 |
HSP511S - HEALTH SCIENCE PHYSICS - 2ND Opp - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
ge
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT: NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
BACHELOR OF HUMAN NUTRITION
BACHELOR OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES
BACHELOR OF HEALTH INFORMATION SYSTEMS MANAGEMENT
BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES
BACHELOR OF HORTICULTURE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC,
O8BOHN, O8BOHS, 07BHIS, O8BBMS,
LEVEL: 5
O07BHOR
COURSE CODE: HSP511S
GNP501S
COURSE NAME: HEALTH SCIENCE PHYSICS
GENERAL PHYSICS 1A
SESSION: JULY 2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) | DR MUNYARADZI ZIVUKU
MR VAINO INDONGO
MODERATOR: | PROF. DIPTI SAHU
Instructions
Answer all questions.
Answer the questions in the booklet provided
All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink
Mark all answers clearly with their respective question
numbers
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 6 PAGE (INCLUDING THIS FRONT PAGE)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
(24)
1.1 Calculate the volume of an ice block with mass of 24.6 g and density
917 kg/m°.
(2)
A. 2.x 6 10-85 m?
B. 3.1 x 104 m3
C. 19.3 x 10-3 ms
D. 2. x 10 0° cm
1.2 A streamline flow is also called ............
(2)
A. Laminar flow
B. Turbulent flow
C. Volume flow
D. Bernoulli's flow
1.3 A steel bar is precisely 1.6 m at 25° C. At what temperature will its length
be 1.4 mm longer?
(2)
A. 48°C
B. 98°K
C. 48°K
D. 98°C
1.4 When a liquid freezes to become a solid:
A. it absorbs energy
C. its temperature decreases
(2)
B. its temperature increases
D. it emits energy
1.5 How much heat is required to raise the temperature of a 0.04 kg stainless
steel cup from 20°C to 50°C if the specific heat capacity of stainless
steel is 0.50 kJ / kg.°C.
(2)
A. 200 J
B. 400 J
C. 800 J
D. 1000 J
1.6 beeeee eee enes Is a vector that is tangential to path of an object in a circle.
(2)
A. angular force
B. centripetal acceleration
C. centripetal velocity
D. centripetal force
1.7 The best term to describe the rate of increase of velocity which is constant,
iS.....
(2)
A. deceleration
B. acceleration
C. uniform retardation
D. uniform acceleration
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.8 Which of these statements is not true about why weight varies?
(2)
A. due to rotation of the earth about its axis
B. due to constant in density of earth
C. due to elliptical shape of the earth
D. due to variation in latitude
1.9 Whenever a liquid is touched slightly, small ripples run across the surface.
This statement is an evidence Of ..............:.
(2)
A. Bernoulli principle
B. Newton s law
C. Pure magic
D. Surface tension
1.10 Which of the following is not relevant in fluid dynamics?
(2)
A. viscosity
B. laminar flow
C. incompressible
D. turbulent flow
Which of the following physical quantity is
dimensionless?
(2)
A. Momentum
B. Strain
C. Stress
D . velocity
1.12 An object is projected from the ground at an angle of 30° to the horizontal with
a velocity of 100m/s. The velocity and the direction of the object 1 sec before
it hit the ground is...
(2)
A. 86.94 m/s and 27.4°
B. 91.78 m/s and 19.3°
C. 88.02 m/s and 52.4°
D. 82.02 m/s and 53.4°
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B
QUESTION 2
(15)
2:1 A vehicle moving with a velocity v experiences a force F, due to air
resistance, given by;
F= 51 Cat uP AY
Where is e the density of air, A is the cross-sectional area of the vehicle and C
is the dimensionless quantity called the drag coefficient.
2.1.1 Use dimensional analysis to find a, B and y
(7)
2.2 When a solid sphere moves through a liquid, the liquid opposes the motion with
a force F. The magnitude of F depends on the coefficient of viscosity n of the
liquid, the radius r of the sphere and the speed of the sphere. Use dimensional
analysis to derive a formula for the force (F).
(8)
QUESTION 3
3.4 Consider the following vectors:
A=i+3j-2k and B=5i-3k
(i) Find:
Ax B
(ii) Determine a unit vector that is perpendicular to both vectors, Aand
(16)
(5)
B (3)
3.5 The position 7 of an object is given by 1.0 t® i - 2.0 27+ 3.0 k.m (with t in
seconds). Determine;
(i)
he magnitude of the position 7 when t = 3 seconds
(4)
(ii)
the acceleration of the particle for 3 seconds.
(4)
QUESTION 4
(15)
4.1. State the law of conservation of momentum.
(3)
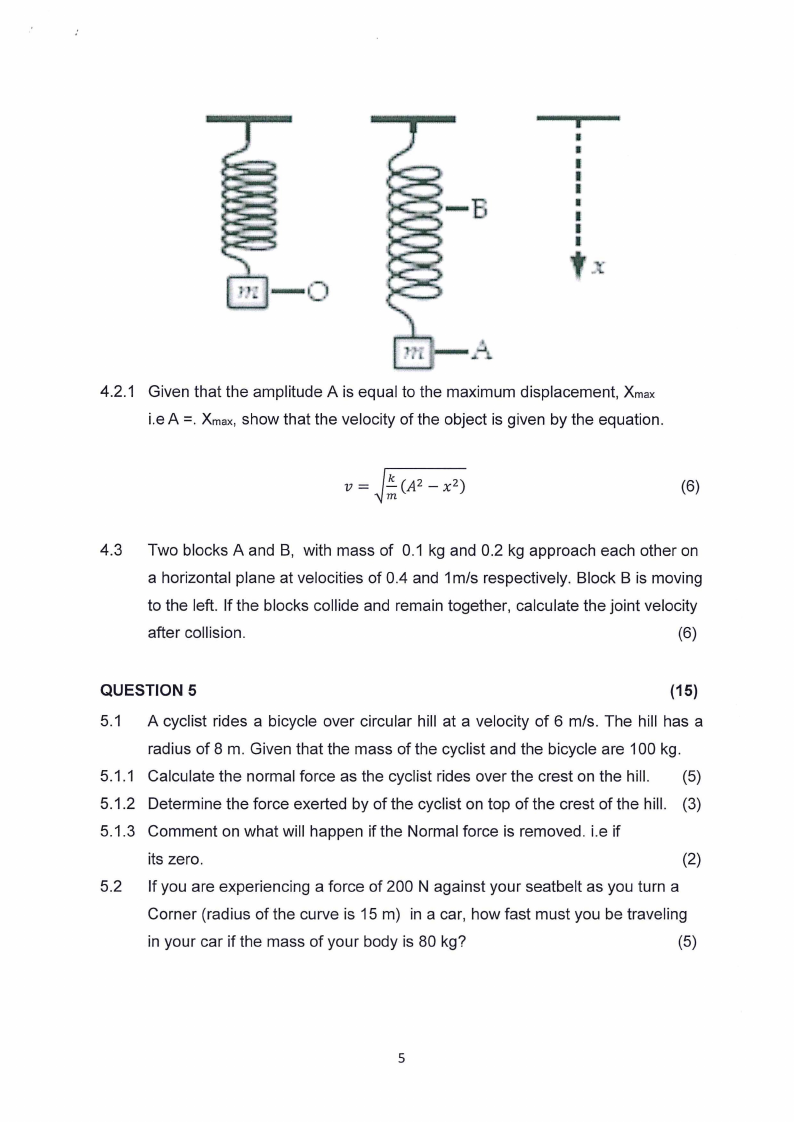
4.2 Aweight of mass m is at rest at O when suspended from a spring, as shown
in figure 1. 0. The energy applied (E) of pulling down the spring is
combination of potential energy (PE) and kinetic energy (KE). When released,
the spring oscillates between positions A and B.
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
i;
4+
4.2.1 Given that the amplitude A is equal to the maximum displacement, Xmax
i.eA =. Xmax, Show that the velocity of the object is given by the equation.
v= [s (A? — x?)
(6)
4.3 Two blocks A and B, with mass of 0.1 kg and 0.2 kg approach each other on
a horizontal plane at velocities of 0.4 and 1m/s respectively. Block B is moving
to the left. If the blocks collide and remain together, calculate the joint velocity
after collision.
(6)
QUESTION 5
(15)
5.1 Acyclist rides a bicycle over circular hill at a velocity of 6 m/s. The hill has a
radius of 8 m. Given that the mass of the cyclist and the bicycle are 100 kg.
5.1.1 Calculate the normal force as the cyclist rides over the crest on the hill.
(5)
5.1.2 Determine the force exerted by of the cyclist on top of the crest of the hill. (3)
5.1.3 Comment on what will happen if the Normal force is removed. i.e if
its zero.
(2)
5.2. If you are experiencing a force of 200 N against your seatbelt as you turn a
Corner (radius of the curve is 15 m) in a car, how fast must you be traveling
in your car if the mass of your body is 80 kg?
(5)
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6
|
(15)
6.1
Define surface tension.
(2)
6.2 Find the density of the copper, given that the copper ball has a radius of 1 cm
with mass of 37.3 g.
(3)
6.3 Discuss the Bernoulli principle both conceptually and mathematically in relation
to water in a dam and water flowing through a gorge.
(5)
6.4 After water has boiled, the temperature of water decrease by 22°C. The
mass of water in the kettle is 0.5 kg. Specific heat capacity of water is
4182 J /kg °C.
6.4.1 Calculate the energy transferred to the surroundings from water.
(3)
6.4.1 Explain why the total energy input to the kettle is higher than the energy used
to heat.
(2)
END OF EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER





