 |
PSF602S - PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION - 2ND OPP - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA untVERSITY
OFSCIEnCEAno TECHno LOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
COURSE CODE: PSF602S
SESSION: JANUARY 2023
LEVEL: 6
COURSE NAME: PLANTSTRUCTURE
AND FUNCTION
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/ SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) DRJEYAKENNEDY
MODERATOR: PROFPERCYCHIMWAMUROMBE
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Write clearly and neatly
2. Number the answers clearly
3. All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers
6. Draw diagrams wherever necessary
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
None
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES
(Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1:
Multiple choices
[14]
Each carry one mark
1.1 Artichoke hearts are tender with a strong flavour. The leaves have a similar flavour
but are fibrous and difficult to chew. The leaves must contain large amounts of
a) collenchyma
b) trichomes
c) phloem
d) sclerenchyma
1.2 Which of the following correctly describes a feature unique to monocot stems?
a) vascular tissue is located all in the centre
b) vascular bundles are scattered throughout
c) vascular bundles are arranged in a ring
d) ground tissue consists mainly of parenchyma
1.3 Heartwood and sapwood consist of ______
_
a) secondary xylem
b) secondary phloem
c) periderm
d) bark
1.4 Collenchyma hypodermis is characteristics of;
a) monocot root
b) monocot and dicot stem
c) monocot stem
d) dicot stem
1.5 This is not a characteristic feature of anatomy of dicotyledonous root;
a) pith little or absent
b) secondary growth
c) radial vascular bundles
d) vascular bundles 15-20
1.6 An olive is an example of a;
a) drupe
b) berry
c) pome
d) aggregate fruit
1.7 Removal of anther is called;
a) emasculation
b) bagging
c ) artificial hybridization
d) pollination
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.8 A new plant forms from a stem that broke off of the parent plant. This is an example
of -------
a) asexual reproduction
b) sexual reproduction
c) tissue culture propagation
d) propagated by grafting
1.9 How do most flowering plants avoid self-fertilization?
a) they discourage pollinators
b) the physical arrangement of stamens and carpels makes self-fertilization unlikely
c) they have self-incompatibility and reject their own pollen
d) stamens and carpels on the same plant mature at different times
1.10 A typical angiospermic anther is;
a) bilobed
b) unilobed
c) trilobed
d) tetralobed
1.11 The figure 1 shows a section through a fruit containing a seed.
Figure - 1
What are the labelled parts in figure 1?
1
A
cotyledon
B
cotyledon
C
radicle
D
radicle
2
radicle
radicle
cotyledon
cotyledon
3
pericarp
testa
pericarp
testa
4
testa
pericarp
testa
pericarp
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
1.12 Which group of seeds has hairy parachutes?
a) water lilies and alder tree
b) dandelion and milkweed
c) coconut and goosegrass
d) poppy and orchid
1.13 Humans often manipulate plants in order to create results that are better fit for their
needs. What process is often used to create new hybrids of grapes for making wine?
a) grafting
b) bulb
c) corm
d) rhizome
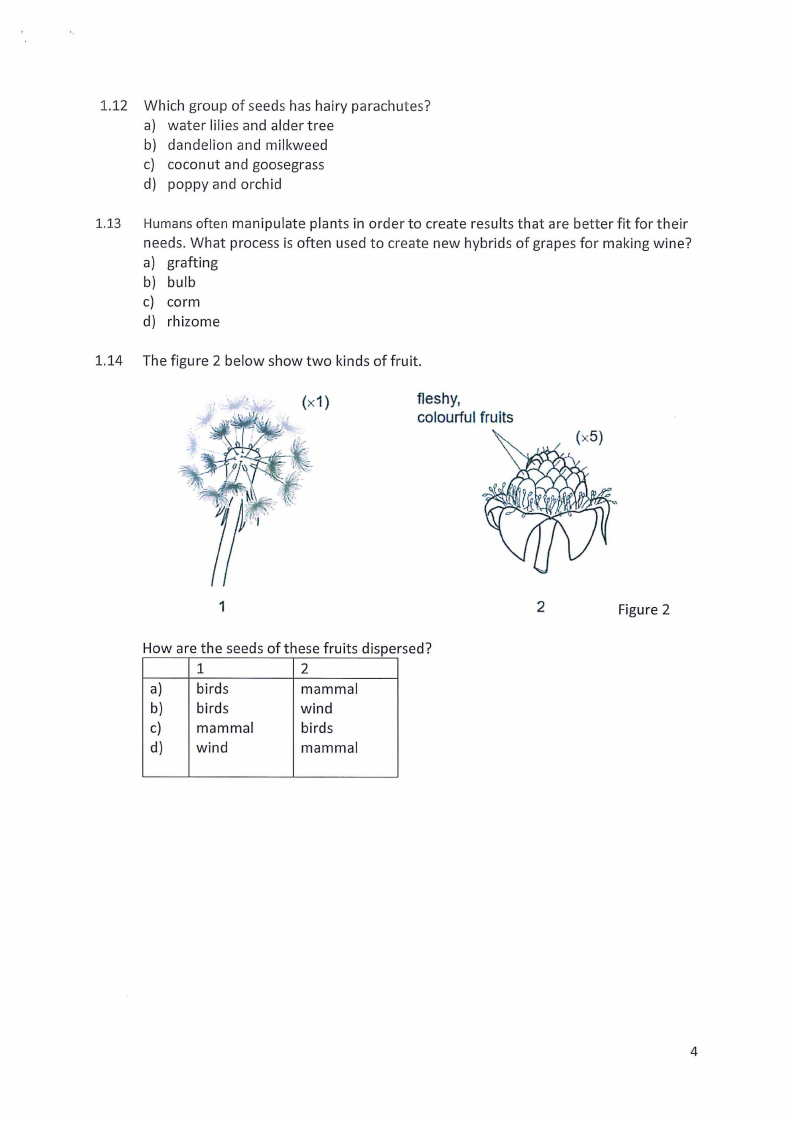
1.14 The figure 2 below show two kinds of fruit.
(x1)
fleshy,
colourful fruits
1
How are the seeds of these fruits dispersed?
1
2
a)
birds
mammal
b)
birds
wind
c)
mammal
birds
d) wind
mammal
2
Figure 2
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2:
One-sentence answers
[4]
Each carry one mark
2.1 Name the secondary metabolite that replaces arginine in insect and changes tertiary
structure; kills insect.
2.2 Name the antimicrobial production of those induced by hypersensitive response
that attack specific pathogen and stimulate changes in the cell wall that confine the
pathogen.
2.3 Why is apple called a false fruit?
2.4 A Venus' flytrap knows to shut by feeling the fly inside the flower. What type of
tropism is this?
QUESTION 3:
Distinguish between the pairs of the following terms.
[6]
Each carry two marks
3.1 Cork cambium and vascular cambium
3.2 Autumn and Spring wood
3.3 Aggregate and simple fruits
QUESTION 4:
Short questions
[15]
4.1 Give one piece of evidence that shows translocation occurs in phloem tissue. (3)
4.2 What is pollination? Explain the different types of pollination.
(4)
4.3 List and describe two mutualistic relationships between roots and other
organisms.
(4)
4.4 Describe the zones of primary growth in roots.
(4)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 5:
Longer questions
[20]
5.1 Discuss the structure of stomata, outline the physiological changes that
accompany stomata! opening during the daytime.
(5)
5.2 Explain any five terms related to the margin of leaf and include a sketch.
(5)
5.3 In the tabular form mention the differences between the process involved in
legume partnerships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria and plant partnerships
with mycorrhiza fungi.
(10)
QUESTION 6:
[13]
Structures and functions
6.1 Use the figure 3 to answer each question.
a
6.1.1 Identify the type of seed germination shown in the diagram a.
Figure 3
(1)
6.1.2 Refer to the diagram a of figure 3 above, where the food is mainly stored.
(1)
6.1.3 Which type of seed germination, the cotyledons remain under or just on the
surface of the soil?
(1)
6.1.4 Name the portion of the embryonic stem above the attachment point of the
cotyledons in bean seed germination.
(1)
6.1.5 Refer to the diagram above. Identify the structure labelled in c, d, g and h.
(2)
6.1.6 Name the portion of the embryonic stem above the attachment point of the
cotyledons in maize seed germination.
(1)
6.1.7 Refer to the diagram b of figure 3 above, where the food is mainly stored.
(1)
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

6.2 Sketch the internal structure of monocot seed and label its parts.
(5)
QUESTION 7:
Essay questions
7.1 Discuss the cross-section of a dicotyledonous stem and describe the
functions of each tissue.
[28]
(15)
7.2 Describe the structure and development of the male gametophyte in the
flowering plant (male gametes). Draw and label a diagram to illustrate this.
(13)
END OF EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
7





