 |
ACS701S - APPLIED COLLOID AND SURFACE CHEMISTRY - 2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
LEVEL: 7
COURSE NAME: APPLIED COLLOID AND SURFACE | COURSE CODE: ACS701S
CHEMISTRY
SESSION: JULY 2022
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S)
Prof Habauka M Kwaambwa
MODERATOR: Prof Edet F Archibong
INSTRUCTIONS
Answer ALL the FIVE questions
Write clearly and neatly
Number the answers clearly
All written work must be done in bule or black ink
No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed
Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
Non-programmable Calculators
ATTACHMENT
List of Useful Constants
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES (Including this front page and List of Useful
Constants)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 1
[27]
(a) Define briefly the following concepts: surface tension; work of adhesion; work
of cohesion.
(6)
(b) Surface active agents are classified according to the nature of their head (polar)
groups. Discuss this statement using the four classifications of surfactants.
(8)
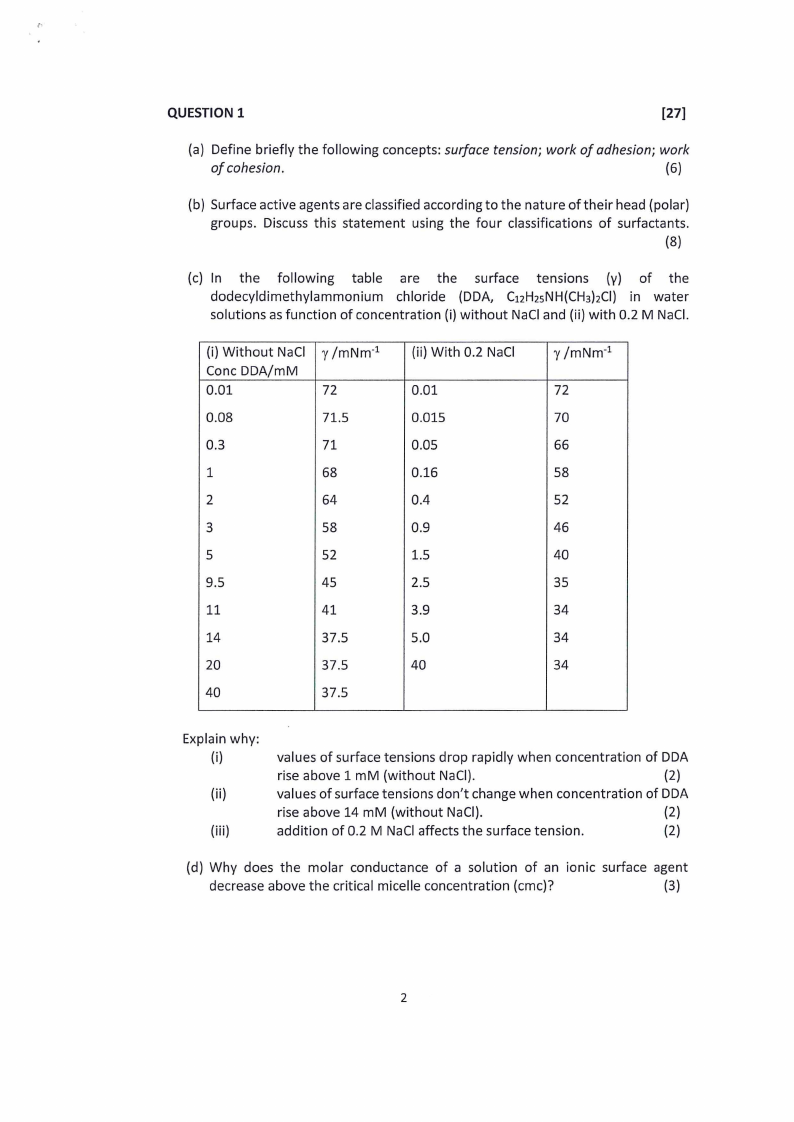
(c) In. the following table are the surface tensions (y) of the
dodecyldimethylammonium chloride (DDA, Ci2HasNH(CH3)2Cl) in water
solutions as function of concentration (i) without NaCl and (ii) with 0.2 M NaCl.
(i) Without NaCl | y /mNm
Conc DDA/mM
0.01
72
0.08
71.5
0.3
71
1
68
2
64
3
58
5
52
9.5
45
11
41
14
37.5
20
37.5
40
37.5
(ii) With 0.2 NaCl
0.01
0.015
0.05
0.16
0.4
0.9
1.5
2.5
3.9
5.0
40
y/mNm*?
72
70
66
58
52
46
40
35
34
34
34
Explain why:
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
values of surface tensions drop rapidly when concentration of DDA
rise above 1 mM (without NaCl).
(2)
values of surface tensions don’t change when concentration of DDA
rise above 14 mM (without NaCl).
(2)
addition of 0.2 M NaCl affects the surface tension.
(2)
(d) Why does the molar conductance of a solution of an ionic surface agent
decrease above the critical micelle concentration (cmc)?
(3)
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

(e) An experiment to study the spreading of benzene on water gave the following
surface and interfacial tension data in the table below.
Initial
Final
Ywater (mNm*)
72.8
62.2
benzene
28.9
28.8
(mNm*)
‘Ywater/benzene = 35 mNm?
Explain the spreading behaviour of benzene on water using the concept of
spreading coefficient.
(5)
QUESTION 2
[14]
(a) Define the term Krafft temperature of a surfactant? Why is the Kraft temperature not
observed for non-ionic surfactants?
(3)
(b) Using a schematic diagram,and quoting appropriate equations, show how the results
might be analysed to yield
(i)
the Gibbs surface excess concentration, and;
(ii)
the area occupied by one surfactant molecule in a surface monolayer.
(6)
(c) Briefly describe how insoluble monolayers are studied using the Langmuir trough.
(5)
QUESTION 3
[17]
(a) Formulation chemistry is the mixing of compounds/substances that do not react with
each other but produce a mixture with the desired characteristics/properties to suit a
particular application/use. As a formulator for detergents and household cleaners
manufacturing company, you propose to the purchasing department the following
ingredients that are necessary: sodium hypochlorite, carboxymethylcellulose, sodium
carbonate and dodecylbenzene sulphonate. State in one or two words the function
of each ingredient.
(4)
(b) Derive the Kelvin equation below relating the vapour pressure over a tiny droplet with
that of the same amount of liquid with a flat surface:
RT In? = Ver
(9)
1
(c) The effect of an impurity on spreading of oil on water depends on whether it is in the
oil or aqueous phase. Explain this statement.
(4)
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 4
[16]
(a) When a drop of an insoluble liquid, such as oil, is placed on a clean liquid, such as
water, it may behave in one of the three ways. Name the three behaviour scenarios
possible.
(3)
(b) State the wetting properties of a liquid on a solid when the contact angle, 0, is: (4)
(i)
O°C
(ii) 75°C
(iii) 150°C
(iv) 180°C
(c) To improve the wetting properties of a liquid, what additive is normally used? Explain
briefly your answer.
(2)
(d) Consider three different liquids mercury (Hg), water, and decane having surface
tensions of 484, 72.8 and 24 mNm’*, respectively. State the differential wetting
properties or behaviour of these liquids on planar surfaces of the following materials
whose surface energies are given in brackets: magnesium oxide, MgO (y = 1200 mNm
1), silica, SiO2 (y = 307 mNm), polyethylene (y = 31 mNm‘) and
polytetrafluoroethylene, PTFE (vy = 18 mNm*?).
(7)
QUESTION 5
[26]
(a) Describe the origins of van der Waals attraction interaction potentials acting
between colloidal particles.
(6)
(b) On the same well-labelled diagram, show schematically the variation of the total pair
potential, Vr = Va + Vr, with particle separation, h, for the following:
(i)
A stable sol
(ii)
A marginally stable sol
(iii)
An unstable sol
(6)
(c) State the conditions to be met if sterically stabilised dispersions are to be prepared.
Give examples of various types of polymer structures that may be used. For a stable
sterically stabilised dispersion of spherical particles, show schematically on the same
well-labelled diagram the variation of the potentials, Vtotal, Vsteric aNd Vvan der Waals With
particle separation, h.
(10)
(d) In paints and coatings formulations, bridging flocculation and depletion flocculation
must be controlled. What do you understand by these two terms?
(4)
END OF EXAM QUESTIONS
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

USEFUL CONSTANTS:
Universal Gas constant
Boltzmann’s constant,
Planck’s constant
Debye-Huckel’s constant,
Faraday’s constant
Mass of electron
Velocity of light
Avogadro’s constant
1 electron volt (eV)
8.314 JK? molt
1.381 x 10°3J K?
6.626 x 1074 Js
0.509 (mol dm’3)!/2 or mol5kg®5
96485 C mol?
9.109 x 10°31 kg
2.998 x 108 ms?
6.022 x 1073
1.602 x 10°29J





