 |
MSC701S - MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY AND CHEMICAL SEPARTION METHODS - 1ST OPP - JUNE 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,NATURAL RESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
SCHOOLOF NATURALAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
DEPARTMENTOF BIOLOGY,CHEMISTRYAND PHYSICS
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BOSC
LEVEL: 7
COURSECODE: MSC701S
COURSENAME: MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPYAND
CHEMICAL SEPARATION METHODS
SESSION:JUNE 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) DR JULIEN LUSILAO
MODERATOR: A/PROF STEFAN LOUW
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions in the answer book provided.
2. Write and number your answers clearly.
3. All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
Non-programmable calculators
ATTACHMENTS
List of Useful formulas and Constants
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 8 PAGES(Including this front page and attachments)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Question 1
[25]
1.1 Define the following terms
(a) Detectors
(2)
(b) Transducers
(2)
(c) Radiant power (or intensity)
(2)
1.2 What principal phenomena are known to cause inaccuracies in the measurement of
transmittance (T) with spectrometric instruments?
(3)
1.3 What is the experimental approach used by analytical chemists to circumvent the
limitation mentioned in 1.2?
(4)
1.4 Differentiate between the quantitative and qualitative information obtained with
spectrometry techniques.
(4)
1.5 The diagram below shows different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
111" 111''
I
I
ynys
I
I
111·" m·"
111" 111"
I
I
A
I
I
m·" urw
_ .....
- lncrca.\\ingFrequency(V)
1111• IO" rn"
I
I
I
BI C
I
m·•
'ol
:
-··''
:.u.r"
I
11r•
E
1010
10'
111• 111' 10'
11r' v(H,1
I
D
~Il~MI
I
I
Lonnsdio waves
Radiowaves
I
II
I
I
I
11r' m" m'
JO'
10•
w• i,(ml
--.... IncreasingWavclcnglh(A).....
\\r,_
,
1•~.;•:,:,1•,
.:·.· '
•,•
•~' .( 'L'
-~- Li_:;.
-,I()-() --------!1-()(-1 --------60-0 --------7-00--
lncrc:1.cinWg a\\·ckni1h(i,) in nm-
(a) Name the regions labelled from A to E.
(5)
(b) What type of quantum transitions are involved in the following regions of the
above diagram?
(i) A region
(1)
(ii) B region
(1)
(iii) C region
(1)
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
Question 2
[25)
2.1 What are the considerations to be taken when developing a quantitative atomic
absorption (AA} method?
(5)
2.2 (a} Why are hollow cathode lamps preferred in AAS instruments instead of the
lamps used in UV-Vis spectrometers?
(2)
(b} Describe the principle of operation of a hollow cathode lamp.
(5)
(c} What are chemical interferences in AAS technique and how do you correct them? (3}
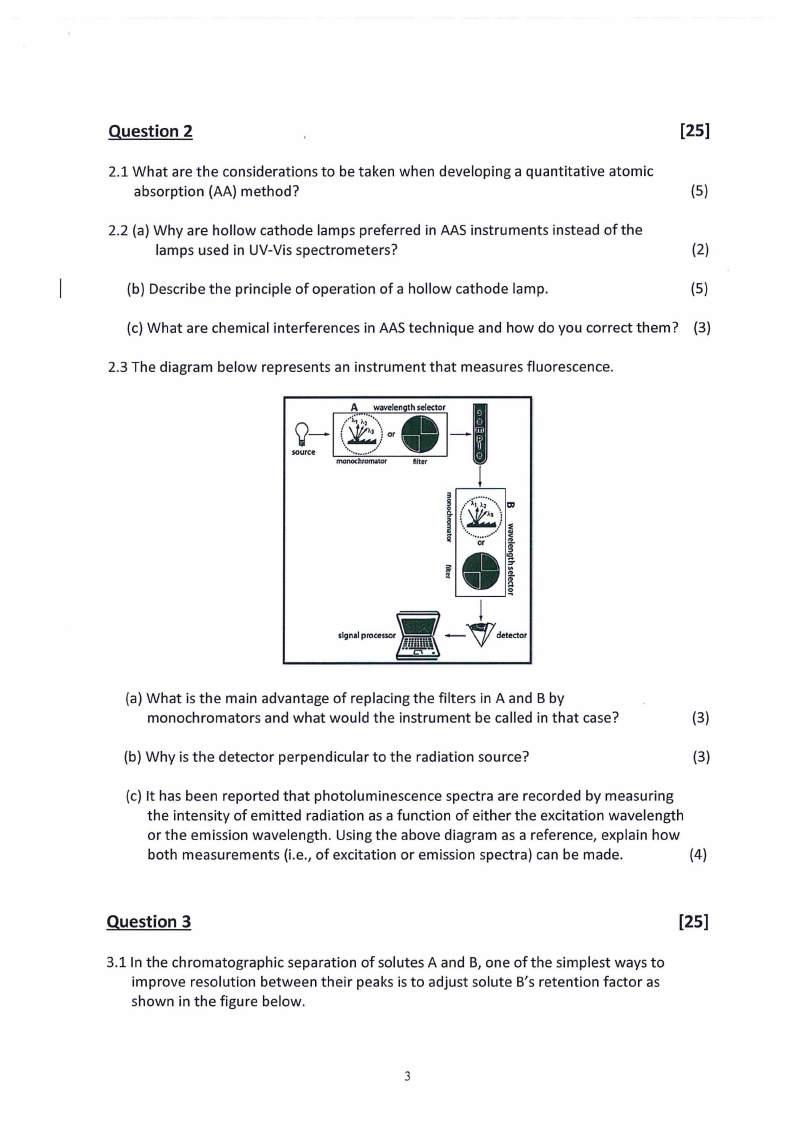
2.3 The diagram below represents an instrument that measures fluorescence.
Q ,....,...,•,_,··· I -
i source
...wavelengthselector
\\....~. jo)t.
.
.
-
·•............. •
monochromator
filter
,,,,.,,~--v-i dmdm
.
(a} What is the main advantage of replacing the filters in A and B by
monochromators and what would the instrument be called in that case?
(3)
(b} Why is the detector perpendicular to the radiation source?
(3}
(c} It has been reported that photoluminescence spectra are recorded by measuring
the intensity of emitted radiation as a function of either the excitation wavelength
or the emission wavelength. Using the above diagram as a reference, explain how
both measurements (i.e., of excitation or emission spectra} can be made.
(4)
Question 3
[25)
3.1 In the chromatographic separation of solutes A and B, one of the simplest ways to
improve resolution between their peaks is to adjust solute B's retention factor as
shown in the figure below.
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
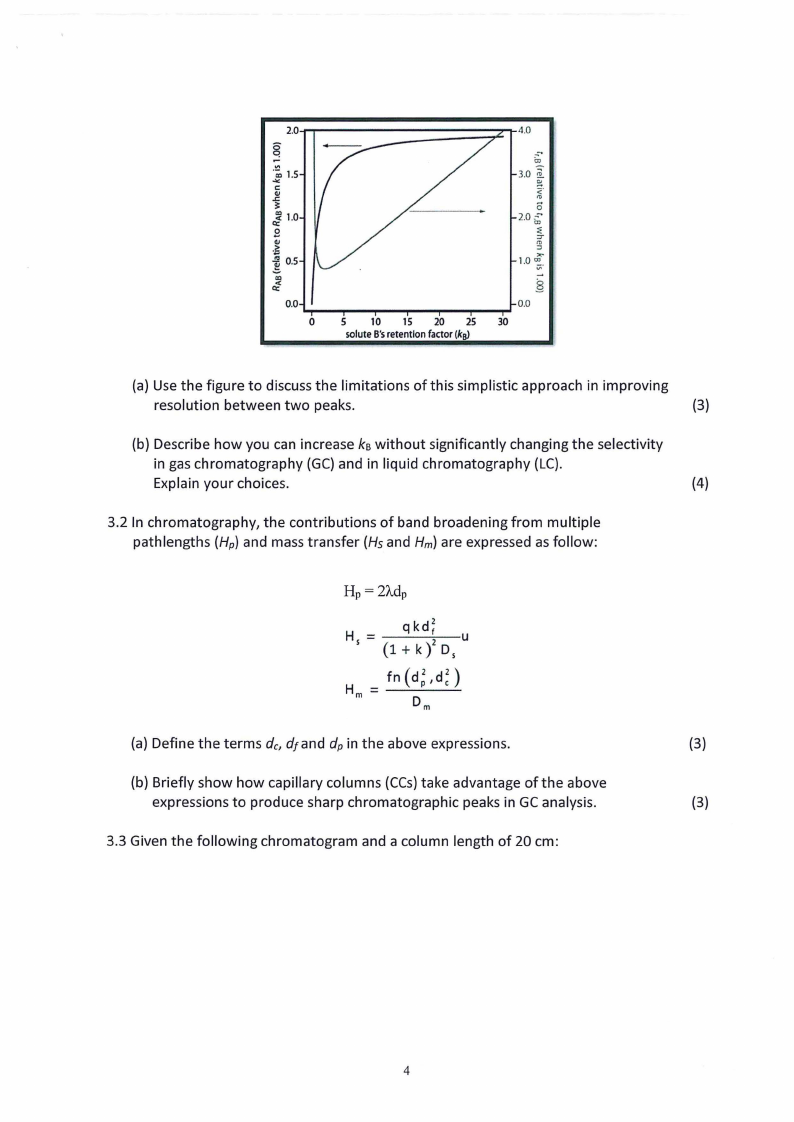
0.0
0
5 10 15 20 25
soluteB'sretentionfactor(ks)
3.0 i
,<...
0
2.0:;;;
:;
-::T
':,:"., ..
1.0 0., ;;·
0.0
(a) Use the figure to discuss the limitations ofthis simplistic approach in improving
resolution between two peaks.
(3)
(b) Describe how you can increase kBwithout significantly changing the selectivity
in gas chromatography (GC) and in liquid chromatography (LC).
Explain your choices.
(4)
3.2 In chromatography, the contributions of band broadening from multiple
pathlengths (Hp)and mass transfer (Hs and Hm)are expressed as follow:
(a) Define the terms de, dt and dp in the above expressions.
(3)
(b) Briefly show how capillary columns (CCs)take advantage ofthe above
expressions to produce sharp chromatographic peaks in GC analysis.
(3)
3.3 Given the following chromatogram and a column length of 20 cm:
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
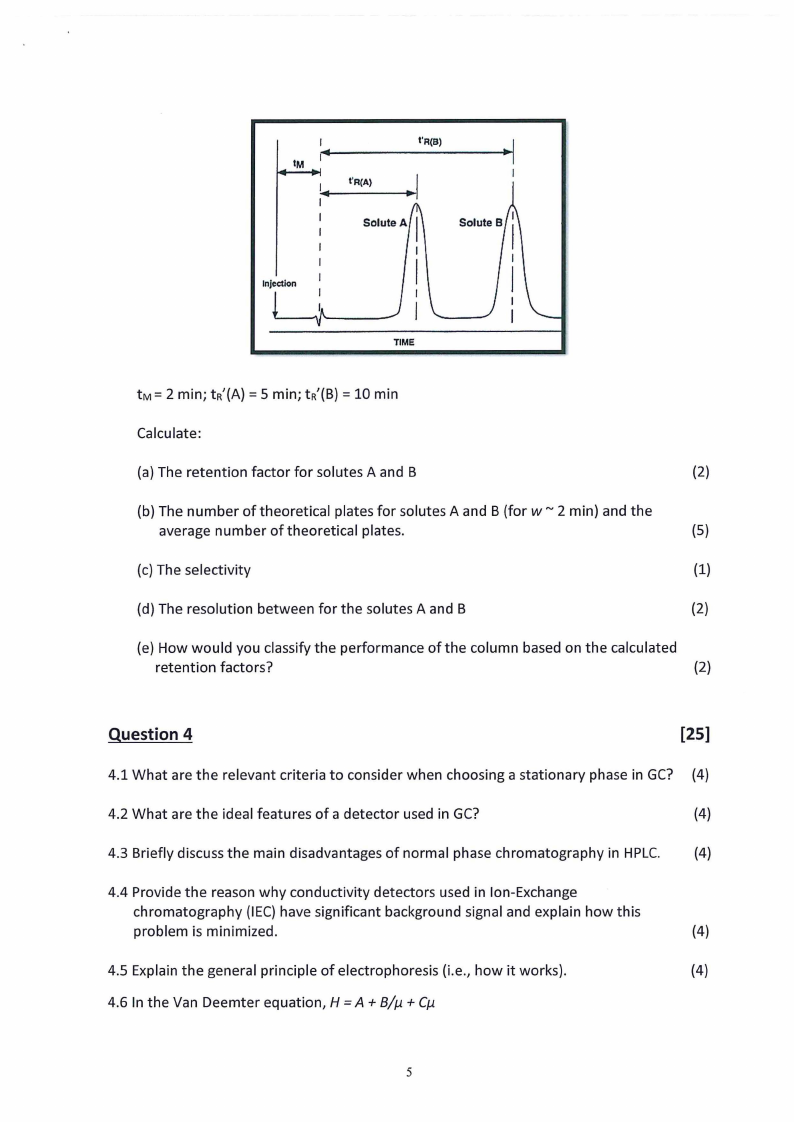
I
IM
1,.
I
t'R(B)
l'R(A)
Solute A
I
Injection
I
TIME
Calculate:
(a) The retention factor for solutes A and B
(2)
(b) The number of theoretical plates for solutes A and B (for w ~ 2 min) and the
average number of theoretical plates.
(5)
(c) The selectivity
(1)
(d) The resolution between for the solutes A and B
(2)
(e) How would you classify the performance of the column based on the calculated
retention factors?
(2)
Question 4
(25]
4.1 What are the relevant criteria to consider when choosing a stationary phase in GC? (4)
4.2 What are the ideal features of a detector used in GC?
(4)
4.3 Briefly discuss the main disadvantages of normal phase chromatography in HPLC. (4)
4.4 Provide the reason why conductivity detectors used in Ion-Exchange
chromatography (IEC)have significant background signal and explain how this
problem is minimized.
(4)
4.5 Explain the general principle of electrophoresis (i.e., how it works).
(4)
4.6 In the Van Deemter equation, H = A + B/µ + Cµ
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

(a) Which term(s) is (are) not applicable to capillary electrophoresis? Explain your
answer.
(3)
(b) What is the direct implication of the observation made in (a) in terms of column
efficiency?
(2)
END
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

Physical Constants
Gas constant
Boltzmann constant
Planck constant
Faraday constant
Avogadro constant
Speed of light in vacuum
Mole volume of an ideal gas
Elementary charge
Rest mass of electron
Rest mass of proton
Rest mass of neutron
Permitivity of vacuum
Gravitational acceleration
Conversion Factors
lW
1J
1 cal
1 eV
1 L atm
1 atm
1 bar
1L
1 Angstrom
1 micron (µ)
1 Poise
1 ppm
Selected Formulae
R
k
h
F
L or NA
c
Vm
e
me
mp
mn
Eo
g
= 8.315 J K-1 moI- 1
= 8.315 kPa dm 3 K-1 mo1-1
= 8.315 Pa m 3 K-1 mo1-1
= 8.206 x 10-2 Latm K-1 mo1-1
= 1.381 X 10-23 J K-1
= 6.626 x 10-34 J s-1
= 9.649 X 104 C mo1-1
= 6.022 x 1023 mo1-1
= 2.998 x 108 m s-1
= 22.41 L mo1-1 (at 1 atm and 273.15 K)
= 22.71 L mo1-1 (at 1 bar and 273.15 K)
= 1.602 x 10-19 C
= 9.109 x 10-31 kg
= 1.673 x 10-27 kg
= 1.675 x 10-27 kg
= 8.854 X 10-12 C2 J-1 m-1 (or F m-1)
= 9.807 m s-2
= 1 J s-1
= 0.2390 cal= 1 Nm= 1 V C
= 1 Pa m3 =1 kg m2 s-2
= 4.184 J
= 1.602 X 10-19 J
= 101.3 J
= 1.013 x 105 N m-2 = 1.013 x 105 Pa
= 760 mmHg
= 1 x 105 Pa
= 10-3 m 3 = 1 dm 3
= 1 x 10-10 m = 0.1 nm= 100 pm
= 10-6 m = 1 µm
= 0.1 Pas= 0.1 N sm-2
= 1 µg g-1 = 1 mg kg-1
= 1 mg L-1 (dilute aqueous solutions only)
7
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |

1-;{ k=
r - t r -t m __ t r_
;{
q=nF
LlG = -nFE
l=E/R
E = E°-RT/nF In ([Bjb/[A] 0)
E (for /SE): Ecell= K + 0.05916/z log[A]
= = E hv (or E he/Ji.)
A = -log T = log Po/P and A = Ebe
V cp =µ cpE
µ= q
cp frrrrir
8





