 |
BNS511S - BIOLOGY FOR NATURAL SCIENCES - 1st OPP - JUNE 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

n Am I BI A u n IVER s I TY
0 F SCIEnCE An D TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTHAND APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF AGRICULTUREAND NATURALRESOURCESSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION:BACHELOROF NATURALRESOURCEMANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 07BNRS
LEVEL: 5
COURSECODE: BNS511S
COURSENAME: BIOLOGYFOR NATURAL SCIENCES
SESSION: JUNE 2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 150
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION QUESTIONPAPER
EXAMINER(S) Mrs Louise Theron
MODERATOR: Mrs Clarence Ntesa
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink
2. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 4 PAGES(excluding this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A
QUESTION 1
Give the scientific term for each of the following:
[10]
1.1 Cell organelle that prevents wilting in plants.
1.2 The solid part in a mixture that gets dissolved.
1.3 When elements combine to form a compound.
1.4 Cell organelle that breaks down food and destroys old cells.
1.5 Cell-wall component of Eubacteria.
1.6 Viruses exist as infectious particles known as ......
1.7 In the life cycle of Ulva the two generations look exactly the same,
we therefore say that Ulva have alternation of ........ generations.
1.8 The name of the Phylum responsible for RedTides in Namibia.
1.9 Fusion of the cytoplasm of compatible mating types (Mycota).
1.10 The Phylum where puffballs, toadstools and bracket fungi belong.
QUESTION 2
Explain the difference between the following pairs of terms.
[10]
2.1 Dilute solution vs Concentrated solution
2.2 Mass number vs Atomic number
2.3 Fat soluble vs Water soluble vitamins
2.4 Coenocytic vs Septate hyphae in fungi
2.5 Rhodophyta vs Phaeophyta
QUESTION 3
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. If false. re-write the statement [10]
to correct it.
3.1 A positively charged ion is known as an anion.
3.2 The Golgi Body is the organelle that directs traffic in the cell.
3.3 Members of the Kingdom Mycota are primarily unicellular, prokaryotic organisms.
3.4 The phase in viral reproduction where viral genomes and proteins are being put
together to form new viruses is known as the Replication phase.
3.5 In the lysogenic cycle of viral reproduction the viral genes are expressed immediately
after the virus infects the host cell.
3.6 Members of the Phylum Deuteromycota reproduce asexually by conidia.
SUB-TOTAL (30}
1
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B
QUESTION 4
4.1 How are elements in the same group on the periodic table similar?
(3)
4.2 Explain the term "catalyst".
(2}
4.3 Which 3 elements make up the "Iron Triad"?
(3}
4.4 Explain what "Bio-fertilisers" are. Provide examples
(2)
[10]
QUESTION 5
5.1 In your OWN WORDS, explain the term BIOTECHNOLOGY.
(2)
5.2 Explain why Biotechnology has become such a big industry worldwide (reasons for its
(3)
growth over the last couple of decades}.
5.3 How do wine manufacturers manage to make different types of wine (red, white,
(4)
rose}?
WRITE FULL SENTENCES!!
5.4 Explain why you find "holes" in your loaf of bread.
(2)
5.5 Explain how we can turn sewage (our own faeces}, and cow dung into useful products
(4)
for ourselves= BIOTECHNOLOGY.
[15]
QUESTION 6
Write a report on the economic importance of viruses. Make use of suitable examples.
[10]
QUESTION 7
Like all other living organisms, bacteria need a source of carbon and a source of energy. Discuss
the different ways bacteria use to get their nutrition and energy by re-drawing and completing
the table.
[12]
Parasites
Symbiotic
heterotrophic
e.g. milk souring bacteria
(lactic acid bacteria}
e.g. bacteria causing
tetanus
autotrophic
Obtain energy by oxidizing
simple inorganic salts
Use sunlight energy to
make their own food
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 8
8.1 Name the four "Protozoa" phyla found in the Kingdom Protoctista and state the motile
organs for each phylum.
(8)
8.2 Explain the difference between the ectoplasma and endoplasma of Amoeba. Also state
the function of each.
(4)
8.3 Provide the causal agents for (a) malaria and (b) Ngana
(2)
8.4 Explain the following structures, found in Paramecium
(5)
(a) Pellicle
(b) Multinucleated
(c) Pathogen
(d) Oral groove
(e) Contractile vacuole
8.5 Explain why malaria patients experience sporadic outbreaks of fever.
(2)
[21]
QUESTION 9
9.1 How do the cell walls of Mycota differ from those of Plantae?
(1)
9.2 Name the 4 Phyla of Mycota discussed in class.
(4)
9.3 Give the economic uses of each of the following fungi species:
(a) Saccharomyces
(b) Terfezia (Kalahari truffles)
(4)
(c) Termitomyces shimperi (Omayowa)
(d) Penicillium notatum
9.4 Clearly distinguish between Monokaryotic and Dikaryotic hyphae in fungi.
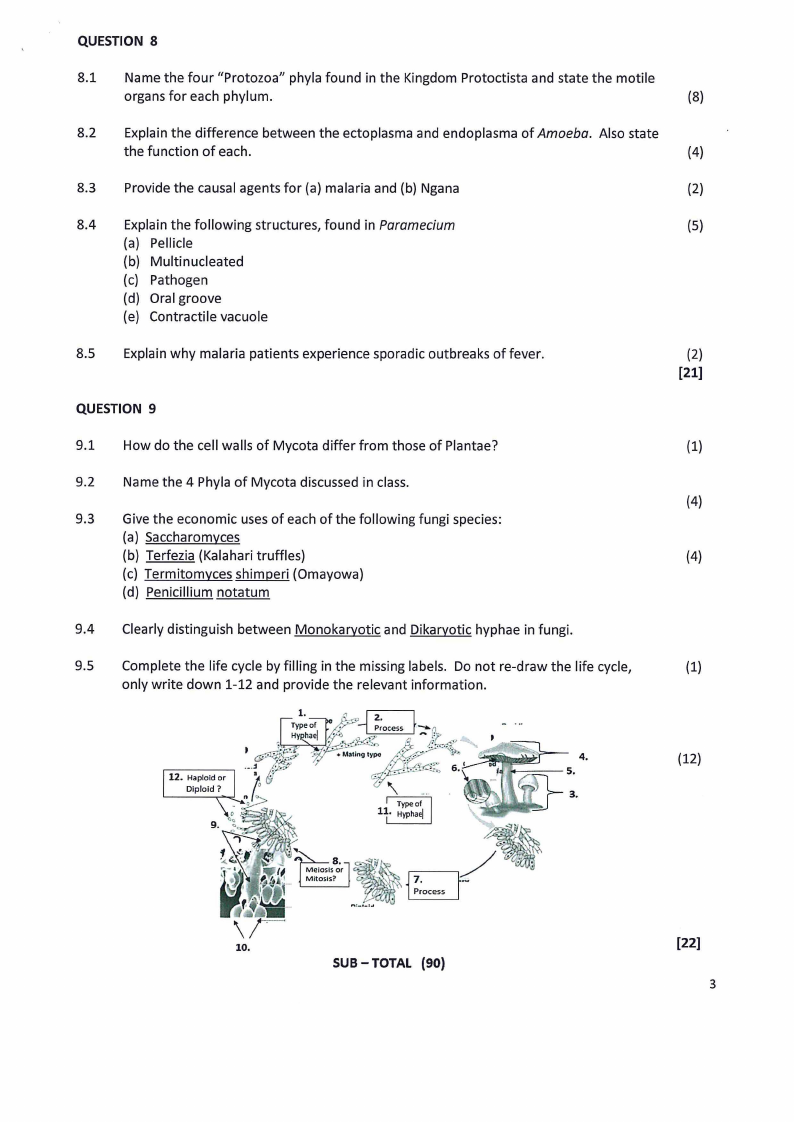
9.5 Complete the life cycle by filling in the missing labels. Do not re-draw the life cycle,
(1)
only write down 1-12 and provide the relevant information.
t .... i
4.
··! .r--
5.
0
3.
Type of
11. Hyphael
/' ~-~n,J~:@:ocerrs·s-
SUB-TOTAL {90)
(12)
[22]
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

SECTION C
QUESTION 10
10.1 State the chemical formula for photosynthesis
(3)
10.2 Where does the light reaction of photosynthesis take place?
(1)
10.3 Name four internal factors that influence the rate of photosynthesis in a plant.
(4)
[8]
QUESTION 11
11.1 Glycolysis it the first anaerobic stage of respiration. State where this stage takes place
and discuss the inputs and outputs used and produced in this stage of respiration.
(5)
11.2 Name the other stages of respiration.
(3)
11.3 Discusshow water and oxygen availability affect respiration.
(4)
[12]
QUESTION 12
12.1 Define osmosis (3) and discuss why it is important to life on earth (3).
12.2 Define the term transpiration.
12.3 State three types of transpiration that occur within a plant.
(6)
(1)
(3)
[10]
SUB-TOTAL [30]
TOTAL [150]
4
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 8
8.1 Name the four "Protozoa" phyla found in the Kingdom Protoctista and state the motile
organs for each phylum.
(8)
8.2 Explain the difference between the ectoplasma and endoplasma of Amoeba. Also state
the function of each.
(4)
8.3 Provide the causal agents for (a) malaria and (b) Ngana
(2)
8.4 Explain the following structures, found in Paramecium
(5)
(a) Pellicle
(b) Multinucleated
(c) Pathogen
(d) Oral groove
(e) Contractile vacuole
8.5 Explain why malaria patients experience sporadic outbreaks of fever.
(2)
[21)
QUESTION 9
9.1 How do the cell walls of Mycota differ from those of Plantae?
(1)
9.2 Name the 4 Phyla of Mycota discussed in class.
(4)
9.3 Give the economic uses of each of the following fungi species:
(a) Saccharomyces
(b) Terfezia (Kalahari truffles)
(4)
(c) Termitomyces shimperi (Omayowa)
(d) Penicillium notatum
9.4 Clearly distinguish between Monokaryotic and Dikaryotic hyphae in fungi.
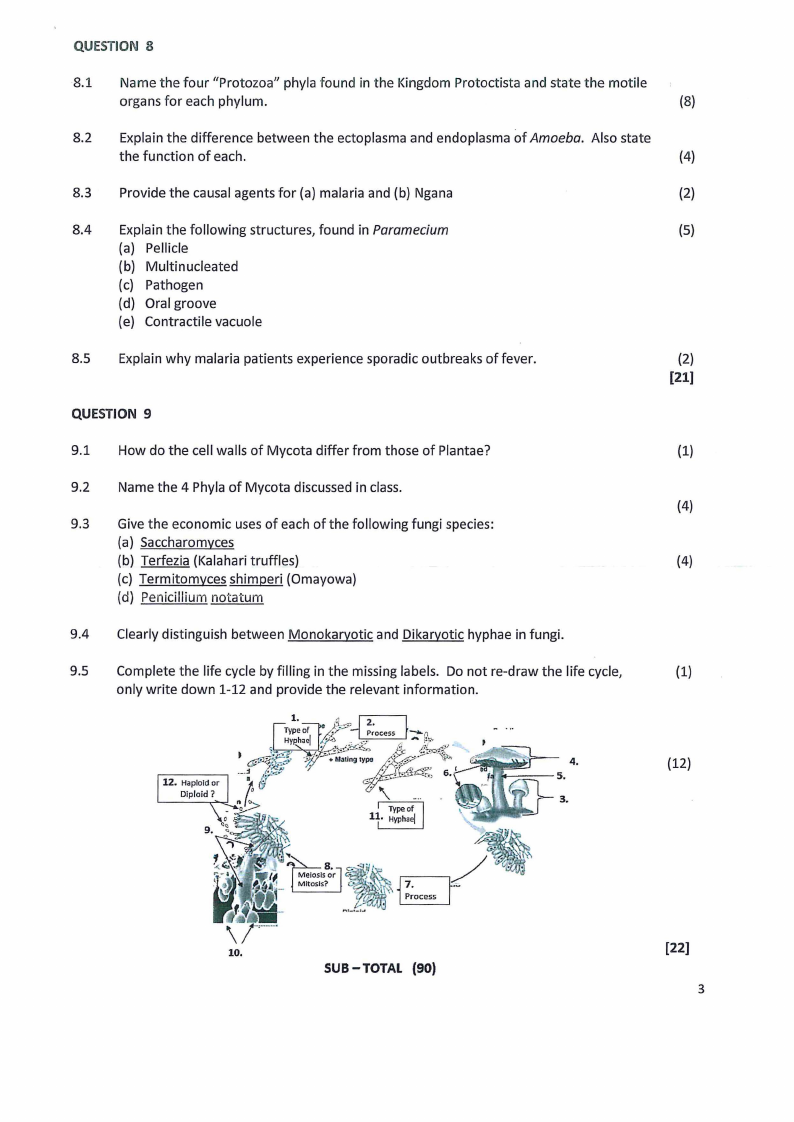
9.5 Complete the life cycle by filling in the missing labels. Do not re-draw the life cycle,
(1)
only write down 1-12 and provide the relevant information.
4.
(12)
Type of
.._. _~5-
JJ._._3r.
11. Hyphael
~··,td
SUB-TOTAL {90}
[22)
3





