 |
MOD621S - MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

.
·nAm I BIA un IVERS ITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECH no LOGY
Facultyof Health, Natural
Resourcesand Applied
Sciences
School of Health Sciences
Department of Clinical
Health Sciences
13 Jackson Kaujeua Street
Private Bag 13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +264 61 207 2970
F: +264 61 207 9970
E: dchs@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR of MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BMLS
LEVEL: 6
COURSE:MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS
COURSECODE: MOD621S
DATE: JANUARY 2024
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/ SUPPLEMENTARY: EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
Ms Vanessa Tjijenda
Ms Cara Mia Dunaiski
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACH EMENTS
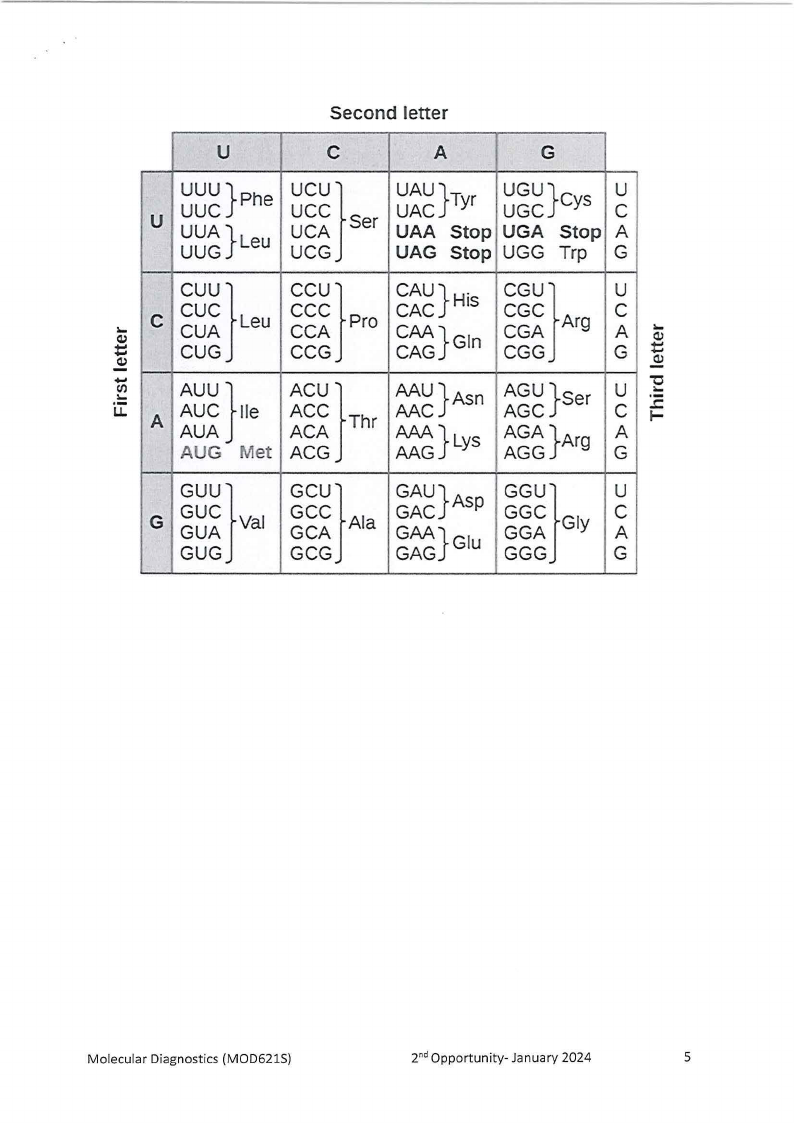
1. Genetic Code
This paper consists of 5 pages including this front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A: TRUE/ FALSE
[10 MARKS)
QUESTION 1: TRUE/FALSE
[10 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements and select whether the statement is true or false. Write the word 'True' or
'False' next to the corresponding number on your ANSWERSHEET.
1.1 The complete set of genetic information of a microorganism is called the genome.
(1)
1.2 A hybridization method that uses DNA attached to a solid media to measure
gene expression simultaneously is called Ion Torrent.
(1)
1.3 Comparative hybridization technique can be used to compare gene expression in
acute myeloid leukaemia and chronic myeloid Leukaemia.
(1)
1.4 Fluorescent in situ Hybridization is used to diagnose Philadelphia Chromosome in
leukaemia patients.
(1)
1.5 Modified form of polymerase chain reaction (PCR)which avoids a non-specific
amplification of DNA by inactivating the DNA polymerase at lower temperatures is
called Hot Start.
(1)
1.6 NGStechnology that sequence DNA via three basic processes: amplify,
sequencing and analyse using a bridging method is called pyrosequencing.
(1)
1.7 Loading dye is used in gel electrophoresis to add weight to the nucleic acid and
help with visualization under UV light.
(1)
1.8 In preparing 250ml of a 0.8 % agarose gel, 0.8 g agarose is dissolved in 250ml TAE buffer (1)
1.9 Proteinase K inactivates nucleases.
(1)
1.10 Short tandem repeats are found in the non-coding region of the DNA in each individual. (1)
Molecular Diagnostics (MOD621S)
2nd Opportunity- January 2024
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B:
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Please answer ALL of the questions in this section.
QUESTION 2
(40 MARKS]
(12)
2.0 Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in both copies
of a person's HBB gene. This gene encodes a component of haemoglobin, the oxygen-
carrying protein in red blood cells. The mutation causes haemoglobin molecules to
stick together, creating sickle-shaped red blood cells. This can lead to blood cell
rupture, anemia, recurring pain, immunodeficiency, organ damage, and early death.
Bone marrow transplants can cure SCD, but appropriate donors are hard to come by.
The procedure also carries risks of dangerous side effects.
Below is the sequence for the normal haemoglobin molecule and the haemoglobin
in SCD:
Normal mRNA sequence (HbA):
5' ACUCCUGAGGAG 3'
Mutated mRNA sequence (HbS):
5' ACUCCUGUGGAG 3'
2.1
Using the genetic code provided, write out the amino acids for HbA and HbS.
(4)
2.2
Identify the type of mutation seen in the mutated mRNA.
(1)
2.3 Why is sequencing better than RFLPto identify such a mutation.
(2)
2.4
Describe the Sanger sequencing method.
(5)
QUESTION 3
(18]
3.0
In a traditional PCR protocol, reaction components are assembled as described below.
The final volume should be 50 µL.
1. Thaw all reagents on ice.
2. Assemble reaction mix into 50 µL volume in a thin walled 0.2 ml PCRtubes.
3. Add reagents in following order: water, buffer, dNTPs, Mg CL2, template primers, Taq
polymerase.
4. Gently mix by tapping tube. Briefly centrifuge to settle tube contents.
s. Prepare negative control reaction without template DNA.
6. Prepare positive control reaction with template of known size and appropriate
primers.
3.1
Identify the reagents that form part of a "master mix".
(4)
3.2
Explain the addition of a negative and positive control and why they are prepared in
that way.
(4)
3.3
Explain important considerations when designing the primers.
(10)
Molecular Diagnostics (MOD621S)
2nd Opportunity- January 2024
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 4:
[10)
4.1 Define restriction enzyme.
(1)
4.2 Design a 10 nucleotides palindrome sequence.
(3)
4.2.1 Digest the palindrome sequence obtained in 4.2 such that it yields a blunt end.
(2)
4.2.2 Digest the palindrome sequence obtained in 4.2 such that it yields a 3' sticky end.
(2)
4.3
Provide the formula for calculating annealing temperature.
(2)
SECTION B: LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Please answer ALL of the questions in this section.
(50 MARKS)
QUESTION 5:
5.1 You are a masters' student at the Namibia University of Science and Technology. You
are required to manually extract DNA from a bacteria culture for your study. Discuss
how you would go about extracting the DNA using the manual chloroform/phenol
protocol. Explain each step-in detail.
(24)
5.2 Microarray is a technique used for gene expression profiling. Discuss in detail the
principle of this technique and mention one advantage and one disadvantage of
using this method. ·
(10)
5.3 Nested PCRand Touch Down PCRare Conventional PCRmethod that can be modified
to increase specificity. Explain how specificity is achieved in each method.
{16)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Molecular Diagnostics (MOD621S)
2nd Opportunity- January 2024
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
Second letter
u
C
A
I
I
G
uuu}Phe
u uuc
UUUUAG }Leu
ucu} UAU}Tyr UGU}cys u
ucc
UAC
UGC
C
UCA Ser UAA Stop UGA Stop A
UCG
UAG Stop UGG Trp G
lo..
Q,)
t::
Q,)
cuu} CCU} C
CUC
CUA
CUG
Leu
CCC
CCA
CCG
Pro
CCAACU}H· IS
CCAAAG} Gin
CGU}u
CGC
C
CGA Arg A
CGG
G
AUU}ACU}AAU}Asn
LL
A
AUC
AUA
AUG
lie
Met
ACC
ACA
ACG
Thr
AAC
~}Lys
AGU }ser
AGC
AGA }Arg
AGG
u
C
.c:
I-
A
G
GUU}GCU} GGU} GAU}Asp
u
G
GUC
GUA
Val
GUG
GCC
GCA Ala
GCG
GAC
GGAAGA} Glu
GGC
GGA Gly
GGG
C
A
G
Molecular Diagnostics (MOD621S)
2nd Opportunity- January 2024
5





