 cigs + /J2faminc, where
bwght is child birth weight in ounces, cigs is the average daily number of cigarettes
smoked per day by the mother during pregnancy, and famine is family income measured
in dollars.
/Jois an estimate of
a) how many cigarettes a day it takes to lower birth weight by I ounce, on average
b) how many ounces an extra cigarette a day lowers bilth weight, on average.
c) how many ounces the average baby weighs, when cigs=0 and faminc=0.
d) the standard error of cigs.
8. The interpretation of the slope coefficient in the model ln~ = {30 + {31 In Xi + ui is as
follows: a
a) change in X by one unit is associated with a 100 % change in Y.
b) 1% change in X is associated with a % change in Y.
c) 1% change in Xis associated with a change in Y of 0.01
d) change in X by one unit is associated with a change in Y.
9. What will be the properties of the OLS estimator in the presence of multicollinearity?
a) It will be consistent, unbiased and efficient
b) It will be consistent and unbiased but not efficient
c) It will be consistent but not unbiased
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
d) It will not be consistent
10. Which one of the following statements best describes a Type II error?
a) It is the probability of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis
b) It is equivalent to the power of the test
c) It is equivalent to the size of the test
d) It is the probability of failing to reject a null hypothesis that was wrong
SECTIONB
[80 MARKS]
QUESTION ONE
r30 MARKS]
a) Between sample one and sample two below, which one do you think estimate population
parameters better i.e. which sample has a small residual sum of square?
[20 marks]
Sample One
Consumption
70
65
90
95
110
115
Income
80
100
120
140
160
180
Sample Two
Consumption
55
80
90
80
118
120
Income
80
100
120
140
160
180
b) The data in the table below refer to a total population of 16 families in a hypothetical
community and their weekly income (I) and weekly consumption expenditure (C), both in
dollars. The 16 families are divided into 4 income groups (from N$80 to N$140) and the
weekly expenditures of each family in the various groups are as shown in the table below.
Weekly Family Income
80
100
120
140
Weekly Family 75
90
110
135
Expenditure
79
89
80
137
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
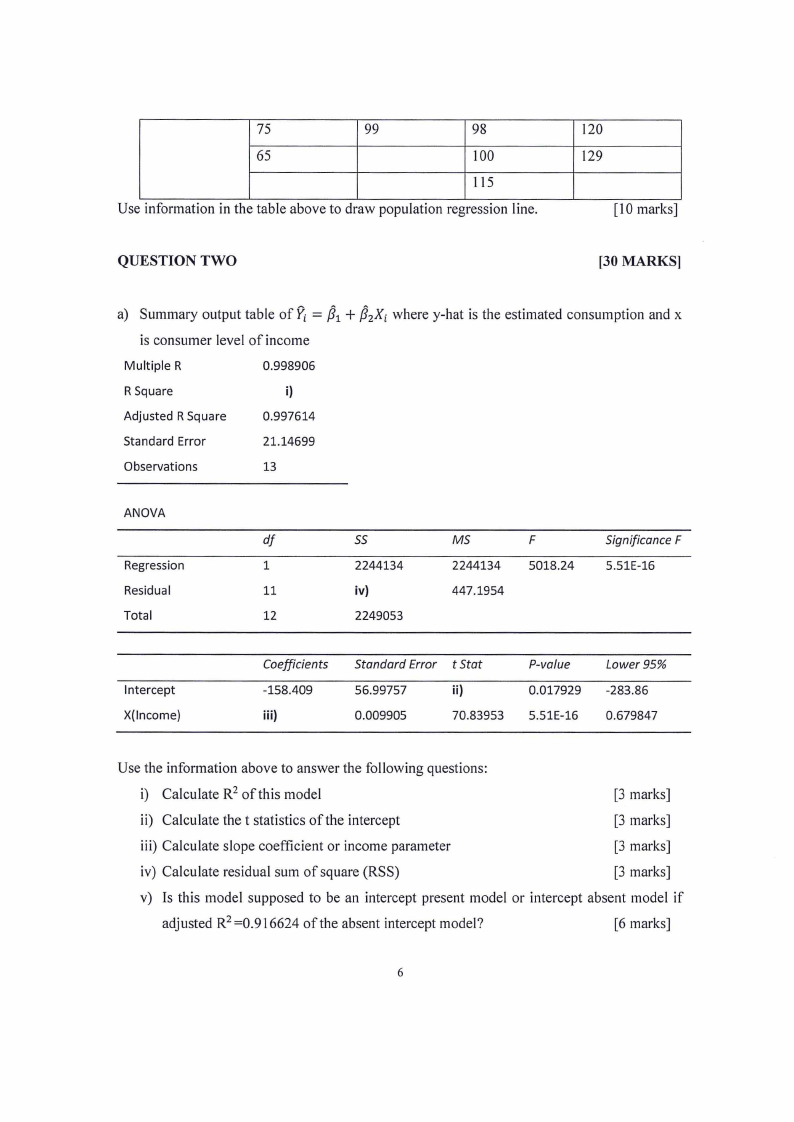
120
129
Use information in the table above to draw population regression line.
[10 marks]
QUESTION TWO
[30 MARKS]
Pi a) Summary output table of Yi = + PzXi where y-hat is the estimated consumption and x
is consumer level of income
Multiple R
0.998906
R Square
i)
Adjusted R Square
0.997614
Standard Error
21.14699
Observations
13
ANOVA
df
ss
MS
F
Significance F
Regression
1
2244134
2244134
5018.24
5.51E-16
Residual
11
iv)
447.1954
Total
12
2249053
Intercept
X(lncome)
Coefficients
-158.409
iii)
Standard Error t Stat
56.99757
ii)
0.009905
70.83953
P-value
0.017929
5.51E-16
Lower 95%
-283.86
0.679847
Use the information above to answer the following questions:
i) Calculate R2 of this model
[3 marks]
ii) Calculate the t statistics of the intercept
[3 marks]
iii) Calculate slope coefficient or income parameter
[3 marks]
iv) Calculate residual sum of square (RSS)
[3 marks]
v) Is this model supposed to be an intercept present model or intercept absent model if
adjusted R2 =0.916624 of the absent intercept model?
[6 marks]
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
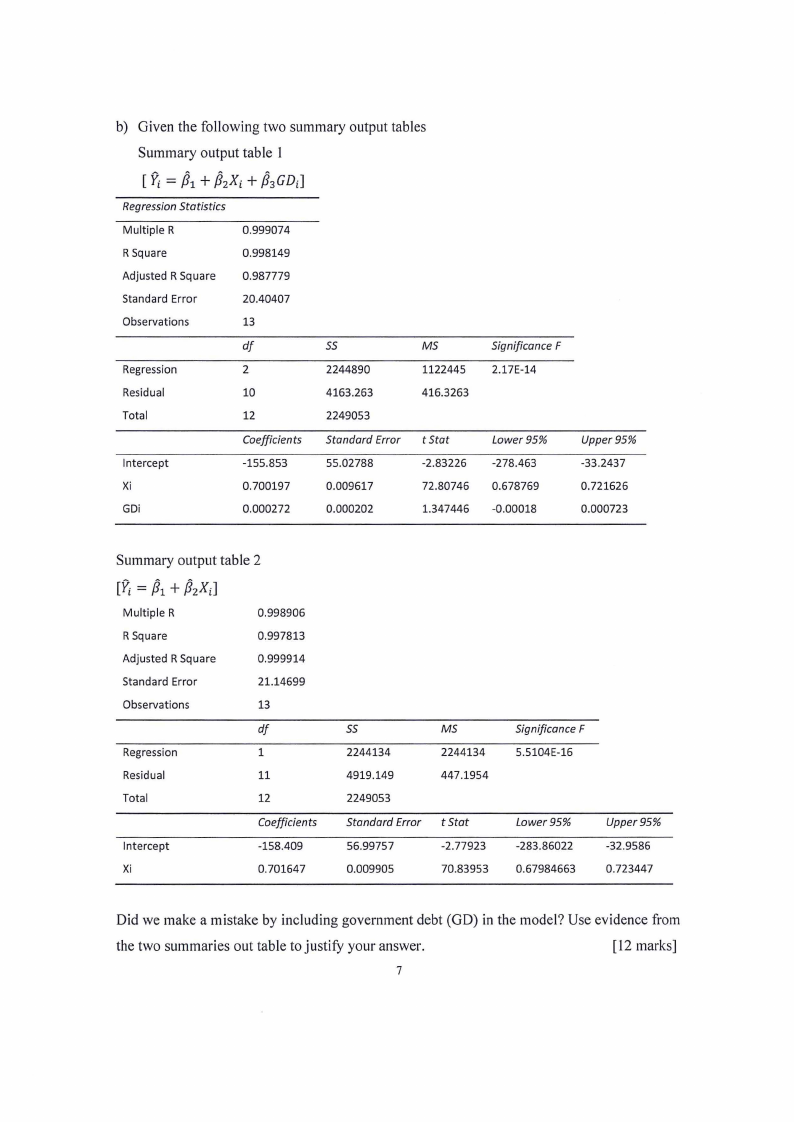
b) Given the following two summary output tables
Summary output table I
[ Yi = P1+ P2Xi + p3GDd
Regression Statistics
Multiple R
0.999074
R Square
0.998149
Adjusted R Square 0.987779
Standard Error
20.40407
Observations
13
df
55
MS
Regression
2
2244890
1122445
Residual
10
4163.263
416.3263
Total
12
2249053
Coefficients Standard Error t Stat
Intercept
-155.853
55.02788
-2.83226
Xi
0.700197
0.009617
72.80746
GDi
0.000272
0.000202
1.347446
Significance F
2.l 7E-14
Lower 95%
-278.463
0.678769
-0.00018
Upper 95%
-33.2437
0.721626
0.000723
Summary output table 2
[Yi= P1+ P2Xd
Multiple R
0.998906
R Square
0.997813
Adjusted R Square
0.999914
Standard Error
21.14699
Observations
13
df
Regression
1
Residual
11
Total
12
Coefficients
Intercept
-158.409
Xi
0.701647
55
2244134
4919.149
2249053
Standard Error
56.99757
0.009905
MS
2244134
447.1954
t Stat
-2.77923
70.83953
Significance F
5.5104E-16
Lower95%
-283.86022
0.67984663
Upper95%
-32.9586
0.723447
Did we make a mistake by including government debt (GD) in the model? Use evidence from
the two summaries out table to justify your answer.
(12 marks]
7
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION THREE
r20 MARKS]
a) Use relevant economics examples to discuss two types of error that arise in hypothetical
conclusions
[8 marks]
b) Discuss three approaches to hypothesis testing. In your discussion, make sure to highlight
the decisions rule associated with each approach.
[12 marks]
All the best
8





