 |
TPH601S - THERMAL PHYSICS - 1ST OPP - JUNE 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
2
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCES AND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
COURSE CODE: TPH601S
SESSION: JUNE 2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
LEVEL: 6
COURSE NAME: THERMAL PHYSICS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) | MR. VAINO INDONGO
MODERATOR: | DR. SYLVANUS ONJEFU
INSTRUCTIONS
Write all your answers in the answer booklet provided.
Read the whole question before answering.
3.
Begin each question on a new page.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
Non-programmable Scientific Calculator
THIS EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 4 PAGES
(INCLUDING THIS FRONT PAGE)
Page 1 of 4
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
[23]
1.1 Define the following thermodynamic terms:
(10)
(a) System
(b) Universe
(c) Control volume
(d) Extensive property
(e) Temperature
1.2 Assume that a system 1 with temperature Ti and system 2 with temperature T2
are in thermal contact with each other. There will be exchange of heat between
the two systems if there is a temperature gradient (i.e., when Ti is not equal to T2).
What would be the thermodynamic state if the process of heat exchange continues
until the temperatures are equal?
(2)
1.3 State the Zeroth Law of thermodynamics.
(2)
1.4 Use the principle of the zeroth law of thermodynamics to briefly discuss the triple
point of water.
(3)
1.5 If the temperature of a system as 0°C, what would be the temperature on the Kelvin
scale?
(2)
1.6 Suppose that you wish to identify an unknown liquid by measuring its boiling
point accurately. You first use a constant-volume gas thermometer to measure
the pressure (p) of the confined gas to be 2.7 atm* at the triple point of water.
Then you bring the same confined gas to equilibrium with the unknown boiling
liquid and measure p = 4.2 atm. What is the temperature of vaporization on the
Kelvin scale?
(4)
QUESTION 2
[41]
2.1 Suppose a copper rod of length | = 5.31 mm was heated and expand to a length of
5.36 mm. The initial and final temperatures for the rod are 275.15 K and 342.15 K
respectively. Calculate the coefficient of linear expansivity (a) of the copper rod.
(4)
2.2 An oil trucker loaded about 21 000 L of diesel on a hot day in Walvis Bay, Namibia.
On his way to deliver the oil in Johannesburg, South Africa, a cold weather
was encountered, where the temperature was 45 °C lower than that of Walvis Bay
and Johannesburg. How many litres were delivered to Johannesburg, when
B = 9.50x 10-4 °C" for diesel and a = 1.10x 10-5 °C? for steel tank?
(5)
Page 2 of4
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

2.3 An aluminium block (c = 9.10 x 10? J.kg K*) of mass 0.50 kg at a temperature of 200°C
is dropped into an aluminium calorimeter cup of mass 0.20 kg containing 1.50 kg of
water (c = 4.2 x 10? J.kg? K+) at 40°C. The system is adiabatically covered and attains
equilibrium at a final temperature Ty-
(a) Use the definition of specific heat capacity, write down heat gained or loss for
each medium and set the equation Qtotai = 0.
(5)
(b) Calculate T; attained during equilibrium.
(5)
2.4 Heat of vaporization is the amount of energy per unit mass that must be transferred
as heat when the sample completely undergoes phase change. The latent heat of
vaporization during the process is 2.256x10° J.kg?. Suppose 0.015 kg of liquid water
at a temperature of 100 °C was converted to steam at standard atmospheric pressure,
1 atm. The volume of water changes from initial volume value of 0.50 x 10-2 m? as a
liquid to 2.50 x 10 -* m? as steam.
(a) How much work is done by the system during this process?
(2)
(b) How much energy is transferred as heat during that process?
(2)
(c) What is the change in internal energy of the system during that process?
(2)
2.5 Complete the table by filling in the correct information. Write down the answer and
the corresponding answer according to the first law the thermodynamics.
(5)
Process
Restriction
Outcomes
Closed cycle
(i) sesso
(1) ee
Free Expansion
(iii) .....0
AU =0
(iV) ...cseeee
Q=0
(V) sesssseseeee
2.6 Suppose a gas is confined in a cylinder with a movable piston with a heavy metal
object placed on top. Its volume is changed from initial state (Vj) to final state (V;)
at a constant pressure. Prove that the differential work done by the system when
the metal object is removed, and a piston moves an infinitesimal distance dS is
W= f,/ pav
(4)
2.7 Consider a system of an ideal gas. Show that the work done in an adiabatic system
is given by:
W= = (pV — p2V2), where y is a ratio of molar specific heat at a constant
pressure to molar specific heat at constant volume, i.e. y = a V1, pi being initial
v
state and V2, p2 is final state of volume and pressure respectively.
(7)
Page 3 of4
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 3
[20]
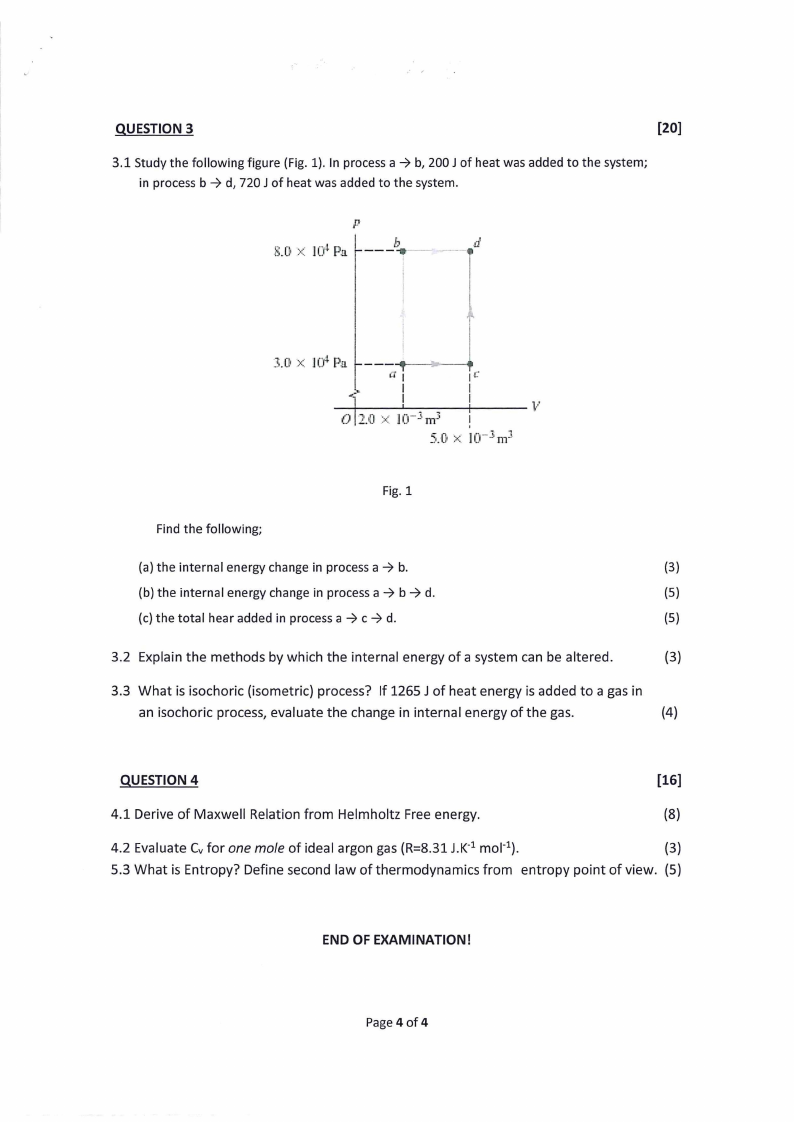
3.1 Study the following figure (Fig. 1). In process a > b, 200J of heat was added to the system;
in process b > d, 720J of heat was added to the system.
8.0% 10¢ Pa | ___5,
|
|
3.0 x 10* Pa L-——-¢— _|
O20 * 10-4nH
5.0 x 10-3m3
Fig. 1
Find the following;
(a) the internal energy change in process a > b.
(3)
(b) the internal energy change in process a> b> d.
(5)
(c) the total hear added in process a > c > d.
(5)
3.2 Explain the methods by which the internal energy of a system can be altered.
(3)
3.3 What is isochoric (isometric) process? If 1265 J of heat energy is added to a gas in
an isochoric process, evaluate the change in internal energy of the gas.
(4)
QUESTION 4
[16]
4.1 Derive of Maxwell Relation from Helmholtz Free energy.
(8)
4.2 Evaluate Cy for one mole of ideal argon gas (R=8.31 J.K+ mol’).
(3)
5.3 What is Entropy? Define second law of thermodynamics from entropy point of view. (5)
END OF EXAMINATION!
Page 4 of 4





