 |
PMV611S - PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF VALUATION - 2ND OPP - JULY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF ENGINEERINGAND THE BUILTENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENT OF LAND AND SPATIALSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION(S): BACHELOROF PROPERTYSTUDIES
DIPLOMA IN PROPERTYSTUDIES
QUALIFICATION(S)CODE: 08BOPS
06DIPS
NQF LEVEL:6
COURSECODE: PMV611S
COURSENAME: PRINCIPLESAND METHODS OF
VALUATION
EXAMS SESSION:JULY 2024
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
SECONDOPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) AMIN ISSA
MODERATOR: SAMUEL ATO K HAYFORD
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Read the entire question paper before answering the Questions.
2. Please write clearly and legibly!
3. Please STARTEACHQUESTION ON A FRESHPAGE.
4. The question paper contains a total of 4 questions.
5. You must answer ALLQUESTIONS.
6. Make sure your Student Number is on the EXAMINATION BOOK(S).
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Non-programmable Scientific Calculator
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 6 PAGES(Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Principles and Methods of Valuation
PMV611S
Question 1
For each of the following statements indicate whether it is true or false. Each correct answer carries 1 (one)
mark.
(24)
a) The Residual Method is used to find the value of special purpose properties and the land on which
they are built.
b) The main challenge in the residual method is in estimating the amounts of the many variables that go
into the valuation.
c) The residual method is used for the purpose of finding the residual value of land only and if the land is
bought then it is also used to find the value of the developments on the land.
d) The expected profit in the residual method is calculated from the Cost of Development (CoD).
e) If the land is already owned by the developer, the profit margin and cost of development can then be
easily calculated.
f) Gross development value is the value of the development intended by the developer and is realised by
either sale of the developed properties or the renting out of rooms in an estate or even income
generated by the hotel.
g) The contingencies that are part of the cost of development include, amongst others, industrial action
by the construction workers, floods, sudden increase in construction materials.
h) In the Profits method of valuation the value of the property will be related to the profits which can be
made from their use in as far as the value is derived from the income generated by the business.
i) Both rental and capital values tend to be directly influenced by the potential for profit and in these
circumstances a valuation having regard to the profits achieved is more likely to produce a realistic
valuation than any application of comparison methods.
Second Opportunity Examination Paper
Page2 of 6
July 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Principles and Methods of Valuation
PMV611S
j) A prospective purchaser may hold the view that current profits could be improved substantially by
better management, improved financial controls, the incorporation of other sales lines or
improvements to the premises. This is called business acumen.
k) Pump prices and income margins available to both dealer and oil company are prescribed and also the
availability of sites for the construction of petrol stations are restricted and these influence the way
valuations are carried out.
I) When the market is weak and few market transactions are available, the applicability of the sales
comparison approach may not be limited.
m) When undertaking valuation assignments, whether to estimate market value or some other defined
non-market value, the valuer is sometimes required to apply one or more valuation methods or
approaches.
n) The cost approach is based upon the premise that the informed purchaser will not pay more for a
property than the cost of constructing an equally desirable substitute less appreciable depreciation.
o) The suitability of the investment method of valuation depends upon a variety of factors, including the
use of realistic yield, an accurate allowance for outgoings and, in the case of leasehold interests, an
appropriate tax rate.
p) If all sales are comparable to the subject, averaging is done if sales are similar in time or we select the
most recent sale and the one most comparable to the subject to place the most weight on.
q) The comparative analysis of properties and transactions focuses on similarities and differences that
affect value but there are variations found in these similarities and differences.
r) Functional obsolescence is caused by the presence of currently desirable layout, design or other
features, or presence of currently desirable features.
s) The basis of valuation for sale/purchase purposes is the Replacement cost/value while the basis of
valuation for mortgage purpose is the full insurable value.
Second Opportunity Examination Paper
Page3 of 6
July 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Principles and Methods of Valuation
PMV611S
t) The cost approach is based upon the premise that the informed purchaser will pay more for a
property than the cost of constructing an equally desirable substitute less appreciable depreciation.
u) Under the Principle of Substitution of the Comparison method of Valuation, a buyer is willing to pay no
more for a property than the cost of acquiring a similar substitute property.
v) In the Income approach, the Capitalization Rate.reflects the market's expected return on investment
for the property type and risk level.
w) The Residual Method is used to find the value of special purpose properties and the land on which
they are built.
x) Both rental and capital values tend to be directly influenced by the potential for profit and in these
circumstances a valuation having regard to the profits achieved is more likely to produce a realistic
valuation than any application of comparison methods.
(24]
Question 2
a) Explain the two (2) principles relating to the investment method of valuation.
(S)
i) Anticipation and change
ii) Supply and Demand
b) Explain the three (3) main purposes for undertaking a residual valuation.
(6)
c) Outline the eight (8) potential sources of data that you would look for when using the comparative
method of valuation.
(4)
d) Under what circumstances would a valuer use the Cost Method of valuation?
(4)
e) Enumerate the steps involved in the The Discounted Cash Flow Technique
(3)
f) Explain the use of the Profits method of valuation.
(4)
(26]
Second Opportunity Examination Paper
Page4of6
July 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Principles and Methods of Valuation
PMV611S
Question 3
a) Use the information provided to show how the sales comparison approach accounts for differences in
size between comparable properties.
• Subject property: 200 square metres (sq mt)
• Comparable 1: 150 sq mt, sold for N$600,000.
(2)
b) Briefly explain, using a worked example, how depreciation affects the valuation of a property under
the cost approach.
(4)
c) If a comparable property sold for N$320,000 but had an additional bedroom compared to the subject
property, an adjustment might be made to account for this difference. Assuming the adjustment is
N$10,000, calculate the adjusted value of the subject property?
(2)
d) A warehouse needs to be valued. The estimated cost to replace the building with current materials
and labour is N$800,000. However, the building is 15 years old, and the typical depreciation rate for
warehouses in the area is 3% per year.
(4)
e) An apartment building generates a Net Operating Income (NOi) of N$120,000 per year. The prevailing
capitalisation rate for similar properties in the area is 7%. Calculate the value of the building.
(2)
f) The gross rental income (GRI) for Polyheights is N$2,000,000 and operating expenses (OE) are
N$200,000; calculate the Net operating income (NOi) and using a capitalisation rate of 8%, calculate
the estimated value of Polyheights.
(4)
g) Use the following information to value the land using the Residual method. Subject property is a
vacant lot zoned for residential development.
Projected sales revenue or Gross Development Value (GOV): N$2,500,000
Construction costs: N$1,500,000
Expected profit margin: 20%
(4)
Second Opportunity Examination Paper
Page5 of 6
July 2024
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
Principles and Methods of Valuation
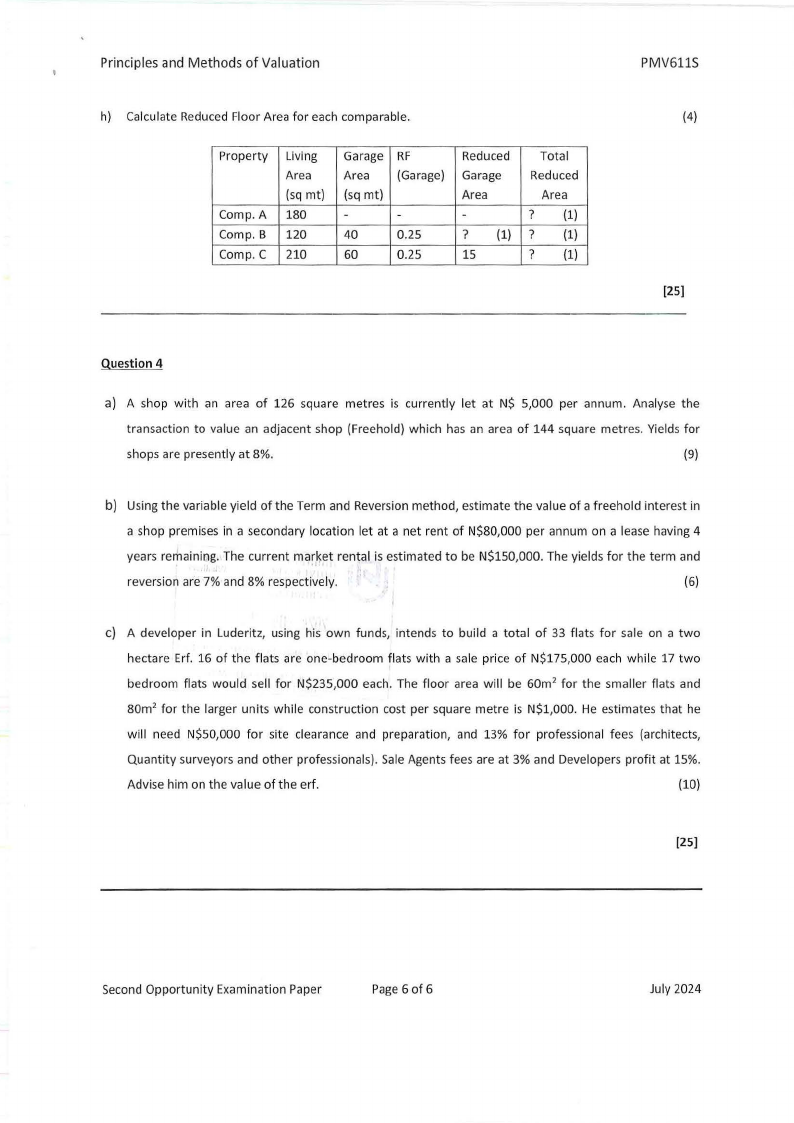
h) Calculate Reduced Floor Area for each comparable.
Property
Comp. A
Comp. B
Comp. C
Living
Area
(sq mt)
180
120
210
Garage
Area
(sq mt)
-
40
60
RF
(Garage)
-
0.25
0.25
Reduced
Garage
Area
-
? (1)
15
Total
Reduced
Area
? (1)
? (1)
? (1)
PMV611S
(4)
[25]
Question 4
a) A shop with an area of 126 square metres is currently let at N$ 5,000 per annum. Analyse the
transaction to value an adjacent shop (Freehold) which has an area of 144 square metres. Yields for
shops are presently at 8%.
(9)
b) Using the variable yield of the Term and Reversion method, estimate the value of a freehold interest in
a shop premises in a secondary location let at a net rent of N$80,000 per annum on a lease having 4
years remaining. The current ma~_ketrental is estimated to be N$150,000. The yields for the term and
reversion are 7% and 8% respectively.
(6)
c) A developer in Luderitz, using his own funds, intends to build a total of 33 flats for sale on a two
hectare Erf. 16 of the flats are one-bedroom flats with a sale price of N$175,000 each while 17 two
bedroom flats would sell for N$235,000 each. The floor area will be 60m2 for the smaller flats and
80m2 for the larger units while construction cost per square metre is N$1,000. He estimates that he
will need N$50,000 for site clearance and preparation, and 13% for professional fees (architects,
Quantity surveyors and other professionals). Sale Agents fees are at 3% and Developers profit at 15%.
Advise him on the value of the erf.
(10)
[25]
Second Opportunity Examination Paper
Page 6 of 6
July 2024





