 |
MAP512S-MICROBIOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY - JAN 2020 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: O8BOHS
LEVEL: 5
COURSE CODE: MAP512S
COURSE NAME: MICROBIOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY
SESSION: JANUARY 2020
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/ SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S)
MS CARA MIA DUNAISKI
MODERATOR:
DR LARAI AKU-AKAI
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
1. CALCULATOR
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 6 PAGES (including this front page)
Page 1 of 6
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A
QUESTION 1
Select the correct answer. There is Only one correct answer.
1.1 The instrument used to sterilize our media:
A.
Incubator
B
Autoclave
Cc
Hot air oven
D
Heating block
1.2
A.
An intestinal parasite causes the
infecting about 1.2 billion people
most parasitic
worldwide:
infections
in
the
world,
Hookworm
B
Malaria parasite
C
Ascaris lumbricoides
D
Chlamydia parasite
1.3
In severe infections, typical
the causative organism?
rice
water
stools
are
passed
continuously.
What
is
A.
Salmonella enterica
B
Escherichia coli
C
Vibrio cholerae
D
Shigella flexneri
1.4
The first person that described
structures of moulds:
microorganisms,
by
demonstrating
the
fruiting
Francesco Redi
Robert Hooke
Zacharias Janssen
Anton Von Leeuwenhoek
5
Most eukaryotic cells reproduce by:
Budding
Sporulation
Binary fusion
None of the above
[45]
[10]
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
Page 2 of 6
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.6 — Bilhazia is caused by species of:
(1)
A.
Amoeba spp.
B
Taenia spp.
C
Schistosoma spp.
D
Plasmodium spp.
1.7. The domains in which thermophiles exist are:
(1)
A
Eubacteria
B
Eukarya
C
Archaea
D
Protista
1.8 The symbiotic relationship most observed in protists, for example, the species
(1)
Trypanosoma protozoa that can cause sleeping sickness:
A
Predation
B
Commensalism
C
Mutualism
D
Parasitism
1.9 The genus of organisms that can cause infection leading to respiratory
(1)
paralysis and ultimately death:
A
Campylobacter
B
Aspergillus
C
Clostridium
D
Staphylococcus
1.10 The process of sterilising milk using heat process is called?
(1)
A.
Heating
B
Radappertization
C
Tyndallisation
D
Pasteurization
QUESTION 2
[15]
Answer the following short questions.
2.1. Which Gram-bacteria are more sensitive to Penicillin?
(1)
2.2 Vessels for industrial fermentation are called bioreactors. Which factors are
(3)
they designed to closely monitor?
2.3. What are the functions of the cell membrane?
(3)
Page 3 of 6
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

2.4
Describe the difference between a bacteriostatic and bactericidal agent?
(2)
2.5 What is the mechanism of action of lysozyme?
(1)
2.6 Describe the method in which heat is used to control the growth of
(2)
microorganisms.
2.7.
Which active surveillance network is used to rapidly trace the course and
(1)
cause of infection in days rather than weeks?
2.8 Which stain is used as a counterstain in Acid-fast staining?
(1)
2.9 Botulism is caused by which bacterial genus?
QUESTION 3
[20]
Define the following terms:
3.1 Zoonosis
3.2 Primary production
3.3 Virulence
3.4 Obligate parasite
3.5 Autotroph
3.6 Biofilms
3.7 Premunition
3.8 Life cycle
3.9 Bacteriocins
3.10 Bioaugmentation
Page 4 of 6
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

SECTION B
[30]
QUESTION 4
[15]
4.1
Give an account of each of Robert Koch’s contribution to the development of
microbiology.
(5)
4.2 Outline Koch’s postulates.
(4)
4.3 Discuss the Germ Theory of Diseases.
(4)
4.4
Name other scientists whose work disputed the Theory of Spontaneous
Generation.
(2)
QUESTION 5
[15]
5.1 Describe the importance of biofilms in human health.
(3)
5.2
Define the
that exist.
term
symbiosis
and
highlight
the
different
symbiotic
relationships
(8)
5.3. Give two examples of normal microbiota benefiting a host.
(4)
SECTION C
[25]
QUESTION 6
[25]
6.1
Enumerate the conditions necessary for successful endemic parasitism.
(4)
6.2
One of the effects of
substances. Describe
parasites on hosts are to deprive the host
how hookworm goes about this action.
of
essential
(2)
6.3
Below is the life cycle of Toxoplasma
relating to the parasite.
species.
Answer
the
questions
below
Page 5 of 6
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
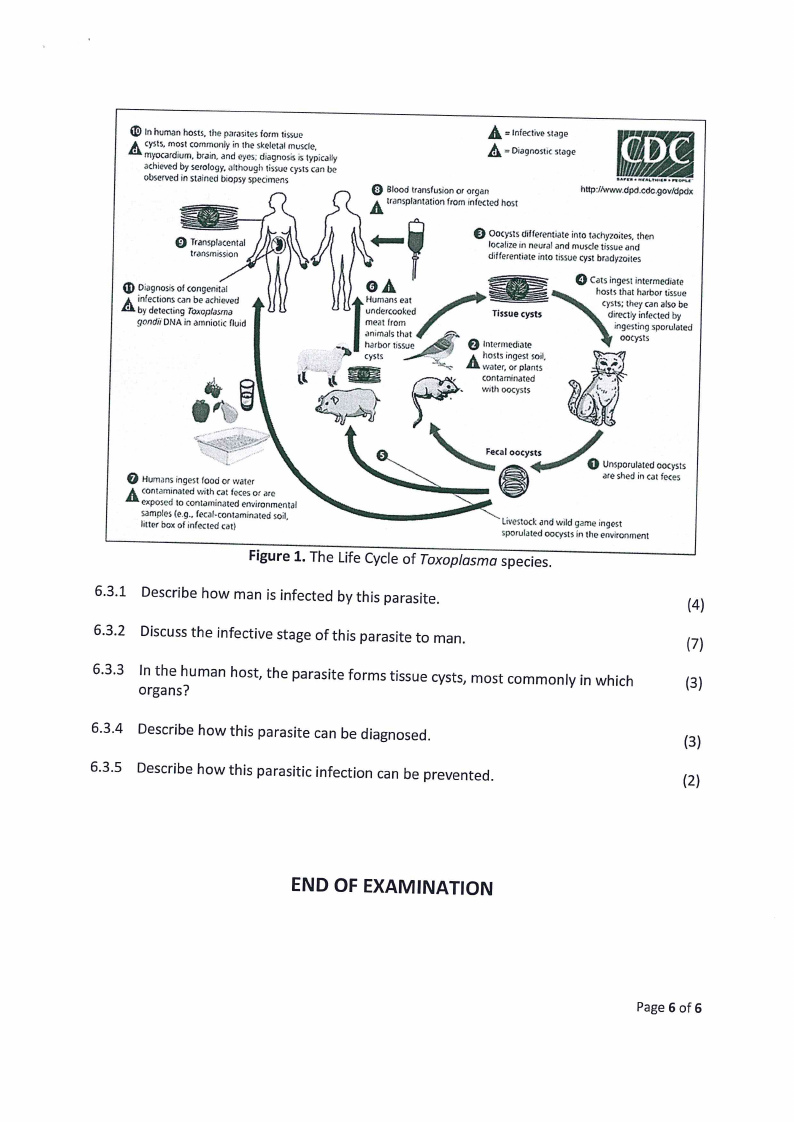
© In human hosts, the parasites form tissue
A cysts, most commonly in the skeletal muscle,
myocardium, brain, and eyes; diagnosis is typically
achieved by serology, although tissue cysts can be
observed in stained biopsy specimens
A infective stage
A = Diagnostic stage
© Blood transfusion or organ
A transplantation from infected host
hitp:/iwwaw.dpd.cde.govidpdx
© Transpiacental
transmission
Avneay eeeen’ @® Diagnosis of congenitat
gondit DNA in amniotic fluid
(oma
@A
uHnudmearncsookeaetd
meat from
a
ahanribmoarls
that
tissue
» cysts
© Oocysts differentiate into tachyzoites, then
localize in neural and muscle tissue and
differentiate into tissue cyst bradyzoites
=
— Tissue yt
Lay
?,
=
he
Q
/
intermediate —
Aw ingest soil,
water, or plants
contaminated
with oocysts
O Cats ingest intermediate
hosts that harbor tissue
dee tect cysts; they can also be
ingesting sporulated
ootysts
@ Humans ingest food or water
A contaminated with cat feces or are
exposed to contaminated environmental
samples (e.g., fecal-contaminated soil,
litter box of infected cat)
Fecal oocysts
@
@ Unsporulated oocysts
are shed in cat feces
Livestock and wild game ingest
sporulated oocysts in the environment
Figure 1. The Life Cycle of Toxoplasma species.
6.3.1 Describe how man is infected by this parasite.
(4)
6.3.2 Discuss the infective stage of this parasite to man.
(7)
6.3.3 In the human host, the Parasite forms tissue cysts, most commonly in which
organs?
(3)
6.3.4 Describe how this parasite can be diagnosed.
6.3.5 Describe how this parasitic infection can be prevented.
(2)
END OF EXAMINATION
Page 6 of 6





