 |
IGD411S - INTRODUCTION TO GEOSPATIAL DATA - 2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE
TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF ENGINEERINGAND SPATIALSCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF ARCHITECURE AND SPATIAL SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF NATURAL RESOURCEMANAGEMENT (NATURE CONSERVATION),
BACHELOR OF GEOINFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, BACHELOR OF LAND ADMINISTRATION, BACHELOR OF
PROPERTY STUDIES HONOURS, BACHELOR OF REGIONAL AND RURAL DEVELOPMENT, BACHELOR OF
TOWN AND REGIONAL PLANNING, DIPLOMA IN PROPERTYSTUDIES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BNRS, 07BGEI,
07BLAM, 08BPRS, 07BRAR, 07BTAR, LEVEL: 4
06DPRS
COURSE:
INTRODUCTION TO
GEOSPATIAL DATA
COURSE CODE: IGD411S
SESSION: JULY 2022
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 2 HOURS
MARKS:
80
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/ SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MS. D. HUSSELMANN
MODERATOR:
MR E. NAOSEB
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. Answers to calculations must be rounded off to three decimal places,
excluding answers to co-ordinate conversions
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. Examination paper.
2. Examination script.
3. Calculators and other drawing equipment.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
Introduction to Geospatial Data
Question 1
IGD411S
State whether the following is True or False.
(10)
1.1. Lines of latitude run north to south and shows direction north and south.
1.2. A spatial point is defined by an exact location in space. It has no volume, area or length.
1.3. Geospatial data is special data that is referenced to the earth.
1.4. Maps are flat, but the surfaces they represent are curved.
1.5. Linear interpolation is used to determine the distance between two contour lines.
1.6. Your eyes can be considered as a remote sensor.
1.7. Aerial photographs are also generalised or symbolised as maps.
1.8. GPSstands for Geographical Positioning System
1.9. GPSworks anywhere in the world, 24 hours a day.
1.10. The lower the POOP,the more reliable the GPSposition.
[10]
Question 2
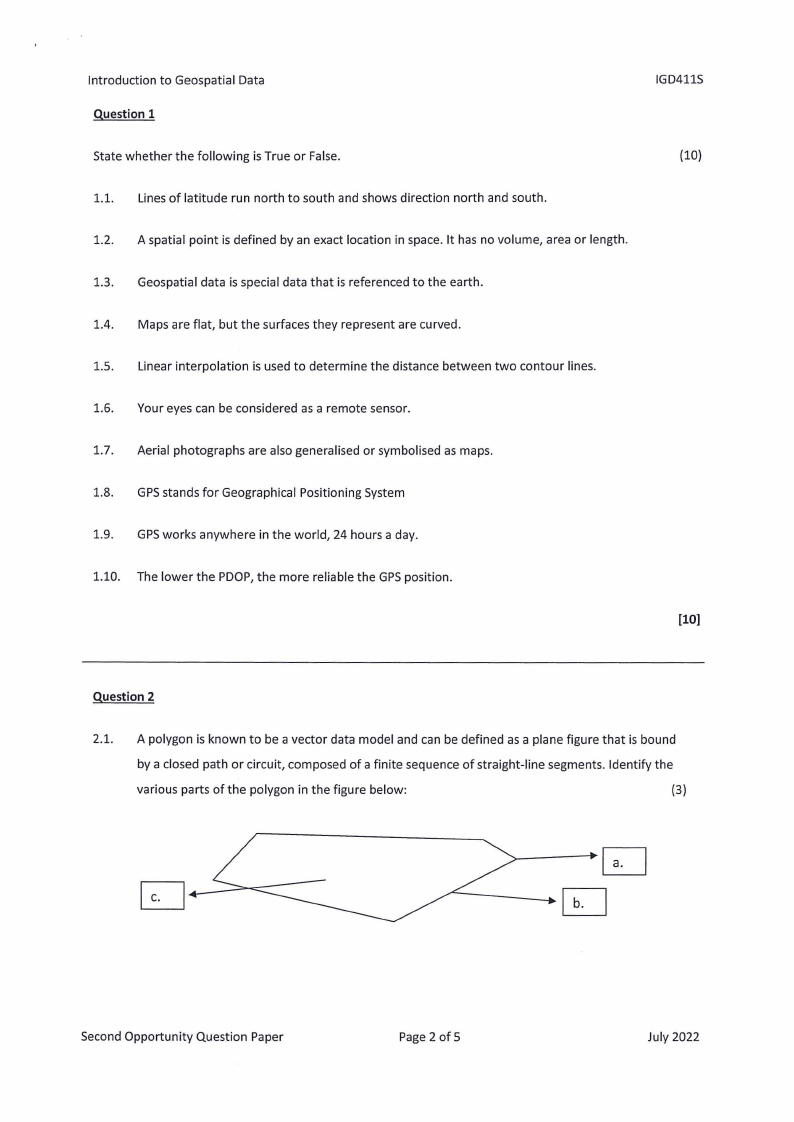
2.1. A polygon is known to be a vector data model and can be defined as a plane figure that is bound
by a closed path or circuit, composed of a finite sequence of straight-line segments. Identify the
various parts of the polygon in the figure below:
(3)
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page 2 of 5
July 2022
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Introduction to Geospatial Data
2.2. What type of data model is illustrated by picture (a) and picture (b)?
a.
b.
IGD411S
(2)
2.3. Differentiate between Meridians and Parallels.
2.4. Calculate the distance from 1T Eto 29° Eat 34.5608° S.
2.5. What is the result of referencing geodetic coordinates to the wrong datum?
Question 3
3.1. Calculate the spherical distance from A to C.
A
22.8765° S
16.8596° E
C
22.0356° S
14.2143° E
3.2. Convert 46°38'29" S to Decimal Degrees. Show your work.
3.3. Convert 78,1943° to Degrees Minutes and Seconds. Show your work.
Question 4
4.1 Why is the title of a map important?
4.2 What is a contour interval?
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page 3 of 5
(4)
(4)
(1)
(14)
(10)
(2)
(2)
(14)
(1)
(1)
July 2022
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Introduction to Geospatial Data
4.3 List the six activities that constitute the map generalisation process.
4.4 Given the following co-ordinates:
y
A
-7 809.68
B
-7 884.32
X
+60 475.25
+60 511.49
z
1665.77
1650.51
a. Calculate the slope in degrees from point A to B.
b. Convert your slope degrees to percentage.
IGD411S
(3)
(4)
(3)
[12]
Question 5
5.1 What is Aerial Photography?
(2)
5.2 Name two characteristics of aerial photographs.
(2)
5.3 List all the (a) advantages and (b) disadvantages of orthophotos.
(5)
5.4 Aerial photographs are useful for providing spatial information, but they usually contain geometric
distortions. Name three types of displacements that cause geometric distortion.
(3)
5.5 Calculate the size of the area covered by a photograph measuring 18 cm by 9 cm on a scale of
1:7000. Give your answer in hectares.
(6)
[18]
Question 6
6.1 Name and differentiate between two types of GPSpositioning modes. State which one is more
accurate right next to its name.
(5)
6.2 List the 4 types of dilution of precision (DOP). Write them out in full words and not abbreviations. (4)
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page4 of 5
July 2022
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Introduction to Geospatial Data
IGD411S
6.3 The number of satellites is tracked by two different receivers; receiver A and receiver B. Name the
receiver that will result in the most accurate position if receiver A tracks 4 satellites and receiver B
tracks 8 satellites.
(1)
6.4 What does SV stand for?
(1)
6.5 What is the minimum number of satellites required to compute a reliable GPSposition?
(1)
[12]
Second Opportunity Question Paper
Page 5 of 5
July 2022





