 |
PMI511S-PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS-2ND OPP-JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Pages 1-10 |
▲back to top |
 |
1.1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

 |
1.2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

 |
1.3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

 |
1.4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

 |
1.5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

 |
1.6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

 |
1.7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

 |
1.8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

 |
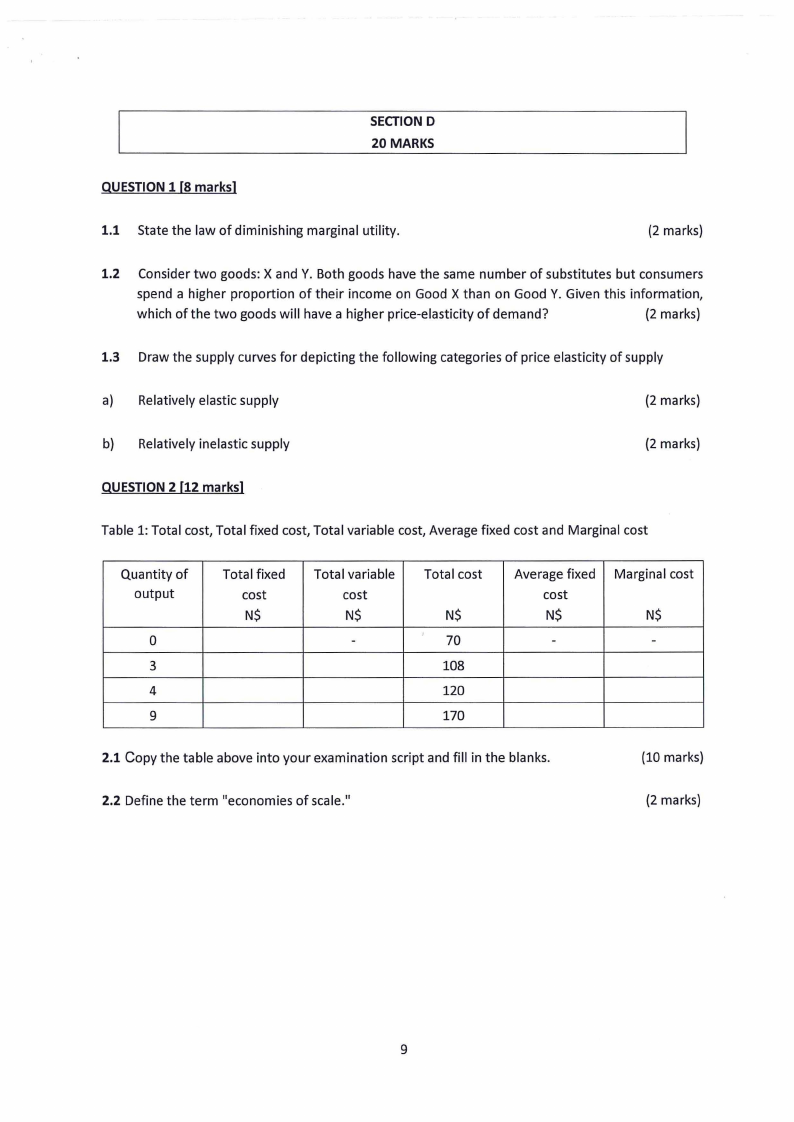
1.9 Page 9 |
▲back to top |
 |
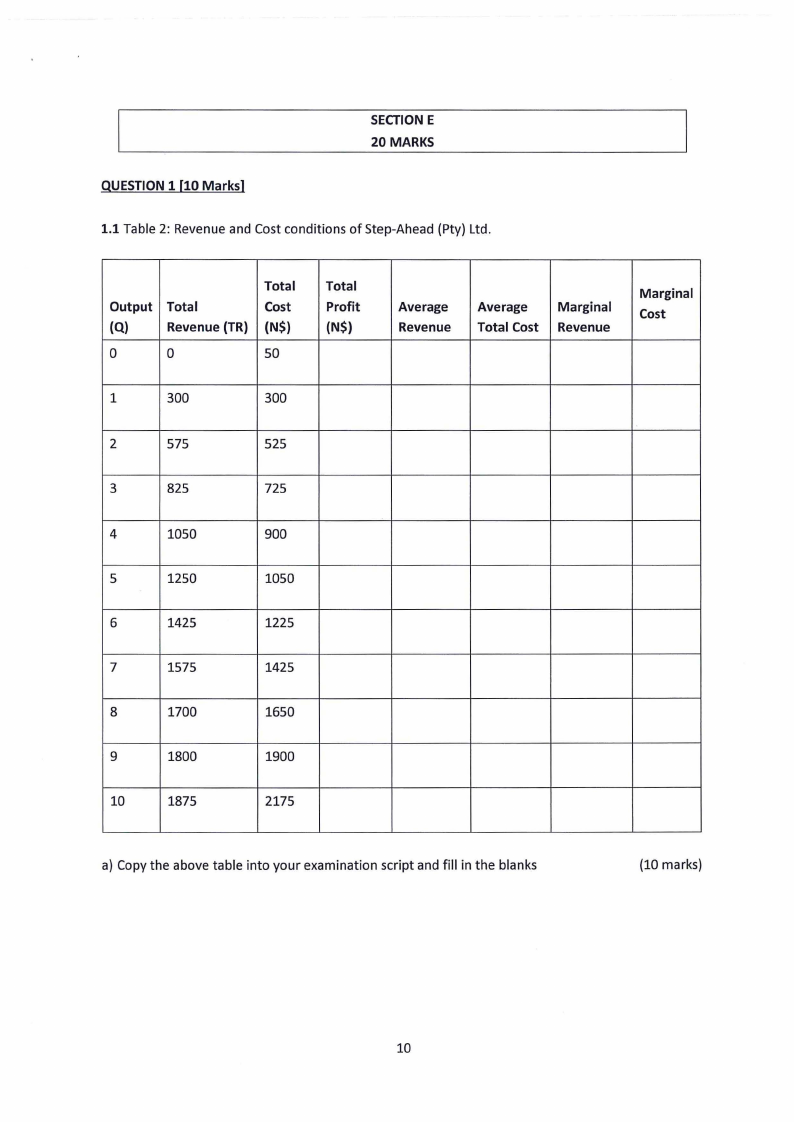
1.10 Page 10 |
▲back to top |
 |
2 Pages 11-20 |
▲back to top |
 |
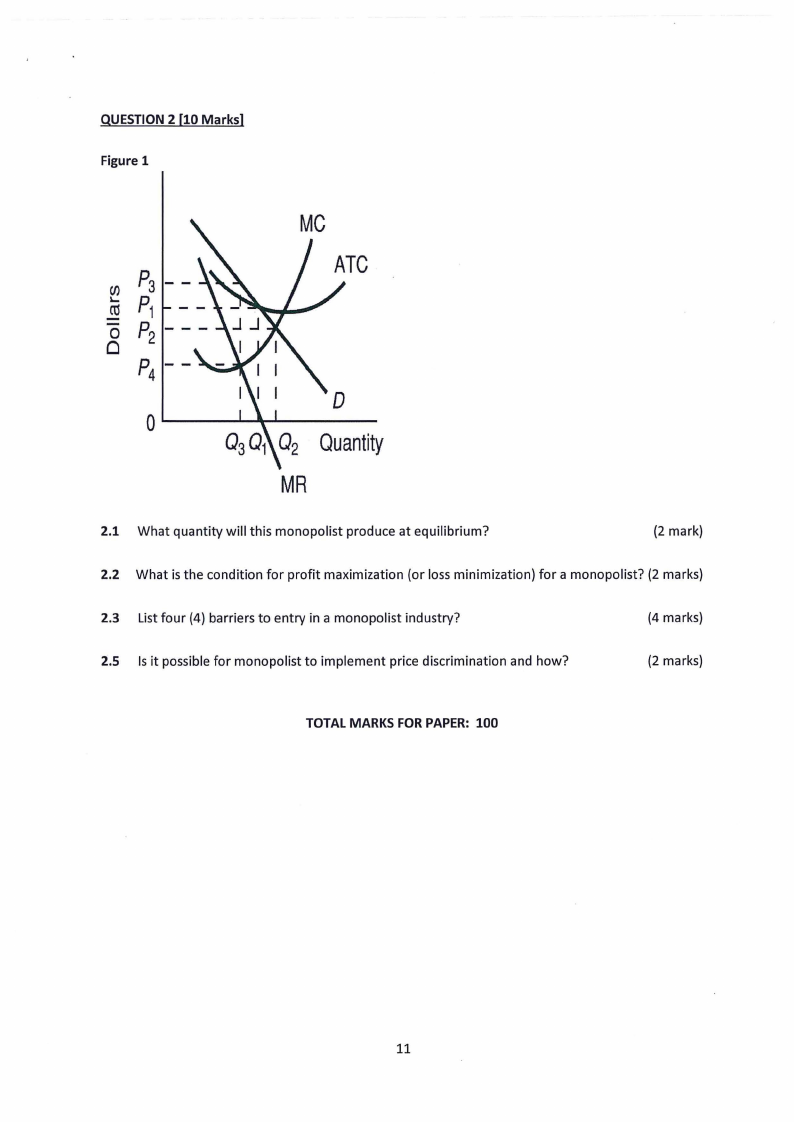
2.1 Page 11 |
▲back to top |
 |
2.2 Page 12 |
▲back to top |

 |
2.3 Page 13 |
▲back to top |

 |
2.4 Page 14 |
▲back to top |






