 |
IGD411S - INTRODUCTION TO GEOSPATIAL DATA - 2ND OPP - JULY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

.•
n Am I BI A u n IVER s ITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF ENGINEERINGAND THE BUILTENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENTOFLANDAND SPATIALSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF NATURAL RESOURCEMANAGEMENT (NATURE CONSERVATION),
BACHELOR OF GEOINFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, BACHELOR OF LAND ADMINISTRATION, BACHELOR OF
PROPERTY STUDIES HONOURS, BACHELOR OF REGIONAL AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT, BACHELOR OF
URBAN AND REGIONAL PLANNING, DIPLOMA IN PROPERTYSTUDIES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BNRS, 07BGEI,
07BLAM, 08BOPS, 07BORR, 07BURP, LEVEL:4
06DIPS
COURSE: INTRODUCTION TO
GEOSPATIAL DATA
COURSECODE: IGD411S
SESSION: JULY 2024
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 2 HOURS
MARl(S:
80
SECONDOPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTAREYXAMINATIONQUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER: Ms D. Husselmann
MODERATOR: Mr E. Naoseb
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 5 PAGES(Including this front page)
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. Answers to calculations must be rounded off to three decimal places, excluding
answers to co-ordinate conversions
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examination paper.
2. Examination ~cript.
3. Calculators and other drawing equipment.
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Introduction to Geospatial Data
Question 1
1.1. What do the following acronyms stand for?
a. MSL
b. TIN
c. DTM
d. UTM
e. GPS
IGD411S
(5)
1.2. State whether the following are true or false.
(5)
a. A thematic map show as much detail of the landscape, elevations, roads, towns
etc. as possible.
b. Geospatial data is positional data collected about a geographic phenomenon.
c. Map generalisation is the process of amplifying the amount of details on a map.
d. Aerial photographs are also generalised or symbolised as maps.
e. At least four satellites are required to obtain a fixed GPSposition.
1.3. Fill in the missing word.
(5)
a. Data models enable complex ... features to be viewed in a simplified form that
can easily be understood.
b. A line is a ..., it has both magnitude and direction.
c. A ... shows all the graphic symbols used to design the map.
d. ... photographs results when two photographs are taken from slightly different
angles making them to appear three-dimensional when viewed together.
e. Dilution of Precision is a measure of the ... of satellite geometry and is related to
the spadng and position of the satellites in the sky.
(15)
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page2 of 5
July 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
Introduction to Geospatial Data
Question 2
2.1. Which data model uses pixels to show location?
IGD411S
(1)
2.2. Which datum enable us to:
(2)
a. determine x and y positions and
b. determine height.
2.3. What do we call the mathematical formulas that are used to convert the three-dimensional
(1)
earth to a two-dimensional flat surface?
2.4. Give one word for: The pattern formed by the lines of latitude and longitude.
(1)
2.5. Calculate the distance from 56.178° S to 30.294° S.
(3)
2.6. Match each co-ordinate system with the correct co-ordinate format by writing down the co- (3)
ordinate system and the format next to it.
CO-ORDINATE SYSTEM
CO-ORDINATE FORMAT
Polar
Y,X
Geographic
Direction, Distance
Projected
Latitude, longitude
Question 3
3.1. Convert the following Degrees Minutes and Seconds to Decimal Degrees. Show your work.
(6)
a.
22° 28' 13" S
b.
23° 08' 15" E
(8)
3.2. A Land parcel located in the Usakos area has the following co-ordinates:
Point
y
X
A
-10 697.20
+20 719.20
B
-13 742.20
+21546.70
C
-14 050.60
+22 829.50
D
-11 581.50
+23 233.60
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page 3 of 5
July 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Introduction to Geospatial Data
i. Calculate the area of the land parcel. Give your answer in hectares.
IGD411S
3.3. Calculate the scale if the length of the Fish river is 7 cm on the map and 9 km in reality. Round (4)
your scale off to the nearest 100th place.
(18]
Question 4
4.1 There are three types of orientation systems for direction on a map. Name these three (3)
different types of North arrows.
(5)
4.2 List five map elements.
4.3
Given a slope of 27 .36°1 convert your slope to percentage.
(3)
4.4 Given the figure below interpolate the height of point X.
(4)
1350
12cm
X
1330
Question S
5.1 Name the two characteristics of aerial photographs.
5.2 Name three types of displacement associated with aerial photographs.
5.3 Which have a larger scale; aerial photograph or satellite image?
[15]
(2)
(3)
(4)
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page 4 of 5
July 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
Introduction to Geospatial Data
IGD411S
5.4
Calculate the size of the area covered by a photograph measuring 18 cm by 9 cm on a scale of (6)
1:10 000. Give your answer in hectares.
[15]
Question 6
6.1 List the four types of DOP measures.
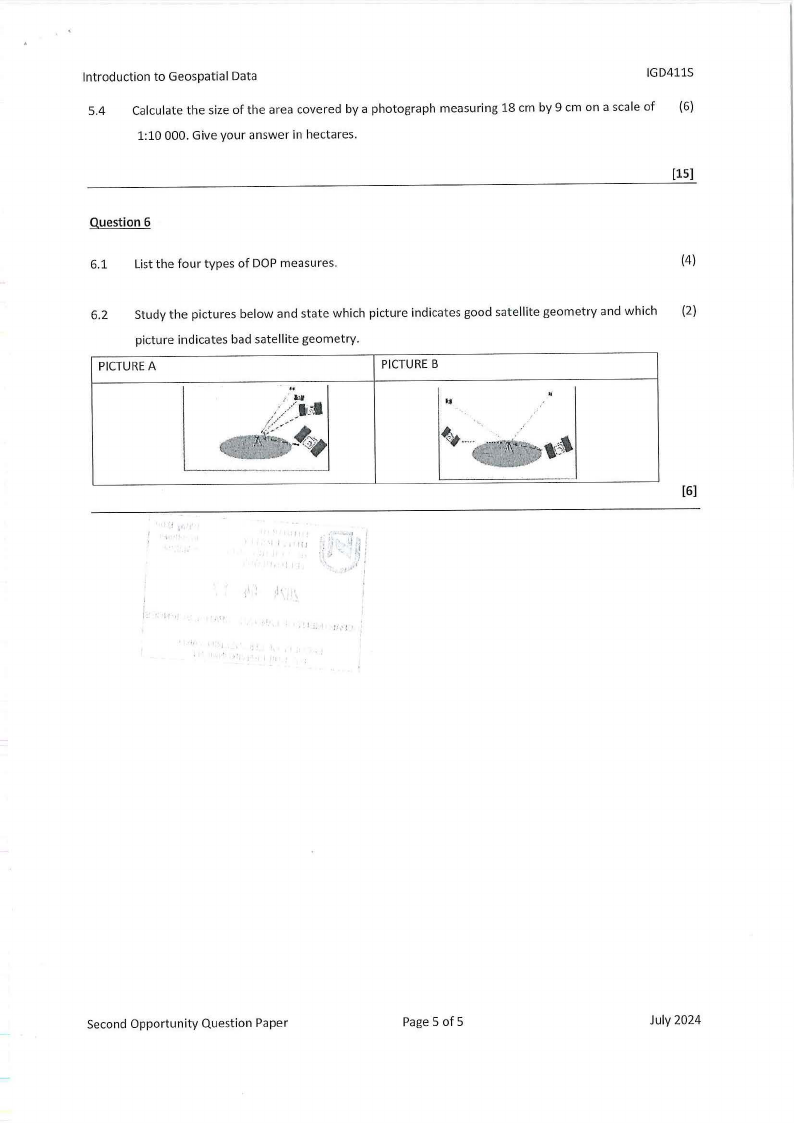
(4)
6.2 Study the pictures below and state which picture indicates good satellite geometry and which {2)
picture indicates bad satellite geometry.
PICTUREA
PICTUREB
[6]
II
,u
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page5 of 5
July 2024





