 |
MAB702S - MARINE BIOLOGY 3B - 1ST OPP - NOVEMBER 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

f
nAm I BIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE
FacultyofHealth,Natural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoolof Natural and Applied
Sciences
Department ofBiology,
Chemistryand Physics
13JacksonKaujeuaStreet
Private Bag13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +264612072012
F: +264612079012
E: dbcp@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
LEVEL: 7
COURSE:MARINE BIOLOGY 3B
COURSECODE: MAB702S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2024
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
FIRST OPPORTUNITY: QUESTION PAPER
Professor Edosa Omoregie
Professor Johannes litembu
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left-side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHMENTS
None
This question paper consists of 7 pages including this front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A: MULTIPLE CHOICE
[20 MARKS]
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
[20 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate answer
from the given possibilities. Fill in the appropriate letter next to the number of the correct
statement/phrase on your ANSWERSHEET.
[20]
1.1. How does salinity affect the density of seawater?
a) Higher salinity decreases water density, making it harder to float
b) Higher salinity increases water density, making it easier to float
c) Salinity has no effect on water density
d) Salinity only affects freshwater, not seawater
e) Salinity affects only surface water density
1.2. Why is water circulation important in the marine environment?
a) It decreases nutrient availability for marine organisms
b) It leads to the depletion of dissolved gases in the water
c) It affects the physical, biological, and chemical parameters of the marine ecosystem
d) It only influences deep-sea habitats
e) It has no effect on nutrient cycling in marine environments
1.3. How do marine organisms typically acclimate to environmental changes?
a) Through gradual physiological adjustments over time to reach a new equilibrium
b) By maintaining their physiological state without adjustment
c) Through immediate genetic changes
d) By permanently migrating to new environments
e) By reducing their metabolic rate indefinitely
1.4. Which of the following is a key adaptation of marine fish to regulate salinity in their
environment?
a) Drinking large amounts of freshwater
b) Excreting salts through their skin
c) Selectively excreting salts through specialized gill cells
d) Absorbing salts directly from seawater
e) Reducing metabolic activity to conserve water
1.5. How do environmental changes, such as temperature shifts, impact the energy balance
of marine organisms?
a) They have no effect on metabolic energy
b) They lead to increased growth and reproduction
c) They allow organisms to consume less food
d) They cause organisms to reproduce at higher rates during extreme conditions
e) They increase energy consumption for acclimation, reducing available energy for growth
1.6. Which of the following products is obtained from Laminaria?
a. Spirulina
Marine Biology 3B (MAB702S)
l't Opportunity- November 2024
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

b. Carrageenan
c. Agar
d. Iodine
e. Chlorellin
1.7. Under which group of zooplankton will the fish larva be classified?
a. Holoplankton
b. Meroplankton
c. Microplankton
d. Nanoplankton
e. Phytoplankton
1.8. Why are plankton critical in the marine food web?
a) They are the primary source of energy for nekton and larger marine animals
b) They provide the majority of oxygen in deep-sea environments
c) They contribute to ocean floor sediment formation
d) They only serve as detritivores in benthic ecosystems
e) They have no direct impact on the marine food web
1.9. Which of the following is a consequence of upwelling in the open sea?
a) Decrease in biodiversity due to cooler water
b) Reduction in marine primary productivity
c) Increase in nutrient availability, promoting phytoplankton growth
d) Inhibition of deep-sea currents
e) Formation of sedimentary rocks
1.10. Which of the following best describes the ecological role of benthic organisms in marine
ecosystems?
a) They contribute solely to the nutrient cycling of the water column
b) They primarily produce oxygen through photosynthesis
c) They only consume detritus without contributing to nutrient recycling
d) They are passive organisms with little impact on ecosystem productivity
e) They stabilize sediments and play a crucial role in nutrient cycling at the sea floor
1.11. What is the key difference between infauna! and epibenthic organisms?
a) Infauna! organisms live on the surface of the sediment, while epibenthic organisms live
buried in the sediment
b) Epibenthic organisms live attached to hard surfaces, while infauna! organisms burrow
within the sediment
c) Infauna! organisms feed through active suspension, while epibenthic organisms filter feed
passively
d) Infauna I organisms are only found in deep-sea environments, while epibenthic organisms
live in the intertidal zone
e) There is no functional difference between infauna! and epibenthic organisms
1.12. Which of the following best explains the vertical zonation observed in intertidal zones?
a) Organisms are randomly distributed according to tidal cycles
Marine Biology 38 (MAB7025)
1'1 Opportunity- November 2024
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

b) Zonation results from competition, predation, and the ability of organisms to tolerate
environmental stressors
c) Zonation is solely caused by wave action in the intertidal zone
d) Zonation depends only on the distance from shore and water depth
e) It is due to the equal distribution of nutrients at all levels of the intertidal zone
1.13. What is a common adaptation among intertidal organisms to prevent desiccation during
low tide?
a) Increased metabolic rates
b) Burrowing into the sediment or closing their shells tightly to retain moisture
c) Moving to higher intertidal areas
d) Shedding their outer layers to reduce water loss
e) Absorbing excess water from the surrounding environment
1.14. What is the primary characteristic of estuarine environments that distinguishes them
from other marine ecosystems?
a) Constant temperature throughout the year
b) Stable salinity levels
c) Fluctuating salinity due to the mixing of freshwater and saltwater
d) Lack of biodiversity compared to marine ecosystems
e) Exclusive presence of deep-sea organisms
1.15. What is the main factor that limits coral reefs to shallow waters?
a) High nutrient levels in deeper waters
b) Requirement for strong wave action
c) Higher oxygen levels in deep-sea habitats
d) Absence of predators in shallow waters
e) Need for sunlight for symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) to photosynthesize
1.16. How do zooxanthellae benefit from their symbiotic relationship with coral polyps?
a) By providing protection from predators
b) By receiving organic nutrients produced by corals
c) By acquiring oxygen from the coral polyps
d) By using coral excretions for nitrogen and phosphorus
e) By removing harmful toxins from coral tissue
1.17. How does the Maximum Sustainable Yield (MSY) model help in fisheries management,
and what is one of its limitations?
a) MSY helps determine the maximum yield without depleting stocks, but it ignores
environmental variations affecting fish reproduction.
b) MSY guarantees long-term sustainability of fish populations by encouraging
overharvesting in the short term.
c) MSY focuses on predator-prey relationships but does not account for bycatch.
d) MSY ensures economic profits for fishers, but it cannot be applied to aquaculture systems.
e) MSY prioritizes ecosystem diversity but neglects socioeconomic impacts on fishing
communities.
Marine Biology 3B (MAB702S)
1'1 Opportunity- November 2024
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

1.18. What are the most significant impacts of cultural eutrophication on marine biodiversity
and ecosystem functioning?
a) It leads to increased oxygen levels, which support the growth of larger fish populations.
b) It causes harmful algal blooms and dead zones, reducing oxygen and biological
productivity.
c) Eutrophication accelerates coral reef growth by adding necessary nutrients to the water.
d) Cultural eutrophication primarily benefits fisheries by increasing fish harvests.
e) It enhances marine biodiversity by promoting the growth of new species in affected areas.
1.19. How does ocean acidification affect marine organisms with calcium carbonate
structures, and what are the broader implications for marine ecosystems?
a) Ocean acidification enhances the formation of calcium carbonate structures, increasing
biodiversity.
b) Marine organisms quickly adapt to ocean acidification by switching to silicon-based
structures.
c) Acidification increases plankton blooms, benefiting organisms higher in the food chain.
d) Acidification has no significant impact on marine life due to the ocean's buffering capacity.
e) Ocean acidification weakens the shells of marine organisms like mollusks and corals,
disrupting marine food webs and decreasing ecosystem stability.
1.20. What is the role of the biological pump in regulating atmospheric CO2,and how does
ocean acidification threaten its function?
a) The biological pump circulates heat, but ocean acidification has no impact on its
efficiency.
b) The biological pump captures and stores atmospheric CO2through the sinking of organic
material, but ocean acidification slows down calcification in marine organisms, reducing
CO2sequestration.
c) The biological pump increases the pH of the ocean, promoting faster calcification.
d) The biological pump disperses carbon emissions, increasing the concentration of CO2in
coastal waters.
e) Ocean acidification enhances the biological pump by increasing the rate of organic carbon
deposition.
SECTION B: SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
QUESTION 2: PRACTICAL SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Please answer ALL of the questions in this section.
[20 MARKS)
2.1. Identify the morphometry indices A, B, C, D and E in the fish diagram below.
(5)
A
Marine Biology 38 (MAB702S)
1'1 Opportunity- November 2024
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
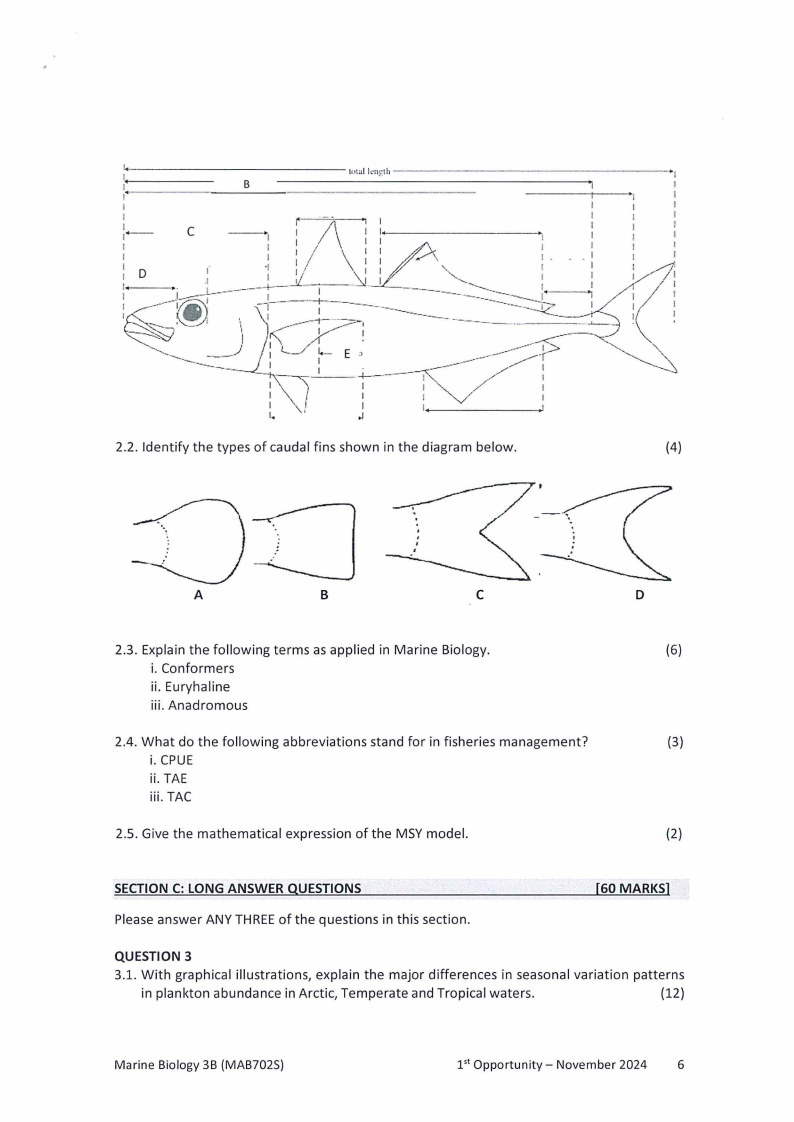
2.2. Identify the types of caudal fins shown in the diagram below.
(4)
A
B
C
D
2.3. Explain the following terms as applied in Marine Biology.
(6)
i. Conformers
ii. Euryhaline
iii. Anadromous
2.4. What do the following abbreviations stand for in fisheries management?
(3)
i. CPUE
ii. TAE
iii. TAC
2.5. Give the mathematical expression of the MSY model.
(2)
SECTION C: LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Please answer ANY THREEof the questions in this section.
[60 MARKS]
QUESTION 3
3.1. With graphical illustrations, explain the major differences in seasonal variation patterns
in plankton abundance in Arctic, Temperate and Tropical waters.
(12)
Marine Biology 3B (MAB702S)
1'1 Opportunity- November 2024
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

3.2. Discuss the impact of zoo plankton grazing on the productivity of the marine waters. (8)
QUESTION 4
4.1. Explain the process of ecological succession in rocky intertidal zones. How do
disturbances, such as storms or human activity, create opportunities for colonization, and
how does the succession process progress over time?
(8)
4.2. With suitable examples, discuss the various environmental challenges faced by intertidal
communities, highlighting the survival strategies employed by the organisms in coping
with these challenges.
(12)
QUESTION 5
5.1. Briefly explain the impacts of trawling on the seabed and benthic communities.
(5)
5.2. Discuss the significant impacts of global warming and acidification on the ocean
physicochemical parameters and explain how these impacts will affect the biology,
habitat and behaviour of major fish stocks.
(15)
QUESTION 6
6.1. With suitable graphical illustrations, discuss the concept of Maximum Sustainable Yield
(MSY) and Maximum Economic Yield (MEY) in fisheries management.
(14)
6.2. Briefly explain the various traditional fisheries Management tools employed by
government agencies in combating overfishing.
(6)
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Marine Biology 3B (MAB702S)
1'1 Opportunity- November 2024 7





