 |
MAB702S - MARINE BIOLOGY 3B - 2ND OPP - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
n Am I BI A u n IVER s I TY
OF SCIEnCE AnDTECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,NATURAL RESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURALAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
COURSE CODE: MAB702S
SESSION: JANUARY2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
LEVEL: 7
COURSE NAME: MARINE BIOLOGY3B
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/ SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER {S):
Dr. Edosa Omoregie
MODERATOR:
Dr. Johannes litembu
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions in Sections A, Band C
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number your answers clearly.
4. Draw diagrams wherever necessary
Material/sallowed
Scientific Calculator
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS
(Including this front page)
Section A:
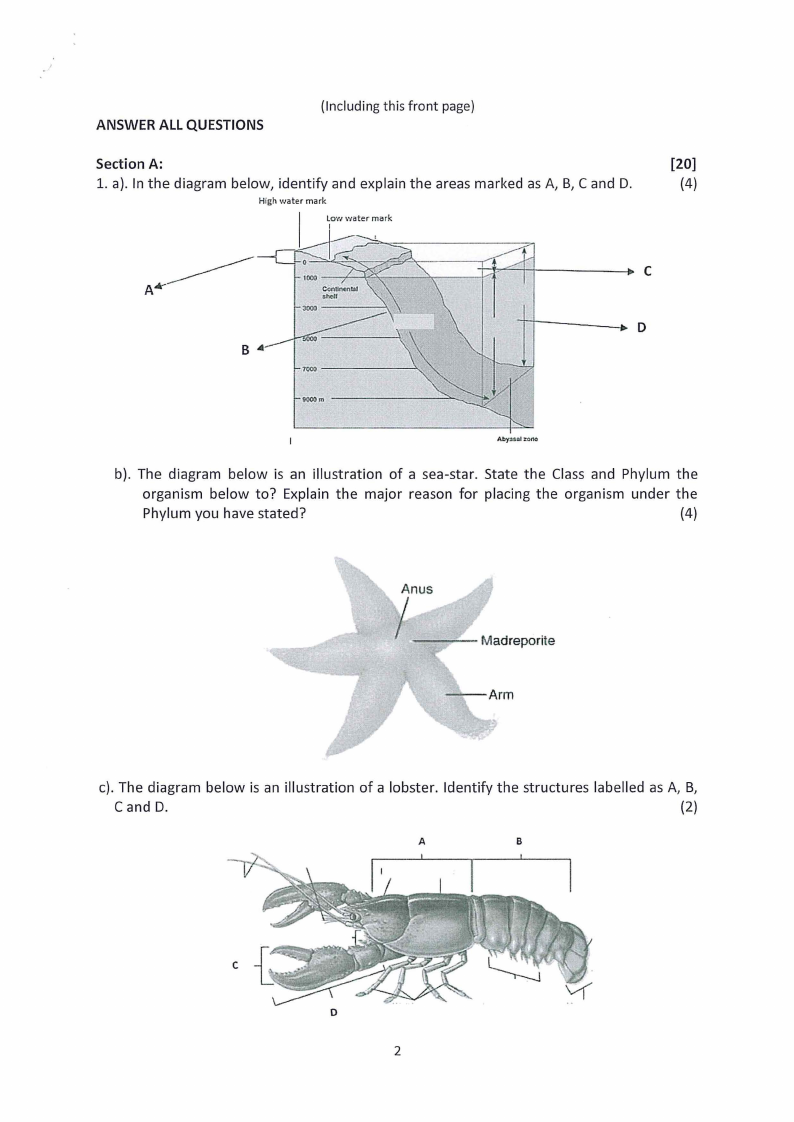
1. a). In the diagram below, identify and explain the areas marked as A, B, C and D.
High water mark
Low water mark
I
[20]
(4)
A.---------
C
Abyual:t0()6
b). The diagram below is an illustration of a sea-star. State the Class and Phylum the
organism below to? Explain the major reason for placing the organism under the
Phylum you have stated?
(4)
Anus
I____ Madreporite
c). The diagram below is an illustration of a lobster. Identify the structures labelled as A, B,
C and D.
(2)
A
B
D
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

2.The star fish belong to which group of the following animals?
(1)
a. Molluscs
b. Foraminifera
c. Brachiopods
d. Ctenophores
e. Echinoderms
3. To which of the following kingdoms do the Barnacles belongs to?
{1)
a. Fungi
b. Metazoa
c. Monera
d. Protista
e. Metaphyta
4. Oysters belongs to which kingdom?
{1)
a. Foraminifera
b. Coccoliths
c. Metazoa
d. Brachiopods
e. Metaphyta
5. Sea urchins are classified under?
(1)
a. Foraminifera
b. Mollusks
c. Brachiopods
d. Echinoderms
e. Ctenophores
6. Salt tolerant plants such as Salicornia spp. are ecologically referred to as?
(1)
a. Mangroves
b. Angiosperms
c. Gametophytes
d. Halophytes
e. Sporophytes
7. Mussels and other filter feeders use which ofthe following options as food source? {1)
a. Particulate organic matters suspended in water
b. Decomposed organic matters
c. Dissolved organic nutrients
d. Dead benthic organisms
e. Nekton
8. Marine organisms that live within the sediment of the sea bottom are referred to as? {1)
a. Aphotic
b. Epifauna
c. Infauna
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

d. Nekton
e. Pelagic
9. Which of the following options is not a source of food deep-sea organisms?
(1)
a. Dead phytoplankton
b. Dead zooplankton
c. Feacal droppings from pelagic fish
d. Dead intertidal zone benthos
e. Macrophyte detritus
10. Which of the following vertical profile of the marine benthic environment
sponges be the most dominate species in the ecological communities?
a. 0 to 100 m
b. 100 to 500 m
c. 500 to 1000 m
d. 1000 to 2000 m
e. 2000 to 7000 m
will the
(1)
11. The full scientific name of the largest bacteria discovered in the Namibia marine
environment is -------
(1)
Section B:
[20]
12. a). With the aid of graphical illustration, briefly explain how a conformer and a regulator
will respond to changes in their respective environment.
(6)
b). Name any group of marine organisms with each of the following
transportation in their blood:
i. Haemocyanin
ii. Haemerythrin
iii. Chlorocruorin
pigments for oxygen
(3)
c). With suitable examples, explain how marine benthic organisms are adapted to
withstanding effects of water currents.
(4)
d). With the aid of suitable diagram, discuss hydro-mechanical burrow by benthos on the
seabed.
(7)
Section C:
[60]
13. a). Using suitable examples, explain the various evolutionary strategies used by marine
prey organisms in avoiding predators in the environment.
(7)
b). With suitable ecological examples, explain the major causes of patchiness in the
distribution of marine plankton.
(13)
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

14. a). With suitable labelled diagram and reference to type of marine organisms, discuss
the main characteristics of the high-intertidal zone. How does this zone differ from
the low-intertidal zone?
(16)
b). List any four ecological roles of benthos in the marine ecosystem.
(4)
15. a). Briefly describe the formation of coral reefs.
(8)
b). Discuss the ecological characteristics of the deep-sea environment.
(8)
c). Explain the impacts of trawling on the seabed and benthic communities.
(4)
5





