 |
BNS511S-BIOLIOGY FOR NATURAL SCIENCE-2ND OPP-JULY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEncE AnOTECHnOLOGY
FacultyofHealth,Natural
ResourceasndApplied
Sciences
Schoolof Agriculture and
Natural ResourcesSciences
Department of Natural
ResourceSciences
13JacksonKaujeuil Str?et
Private Bilg13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +264 61207 2141
E: dnrs@nust.na
•trwww.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELORof NATURALRESOURCEMANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 07BNRS
LEVEL:7
COURSE:BIOLOGYFOR NATURALSCIENCES
COURSECODE: BNSSllS
DATE: JULY2024
SESSION:
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 150
SECOND OPPORTUNITY: QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
Mrs Gertruida Louisa Theron
Mr. Helmuth Tjikurunda
INSTRUCTIONS
Answer all questions in the exam script/book.
1. Pleasewrite neatly and legibly.
2. Do not use the left-side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the examiner.
3. No books, notes, and other additional aids are allowed.
4. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
This paper consists of 5 pages including this front page
Biology for Natural Sciences (BNS511S)
2nd Opportunity July 2024
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

2
SECTIONA: SHORTQUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
Give the scientific term for each of the following: (Mostly 1 but sometimes 2 words!)
1.1 The state of matter where the intermolecular forces are the weakest.
1.2 Type of reaction that takes place when an ice cube melts.
1.3 Atoms of the same element, but with different mass numbers.
1.4 When a solid turns directly into a gas.
1.5 When elements combine to form a compound.
1.6 An atom that has lost one or more electrons.
1.7 Structures used by viruses to attach themselves to their host.
1.8 Viruses that infect members of the Kingdom Eubacteria.
1.9 The cell organelle that puts lipids and proteins into packets.
1.10 The Kingdom that the extremophiles belong to.
[30 MARKS]
[10)
QUESTION 2
Explain the difference between the following pairs of terms.
[10)
2.1
Dilute solution vs Concentrated solution
(2)
2.2
Mass number vs Atomic number
(2)
2.3
Fat-soluble vs Water soluble vitamins
(2)
2.4
Rhodophyta vs Phaeophyta
(2)
2.5
Monokaryotic hyphae and Dikaryotic hyphae
(2)
QUESTION 3
State whether each of the following statements is True OR False.
[10)
3.1
Impurities lower the freezing point of a substance and raise its boiling point.
3.2
Porphyra and U/va are typical examples of algae that have alternation of isomorphic
generations.
3.3
The process whereby compounds are split up to give simpler substances is known as
synthesis.
3.4
Sperm and eggs are examples of anisogametes.
3.5
The process whereby a solid turns into a gas is known as sublimation.
3.6
Agar and Carrageenan are commercially important cell wall products harvested from
Chlorophyta.
3.7
Compounds can be decomposed by ordinary chemical means.
3.8
Members of the Phylum Apicomplexa are multinucleated.
3.9 An Archegoinum is a gametangium producing eggs.
3.10 Anisogametes have the same size, shape and mobility.
Biology for Natural Sciences (BNSSllS)
2nd Opportunity July 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

3
SECTION B: LONGER QUESTIONS
[120 MARKS]
QUESTION 4
4.1
For each of the following sentences, choose the correct term from the two options
given. Write down ONLYthe letters a-d, and the correct term next to each letter. Do
NOT re-write the sentences.
(4)
a) The kinetic theory of matter states that the higher the temperature, the (lower/higher)
the average kinetic energy of the particles.
b) The process whereby compounds are split up to give simpler substances is known as
(synthesis/decomposition).
c) The process whereby a gas is cooled, the movement of the particles slowed down and
eventually a liquid is formed is known as (condensation/sublimation).
d) The elements in Group 8 on the periodic table are known as (halogens/noble gases).
4.2
Explain the structural differences between (saturated fats and unsaturated fats), and
also between (monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats).
(4)
4.3
What is the main structural difference between a carbohydrate molecule and a protein
molecule?
(2)
[10]
QUESTION 5
5.1
How do Archaebacteria manage to survive desiccation and or extreme temperatures?
(1)
5.2
Distinguish between a virulent phage and a temperate phage.
(2)
5.3
Name five (5) ways in which we as humans benefit from bacteria
(5)
5.4
Bacteria cannot survive in an environment with less than 15-20% moisture. Explain how (2)
we can use this to our advantage.
5.5
Write a report on the economic importance of viruses. Make use of suitable examples.
(5)
[15]
QUESTION 6
6.1
Explain the following terms, as they relate to the Protoctista.
(5)
(a) Pellicle
(b) Multinucleated
(c) Pathogen
(d) Oral groove
(e) Contractile vacuole
6.2
Give ONE word for each of the following terms:
(7)
a) Organelle that regulates the water content inside Amoeba
b) Protoctistan phylum with one macronucleus and one micronucleus for each organism.
c) The granular cytoplasm of Amoeba. responsible for forming pseudopodia.
d) The firm, flexible body covering of Euglena
e) The infectious stage found in Apicomplexa
f) The inactive stage in which Euglena survives harsh conditions
g) The opening (NOT the groove) where food enters the body of Paramecium
6.3
Explain (in detail) how, and on what, Paramecium feeds. Make use of FULLsentences!
(8)
[20]
Biology for Natural Sciences (BNSSllS)
2nd Opportunity July 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
4
QUESTION 7
7.1
In your own words - explain what happens during Red Tide along the Namibian coast.
(8)
7.2
Explain the term "fossil".
(2)
[10]
QUESTION 8
8.1
Name two cell-wall compounds found in red algae and explain the importance/use of
(6)
each.
8.2
Provide the correct term for each of the following descriptions.
(5)
a) Gametes that look alike, they have the same shape, size and mobility
b) Gametes that differ in shape, size and mobility
c) Gametangium producing sperm (male gametangium)
d) Gametangium producing eggs (female gametangium)
e) Non-motile spores (cannot move by themselves)
8.3
Explain the ecological importance of kelp forests (Phaeophyta).
(4)
[15]
QUESTION 9
9.1
In your OWN WORDS- explain the difference between Plasmogamy and Karyogamy.
(4)
9.2
Discuss three examples of how the Ascomycota influences our lives. You can refer to
(3)
positive AND negative influences.
9.3
Explain the difference between septated and coenocytic hyphae.
(2)
9.4
Explain the importance of "bracket fungi"
(5)
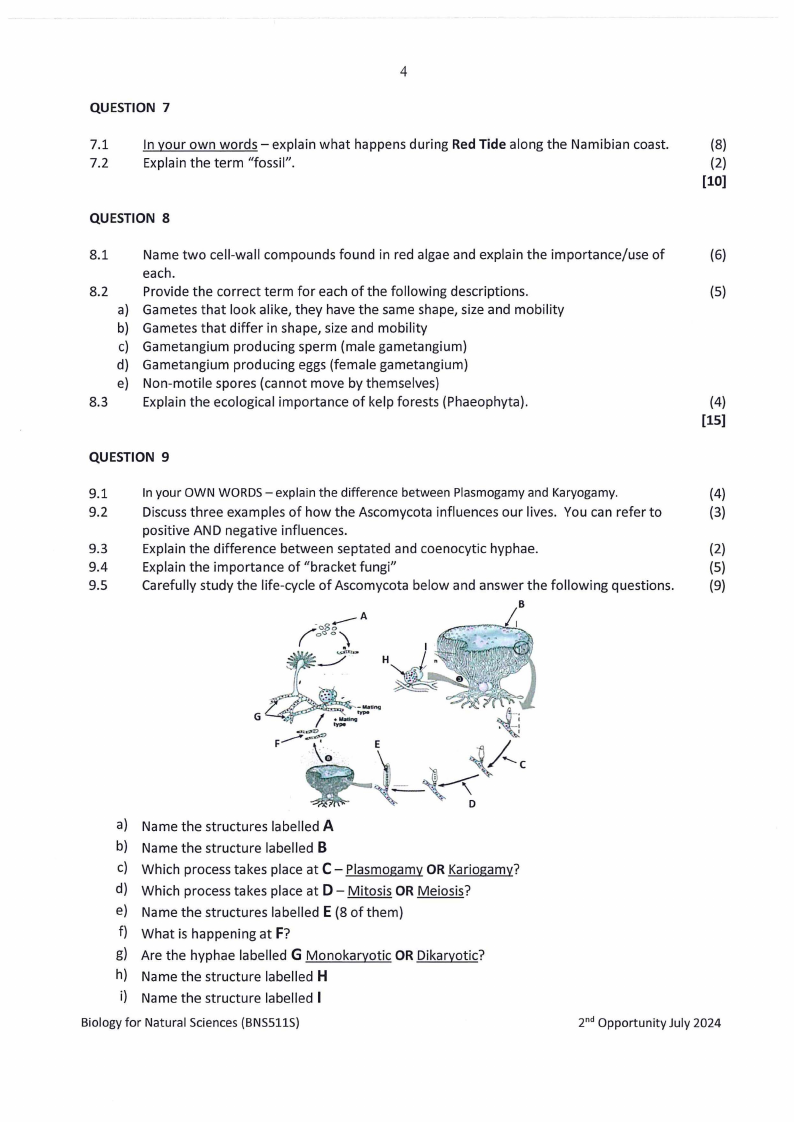
9.5
Carefully study the life-cycle of Ascomycota below and answer the following questions.
(9)
A
- 8--
(.;>og},-
B
-· _Ii
H
I
.-
-M.IUng
G F_-,=,.I.~.....-...
\\o· E
I
'•-I
i/cI
~~""
D
a) Name the structures labelled A
b) Name the structure labelled B
c) Which process takes place at C- Plasmogamy OR Kariogamy?
d) Which process takes place at D - Mitosis OR Meiosis?
e) Name the structures labelled E (8 of them)
f) What is happening at F?
g) Are the hyphae labelled G Monokaryotic OR Dikaryotic?
h) Name the structure labelled H
i) Name the structure labelled I
Biology for Natural Sciences (BNS511S)
2nd Opportunity July 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

5
9.6
Name and compare the different morphological types of lichens found in Namibia.
QUESTION 10
10.1
10.2
10.3
a)
b)
c)
d)
10.4
Where does the light reaction of photosynthesis take place?
Name FIVE (5) internal factors that influence the rate of photosynthesis in a plant.
Explain how each of the following influences the rate of transpiration:
Number of leaves
Number of stomata
Thickness of the cuticle
Relative humidity
Define the term transpiration.
TOTAL 150
(12)
[35]
(1)
(5)
(8)
(1)
[15]
Biology for Natural Sciences (BNS511S)
2nd Opportunity July 2024





