 |
AMB821S - ADVANCED MICROBIOLOGY - 1ST OPP - NOV 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BI A un IVE RS ITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, NATURAL RESOURCES AND APPLIED SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL AND APPLIED SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCE {Hon)
QUALIFICATION CODE:
LEVEL: 8
COURSE CODE: AMB821S
COURSE NAME: ADVANCED MICROBIOLOGY
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2022
TIME: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER{$)
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATIONS QUESTION PAPER
DR MUNYARADZI ZIVUKU
MODERATOR: PROF JANE MISIHAIRABGWI
Instructions
1. Answer all questions
2. Answer the questions in the booklet provided
3. Write clearly and neatly
4. All written work MUSTbe done in blue or black ink
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 3 PAGES
{INCLUDING THIS FRONT PAGE)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
QUESTION 1 (20)
1.1 Differentiate between continuous culture and batch culture.
(2)
1.2 Describe the significance of antibiotic susceptibility testing.
{3)
1.3 Following the breakdown of glucose to give pyruvate, pyruvate is further metabolised
to give various products. Briefly outline the fate of pyruvate in respiration.
{6)
1.4 Microorganisms are able to carry out fermentation depending on their metabolic
pathways. Briefly evaluate three different types of fermentation common in
microorganisms.
{9)
QUESTION 2 {20)
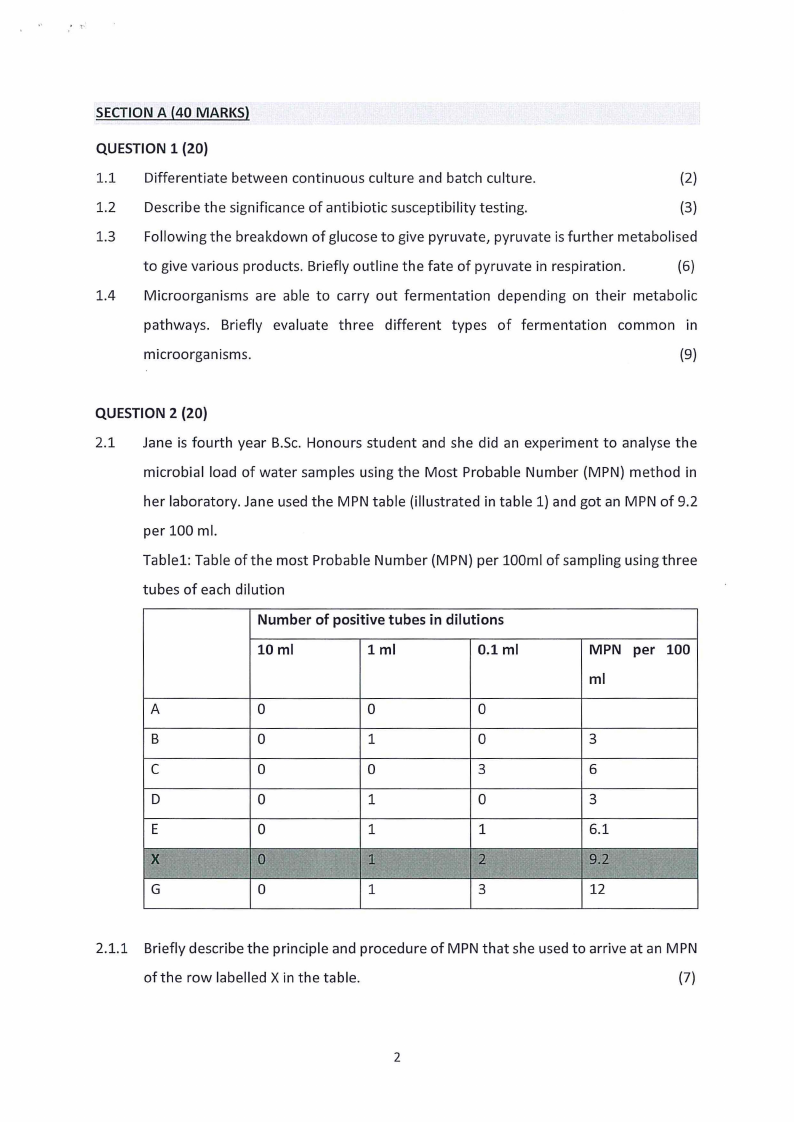
2.1 Jane is fourth year B.Sc. Honours student and she did an experiment to analyse the
microbial load of water samples using the Most Probable Number {MPN) method in
her laboratory. Jane used the MPN table (illustrated in table 1) and got an MPN of 9.2
per 100 ml.
Table 1: Table of the most Probable Number (MPN) per 100ml of sampling using three
tubes of each dilution
Number of positive tubes in dilutions
10ml
1ml
0.1 ml
MPN per 100
ml
A
0
0
0
B
0
1
0
3
C
0
0
3
6
D
0
1
0
3
E
0
1
1
6.1
X
0
1
--
2
--
9.2
..
-
-
G
0
1
3
12
2.1.1 Briefly describe the principle and procedure of MPN that she used to arrive at an MPN
of the row labelled X in the table.
(7)
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

2.2 Briefly describe how microorganisms can be used in the recovery of low grade
ores.
(7)
2.3 Briefly discuss the use of coliforms as diagnostic tools in food and water.
(7)
SECTION B (60 MARKS)
QUESTION 3 (20)
3.1 Discuss how infectious diseases such Ebola virus can be prevented
and controlled.
(5)
3.2 Discuss how protoplast fusion has been used to manipulate microorganisms
genetically for industrial use.
(5)
3.3 Outline the role of the human microbiome.
(10)
QUESTION 4 (20)
4.1 Testing for coliforms is sometimes accompanied by biochemical tests such as IMViC.
What does is the principle underlying the IMViC test in microorganisms?
{8)
4.2 Discuss the role of microorganisms in the production of hard cheese such as
Gouda.
{12)
QUESTION 5 (20)
5.1 Whatare the disadvantages of MPN method as a diagnostic tool in microbiological
samples.
(3)
5.2 Tabulate the differences between cell mediated and human mediated immunity. (7)
5.3 Briefly describe the changes in antibody concentrations following the initial dose of
Covid-19 jab and how that leads to conferment of long lasting immunity to an
individual.
{10)
ENDOF QUESTIONPAPER
3





