 |
CAH610S-COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING FOR HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM-1ST OPP-NOV 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmI BIA un IVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE AnD TECHn OLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BHOM & 07BOTM
COURSE CODE: CAH610S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2024
LEVEL: 6
COURSE NAME: COST& MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING FORHOSPITALITY& TOURISM
PAPER: THEORYAND CALCULATIONS
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER
MODERATOR
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
Sheehama, K.G.H.
Odada, L.
INSTRUCTIONS
1. This question paper comprises four (4) questions.
2. Answer ALL the questions in blue or black ink only. NO pencil
3. Start each question on a new page in your answer booklet and show all workings.
4. Work with four (4) decimal places in all your calculations and only round off only final
answers to two (2) decimal places unless otherwise stated.
5. Questions relating to this examination may be raised in the initial 30 minutes after the
start of the paper. Thereafter, candidates must use their initiative to deal with any
perceived error or ambiguities & any assumption made by the candidate should be
clearly stated.
NON - PROGRAMMABLE CALCUTOR
1. Examination paper
2. Examination script
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 6 PAGES {INCLUDING THIS FRONT PAGE)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
(30 MARKS)
Each of the following questions (1.1-1.12) has only ONE correct answer. Please answer
this question ON the answer sheet provided. E.g., 1.1 a
1.1 The following item is NOT a manufacturing overheads cost:
a) Depreciation of plant and equipment
b) Rent of office
c) Indirect labour
d) Indirect material
1.2
Conversion cost can be defined as:
a) The cost of the first stage of the manufacture of a product
b) The total direct labour and manufacturing overhead costs
c) The total direct costs of manufacturing a product
d) The total costs of manufacturing a product
1.3 The following statement is NOT true:
a) Total ordering cost= Cost per order x Number of orders
b) Safety inventory= Minimum inventory
c) conomic order quantity= Reorder level
d) Average inventory = Minimum inventory level + ½ (Economic order
quantity)
1.4 The following item is NOT an example of direct material cost:
a) Cotton
b) Wood
c) Steel
d) Glue
The following details refer to questions 1.5 - 1.6:
Turtle Ltd supplied the following information for the past year:
Direct material used
Indirect labour cost
Direct labour cost
Indirect material used
Depreciation: plant and equipment
Sundry factory overheads
Depreciation: office building
100 000
50 000
200 000
20000
15 000
10 000
5 000
1.5 The prime costs incurred during the year was:
a) N$150 000
b) N$200 000
c) N$250 000
d) N$300 000
1.6 The total manufacturing/production costs of the past year was:
a) N$295 000
b) N$300 000
c) N$395 000
d) N$400 000
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

The following details refer to questions 1.7 and 1.8:
A business has bought and sold identical items of inventory during 2024 as follows:
1/6/24
Bought
1000 units
@ N$100 each
1/9/24
Bought
1000 units
@ N$160 each
5/9/24
Sold
1200 units
@ N$200 each
1.7 Using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method what is the value of closing inventory.
a) N$128 000
b) N$120 000
c) N$104 000
d) N$100 000
1.8 Using the weighted average method what is the value of the value of closing inventory.
a) N$128 000
b) N$120 000
c) N$104 000
d) N$100 000
1.9 The first-in-first-out(FIFO) method of stock valuation would be most appropriate for:
a) A bicycle components retailer
b) A motor components retailer
c) A construction retailer
d) A food retailer
1.10 A firm produced 5 000 units during the past month and incurred the following costs:
Fixed cost N$8 250; Variable cost N$12 500. The total cost budgeted for the following
month for 3 500 units will be:
a) N$18 000
b) N$17 000
c) N$14 000
d) N$19 000
1.11 Under absorbed overheads occurs when:
a) The amount of actual overheads incurred is less than the overheads that
have been charged to production
b) Actual overheads have fallen in relation to what they were expected to be
c) The amount of budgeted overheads is less than the actual overheads
incurred.
d) The amount of overheads charged to production is lower than the actual
overheads incurred.
1.12 A company has fixed costs of N$600 000 per annum. It manufactures a single
product which it sells for N$200 per unit. Its contribution to sales ratio is 40%.
The company's contribution margin per unit is:
a) N$60
b) N$120
c) N$80
d) N$160
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.13 A company manufactures a single product which it sells for N$160 per unit.
Fixed costs are N$76 800 per month and the product has a variable costs to
sales ratio of 60%. The company's contribution margin ratio is:
a) 60%
b) 50%
c) 40%
d) 30%
1.14 Fast-Food Ltd supplied the following details regarding its product:
Selling price per unit
Variable production cost per unit
Variable selling cost per unit
Fixed production cost per year
Fixed selling costs per year
Contribution margin ratio (%):
a) 60%
b) 50%
c) 40%
d) 30%
N$600.00
N$200.00
N$40.00
N$358 000
N$60 000
1.15 Fast-Food Ltd supplied the following details regarding its product:
Selling price per unit
Variable production cost per unit
Variable selling cost per unit
Fixed production cost per year
Fixed selling costs per year
Variable cost ratio(%):
a) 60%
b) 50%
c) 40%
d) 30%
N$600.00
N$200.00
N$40.00
N$358 000
N$60 000
QUESTION 2
(25 Marks)
Just- Phone Ltd management are in dispute asto which method of inventory valuation should
be used. The records currently show that on 31 July 2024 the store had closing balance of 20
"fake-e-phone" worth N$10 000.
The following information regarding the movement of "fake-e-phones" was provided to you
by the store manager during the month of August 2024:
Receipts from suppliers were as follow:
• 2 August: purchased 30 "fake-e-phones" at N$600 per phone.
• 4 August: purchased 10 "fake-e-phones" at a total cost of N$7 000.
• 7 August: purchased 15 "fake-e-phones" at N$750 per phone.
• 10 August: purchased 10 "fake-e-phones" at a total cost of N$8 000.
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Phones were sold to customers as follow:
• 3 August: sold 25 "fake-e-phones" at N$800 per phone.
• 6 August: sold 20 "fake-e-phones" at N$900 per phone.
• 12 August: sold 30 "fake-e-phones" at N$1200 per phone.
REQUIRED:
Record the above movement of the inventory in the store ledger card of Just -
a)
Phone Ltd by using the Weighted Average Method.
b) Calculate the gross profit/loss of Just - Phone Ltd.
MARKS
17
8
QUESTION 3
(28 MARKS]
KGH Ltd makes and sells one product, the following information is provided:
Actual figures:
Direct material
55 800
Direct labour
59 400
Variable manufacturing overheads
27 000
Variable selling and administrative expenses
8 000
Fixed manufacturing overheads
47 000
Fixed selling and administrative expenses
21 000
Selling price
400
Production units 1 800
Units sold
1 600
KGH Ltd uses machine hours to allocate fixed manufacturing overheads.
The predetermined overhead rate/POR is N$10 per machine hour. Machine hours required
to produce one product is 2.5 and total machine hours incurred during the period are 4 500.
REQUIRED:
c) Calculate the unit product cost using the direct costing method.
d) Calculate the unit product cost using the absorption costing method.
e) Prepare a statement of profit or loss according to the direct costing method.
Prepare a statement of profit or loss according to the absorption costing
f)
method.
MARKS
3
4
8
13
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
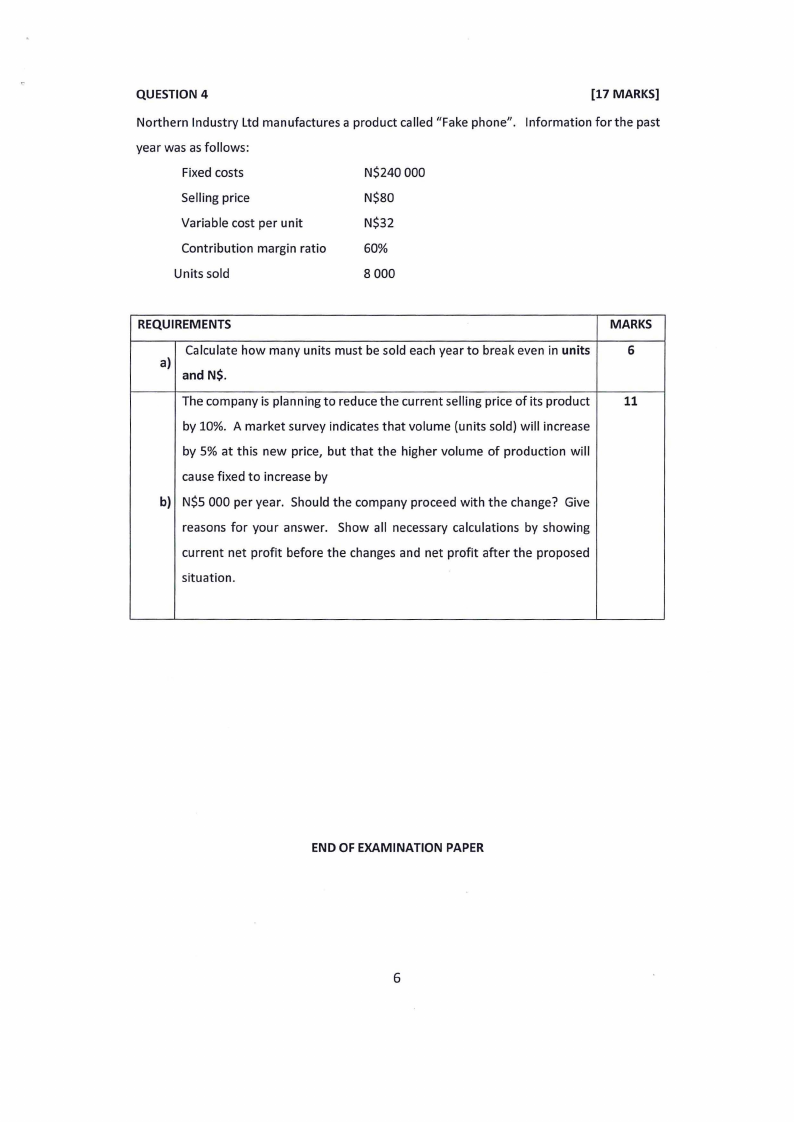
QUESTION 4
[17 MARKS]
Northern Industry Ltd manufactures a product called "Fake phone". Information for the past
year was as follows:
Fixed costs
N$240 000
Selling price
N$80
Variable cost per unit
N$32
Contribution margin ratio
60%
Units sold
8 000
REQUIREMENTS
Calculate how many units must be sold each year to break even in units
a)
and N$.
The company is planning to reduce the current selling price of its product
by 10%. A market survey indicates that volume {units sold) will increase
by 5% at this new price, but that the higher volume of production will
cause fixed to increase by
b} N$5 000 per year. Should the company proceed with the change? Give
reasons for your answer. Show all necessary calculations by showing
current net profit before the changes and net profit after the proposed
situation.
MARKS
6
11
END OF EXAMINATION PAPER
6





