 |
CMA612S-COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING 202-1ST OPP-NOV 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

'I
nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCEAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENTOF ECONOMICS,ACCOUNTING& FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ACCOUNTING
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BGAC
COURSE CODE: CMA612S
LEVEL: 6
COURSE NAME: COST & MANAGEMENT
ACCOUNTING 202
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2024
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: PRACTICAL AND THEORY
MARKS: 100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINERS:
M Modestus, H Namwandi & E Kangootui
MODERATOR: p Erkie
INSTRUCTIONS
• This question paper is made up of four (4) questions.
• Answer All the questions in blue or black ink only.
• You are advised to pay due attention to expression and presentation. Failure to do so
will cost you marks.
• Start each question on a new page in your answer booklet and show all yourworkings.
• Questions relating to this paper may be raised in the initial 30 minutes after the start
of the paper. Thereafter, candidates must use their initiative to deal with any
perceived error or ambiguities and any assumption made by the candidate should be
clearly stated.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
Non-programmable calculator
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 6 PAGES {Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
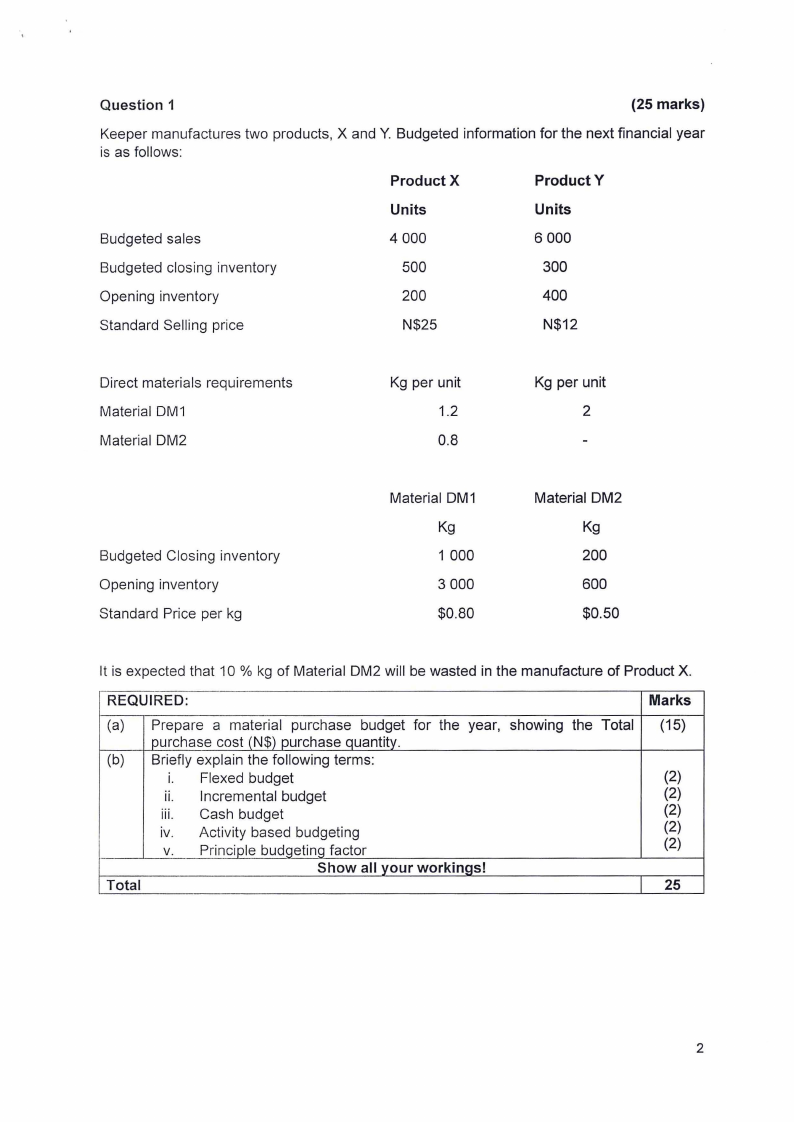
Question 1
(25 marks)
Keeper manufactures two products, X and Y. Budgeted information for the next financial year
is as follows:
Product X
Product Y
Units
Units
Budgeted sales
4 000
6 000
Budgeted closing inventory
500
300
Opening inventory
200
400
Standard Selling price
N$25
N$12
Direct materials requirements
Material DM1
Material DM2
Kg per unit
1.2
0.8
Kg per unit
2
Budgeted Closing inventory
Opening inventory
Standard Price per kg
Material OM 1
Kg
1 000
3 000
$0.80
Material DM2
Kg
200
600
$0.50
It is expected that 10 % kg of Material DM2 will be wasted in the manufacture of Product X.
REQUIRED:
(a) Prepare a material purchase budget for the year, showing the Total
purchase cost (N$) purchase quantitv.
(b) Briefly explain the following terms:
i. Flexed budget
ii. Incremental budget
iii. Cash budget
iv. Activity based budgeting
V. Principle budgeting factor
Show all vour workinas!
Total
Marks
(15)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
25
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
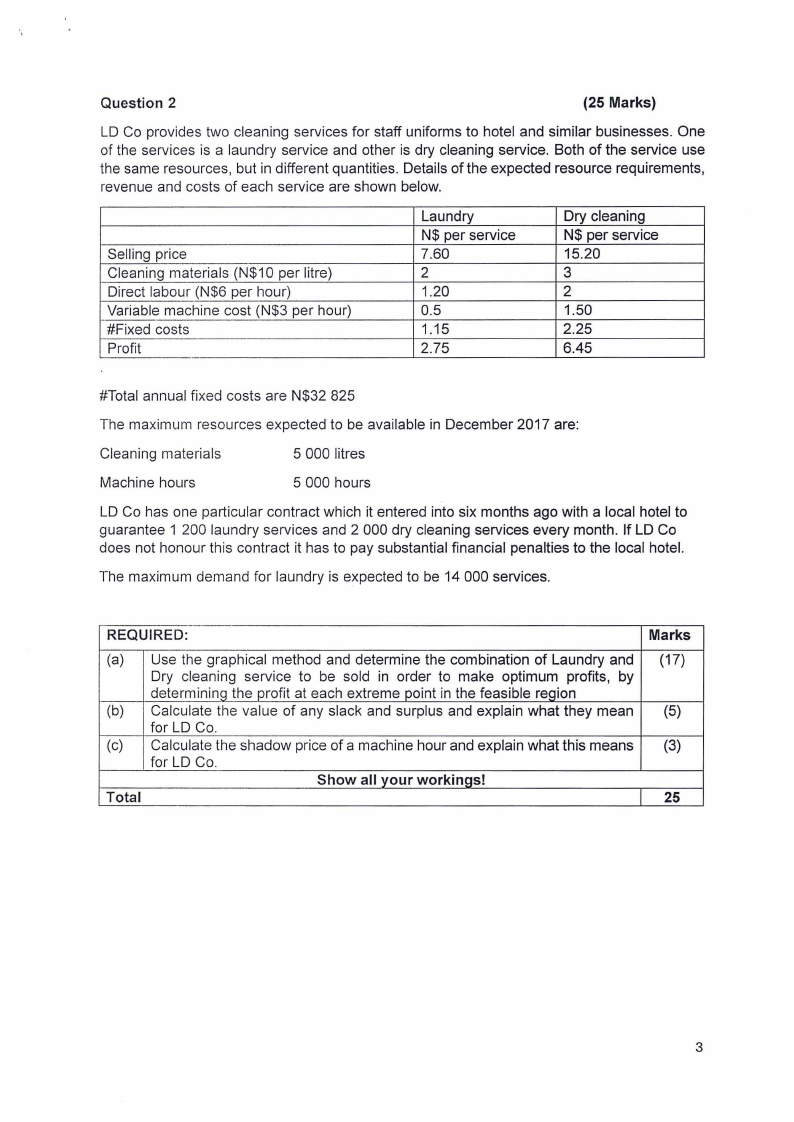
Question 2
(25 Marks)
LO Co provides two cleaning services for staff uniforms to hotel and similar businesses. One
of the services is a laundry service and other is dry cleaning service. Both of the service use
the same resources, but in different quantities. Details of the expected resource requirements,
revenue and costs of each service are shown below.
Selling price
Cleaning materials (N$10 per litre)
Direct labour (N$6 per hour)
Variable machine cost (N$3 per hour)
#Fixed costs
Profit
Laundry
N$ per service
7.60
2
1.20
0.5
1.15
2.75
Dry cleaning
N$ per service
15.20
3
2
1.50
2.25
6.45
#Total annual fixed costs are N$32 825
The maximum resources expected to be available in December 2017 are:
Cleaning materials
5 000 litres
Machine hours
5 000 hours
LO Co has one particular contract which it entered into six months ago with a local hotel to
guarantee 1 200 laundry services and 2 000 dry cleaning services every month. If LO Co
does not honour this contract it has to pay substantial financial penalties to the local hotel.
The maximum demand for laundry is expected to be 14 000 services.
REQUIRED:
(a)
(b)
(c)
Total
Use the graphical method and determine the combination of Laundry and
Dry cleaning service to be sold in order to make optimum profits, by
determining the profit at each extreme point in the feasible region
Calculate the value of any slack and surplus and explain what they mean
for LO Co.
Calculate the shadow price of a machine hour and explain what this means
for LO Co.
Show all your workings!
Marks
(17)
(5)
(3)
25
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
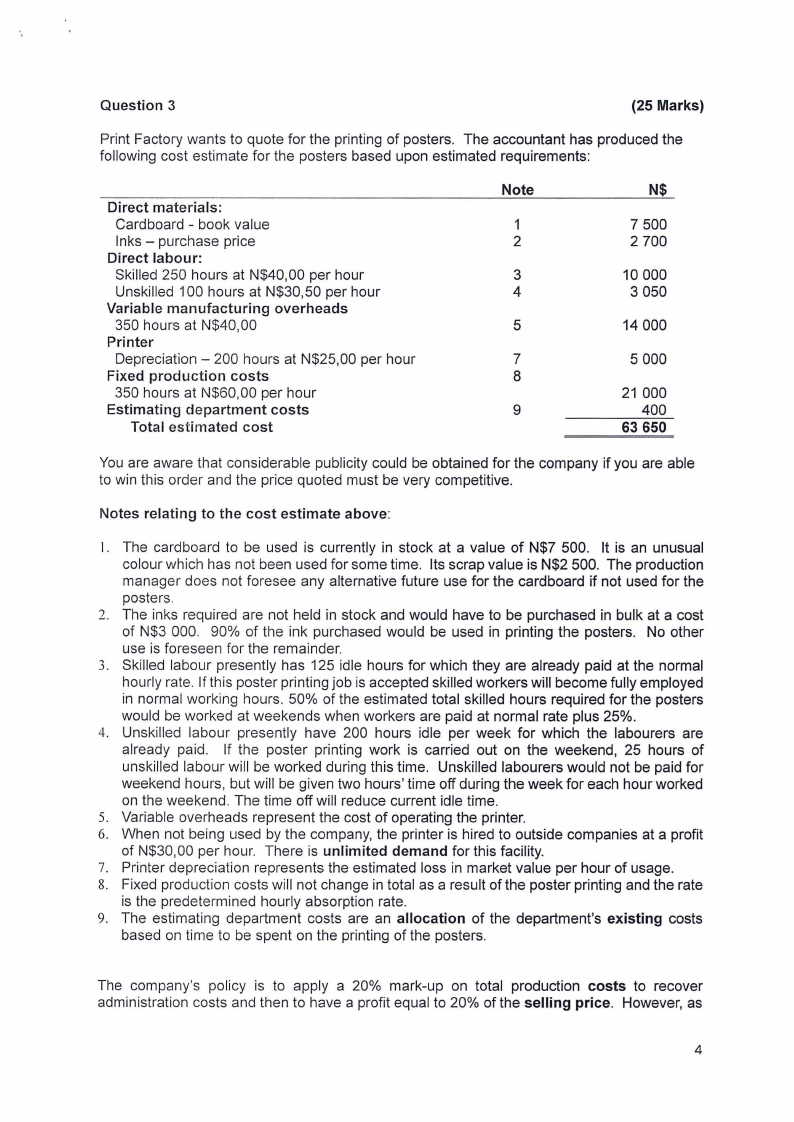
Question 3
(25 Marks)
Print Factory wants to quote for the printing of posters. The accountant has produced the
following cost estimate for the posters based upon estimated requirements:
Direct materials:
Cardboard - book value
Inks - purchase price
Direct labour:
Skilled 250 hours at N$40,00 per hour
Unskilled 100 hours at N$30,50 per hour
Variable manufacturing overheads
350 hours at N$40,00
Printer
Depreciation - 200 hours at N$25,00 per hour
Fixed production costs
350 hours at N$60,00 per hour
Estimating department costs
Total estimated cost
Note
1
2
3
4
5
7
8
9
N$
7 500
2 700
10 000
3 050
14 000
5 000
21 000
400
63 650
You are aware that considerable publicity could be obtained for the company if you are able
to win this order and the price quoted must be very competitive.
Notes relating to the cost estimate above:
I. The cardboard to be used is currently in stock at a value of N$7 500. It is an unusual
colour which has not been used for some time. Its scrap value is N$2 500. The production
manager does not foresee any alternative future use for the cardboard if not used for the
posters.
2. The inks required are not held in stock and would have to be purchased in bulk at a cost
of N$3 000. 90% of the ink purchased would be used in printing the posters. No other
use is foreseen for the remainder.
3. Skilled labour presently has 125 idle hours for which they are already paid at the normal
hourly rate. If this poster printing job is accepted skilled workers will become fully employed
in normal working hours. 50% of the estimated total skilled hours required for the posters
would be worked at weekends when workers are paid at normal rate plus 25%.
4. Unskilled labour presently have 200 hours idle per week for which the labourers are
already paid. If the poster printing work is carried out on the weekend, 25 hours of
unskilled labour will be worked during this time. Unskilled labourers would not be paid for
weekend hours, but will be given two hours' time off during the week for each hour worked
on the weekend. The time off will reduce current idle time.
5. Variable overheads represent the cost of operating the printer.
6. When not being used by the company, the printer is hired to outside companies at a profit
of N$30,00 per hour. There is unlimited demand for this facility.
7. Printer depreciation represents the estimated loss in market value per hour of usage.
8. Fixed production costs will not change in total as a result of the poster printing and the rate
is the predetermined hourly absorption rate.
9. The estimating department costs are an allocation of the department's existing costs
based on time to be spent on the printing of the posters.
The company's policy is to apply a 20% mark-up on total production costs to recover
administration costs and then to have a profit equal to 20% of the selling price. However, as
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
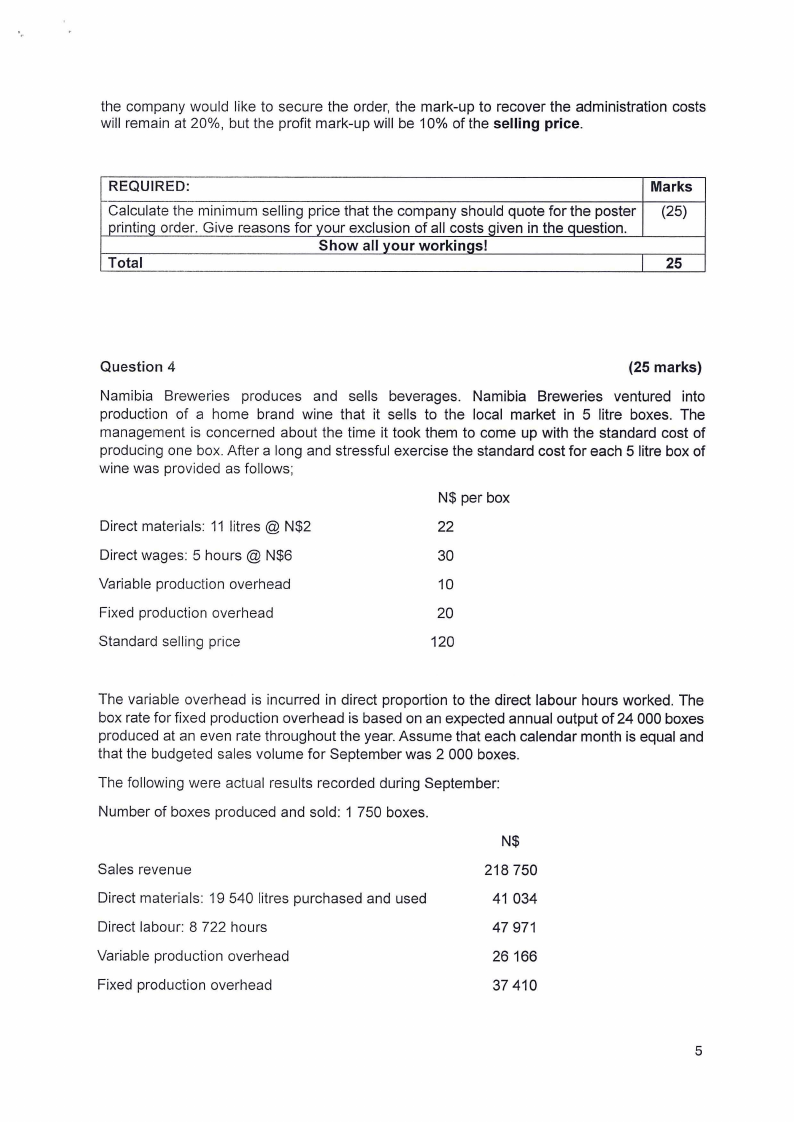
the company would like to secure the order, the mark-up to recover the administration costs
will remain at 20%, but the profit mark-up will be 10% of the selling price.
REQUIRED:
Calculate the minimum selling price that the company should quote for the poster
printing order. Give reasons for your exclusion of all costs given in the question.
Show all your workings!
Total
Marks
(25)
25
Question 4
(25 marks)
Namibia Breweries produces and sells beverages. Namibia Breweries ventured into
production of a home brand wine that it sells to the local market in 5 litre boxes. The
management is concerned about the time it took them to come up with the standard cost of
producing one box. After a long and stressful exercise the standard cost for each 5 litre box of
wine was provided as follows;
N$ per box
Direct materials: 11 litres @ N$2
22
Direct wages: 5 hours @ N$6
30
Variable production overhead
10
Fixed production overhead
20
Standard selling price
120
The variable overhead is incurred in direct proportion to the direct labour hours worked. The
box rate for fixed production overhead is based on an expected annual output of 24 000 boxes
produced at an even rate throughout the year. Assume that each calendar month is equal and
that the budgeted sales volume for September was 2 000 boxes.
The following were actual results recorded during September:
Number of boxes produced and sold: 1 750 boxes.
N$
Sales revenue
218 750
Direct materials: 19 540 litres purchased and used
41 034
Direct labour: 8 722 hours
47 971
Variable production overhead
26 166
Fixed production overhead
37 410
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

REQUIRED:
Marks
(a) Help the management of Namibia Breweries to speed up their standard
setting process by listing two sources of information they can use to set the
following standards:
i. Standard material usage.
(2)
ii. Standard labour rate.
iii. Standard labour times
(2)
(2)
(b) Calculate the operating variances and present them in a statementwhich (19)
reconciles the budQet and actual Qross profit for September.
Show all your workings!
Total
25
THE END
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
,-
I
I
I
I
II
II
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I-
I-I-
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
----





