 |
SSA520S - SOIL SCIENCE - 1ST OPP - NOV 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA UnlVERS ITV
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,NATURALRESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
SCHOOLOF AGRICULTUREAND NATURALRESOURCESSCIENCES
DEPARTMENTOF AGRICULTURALSCIENCESAND AGRIBUSINESS
QUALIFICATIONS: BACHELOROF SCIENCEIN AGRICULTURE
BACHELOROF SCIENCEIN HORTICULTURE
QUALIFICATIONSCODE: 07BAGA LEVEL:7
07BHOR
COURSECODE:SSA520S
COURSENAME: SOIL SCIENCE
DATE: NOVEMBER 2024
PAPER: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
FIRSTOPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
DR. VENAUNE HEPUTE
DR. TENDAI NZUMA
INSTRUCTIONS
1.
Answer all the questions.
2.
Write neatly and clearly.
3.
Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
4.
All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink.
5.
No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Calculator
2. Examination paper
3. Examination script
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 5 PAGES
(ExcludingThis Front Page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

[10 MARKS]
QUESTION 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate answer or
phrase from the given possibilities. Fill in the appropriate letter next to the number of the
correct statement/phrase on your ANSWERSHEET.
[10 marks]
I.
1.1.
Soil formation is the result of interaction between the below soil forming factors,
namely.
a. Parent material, Climate, Tractors, Time and Organisms
b. Parent material, Climate, Topography, Wind and Organisms
c. Parent material, Climate, Topography, Time and Organisms
d. People, Climate, Topography, Wind and Organisms
1.2.
The following are two examples of soil physical properties.
a. Soil pH and Cation Exchange Capacity
b. Plants and humans
c. Soil Texture and Cation Exchange Capacity
d. Soil texture and soil structure
1.3.
a.
b.
c.
d.
The following are two examples of soil chemical properties.
Plants and humans
Soil pH and Cation Exchange Capacity
Soil texture and soil structure
Soil texture and Cation Exchange Capacity
1.4.
The following are two examples of soil biological properties.
a. Soil pH and Cation Exchange Capacity
b. Plants and microorganisms
c. Soil texture and soil structure
d. Soil texture and Cation Exchange Capacity
1.5.
Restoration of eroded agricultural land is achieved through several agronomic and
biological techniques such as:
a. Cover crops
b. Monocropping
c. Maximum tillage
d. None of the above
1.6.
Soil sample that is 60% clay, 25% silt, and 15% sand have which soil texture?;
a. Silty clay
b. Sandy clay
c. Clay
d. Silt
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1. 7.
The structure nutrients include;
a) Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium
b) Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
c) Magnesium, Nitrogen and Sulphur
d) Nitrogen, Oxygen, Calcium
1.8.
The key nutrient necessary for plant leaves and vegetative development
a) Nitrogen
b) Phosphorous
c) Potassium
d) Iron
1.9.
USLEstand for;
a) Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation
b) Universal Soil Loss Equation
c) Run-off Universal Soil Loss Equation
d) Ready Universal Soil Loss Erosion
1.10.
Soil organic matter occupy how many percent(%) of total soil volume composition
fraction.
a) 25%
b) 5%
c) 25%
d) 30%
QUESTION2: TRUE/FALSE9,UESTIONS
[10 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements and select whether the statement is true or false. Write the word 'True' or
'False' next to the corresponding number on your ANSWERSHEET.
[10marks]
2.
2.1 Solum is known as the upper regolith
2.2 In general, the greater the biodiversity of soil microbes, the better is likely to be for soil organic
matter decomposition and nutrients recycling into the soil.
2.3 Pedogenesis is the soil formation processes
2.4 Soil pH determines crop selection and influences the decomposition of organic matter and
nutrients availability in the soil.
2.5 Wind erosion is the loss of topsoil caused by water run-off.
2.6 Ideal healthy soil composition comprised of 45% minerals, 50% air, 25% water and 15% organic
matter.
2.7 Class VIII (8) soil capability classification has slight limitation and requires less conservation,
sustainable practices.
2.8 Class II (2) soils have moderate limitations that reduce the choice of plants or require only
moderate conservation or sustainable practices.
2.9 Arenosols is the most common popular soil order group in Namibia covering over 53% of
Namibian land space.
2.10 Clay soil has larger soil particle size of bigger than 2 mm.
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Please answer ALL the questions in this section.
QUESTION 3: SOIL NUTRIENTS
3.
[20 MARKS]
3.1.
List and explicitly discuss each of the secondary macronutrients, their responsible
functions on crops growth and development.
[9 marks]
3.2.
Briefly describe the deficiency symptoms of Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) and Potassium
(K) on maize plant using leaf deficiency analysis method.
[6 marks]
3.3.
List (5) micronutrients and discuss the importance of micronutrients on crops growth
and development.
{5 marks]
QUESTION4: SOILTEXTURETRIANGLECLASSIFICATIONSYSTEM.
[15 MARKS]
4.
Study the Soil Texture Triangle attached, labelled as Attachment A and answer the following
questions.
4.1.
Provide the name of the missing soil texture marked with letter A, B, C, D and Eon the
Soil Texture Triangle. Write only the correct answer next to the letter on YOURANSWERSHEET;
{5 marks]
4.2.
A soil sample was collected from Rietfontein field B. The soil-water mixture in the jar
has settled after 48 hours and the following soil layer height measurements were recorded;
9.9cm clay, 3cm silt, 3cm sand. Using Soil Texture Triangle, classify the soil texture of this soil
sample, illustrate all calculation steps in YOURANSWERSHEETand shows the line on the Soil
Texture Triangle (Attachment A).
{10 marks]
-
QUESTION5: SOILPROPERTIESAND SOILWATER.
[30 MARKS]
5.
5.1.
Name and briefly discuss three (3) main soil properties groups and the sub-factor
components of each of the main three 3 groups in relation to crop performance.
{15 marks]
5.2.
Briefly discuss the following soil water terminologies in relation to soil water availability
for plant uptake;
5.2.1.
5.2.2.
5.2.3.
5.2.4.
5.2.5.
5.2.6.
Permanent wilting point
Field capacity
Saturation
Available water content
Adhesion
Importance of Soil Organic Matter on soil properties
{2 Marks]
[2 Marks]
{2 Marks]
{2 Marks]
{2 Marks]
[5 Marks]
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6: SOIL FORMATION AND FUNCTIONS
6.
Explicitly discuss the following;
6.1.
Soil functions and ecosystem services
6.2.
Soil mineralogy and any 3 different soil mineral rocks
6.3.
Soil weathering processes
END OF QUESTION PAPER
[~5 MARKS)
{5]
{5}
[5]
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
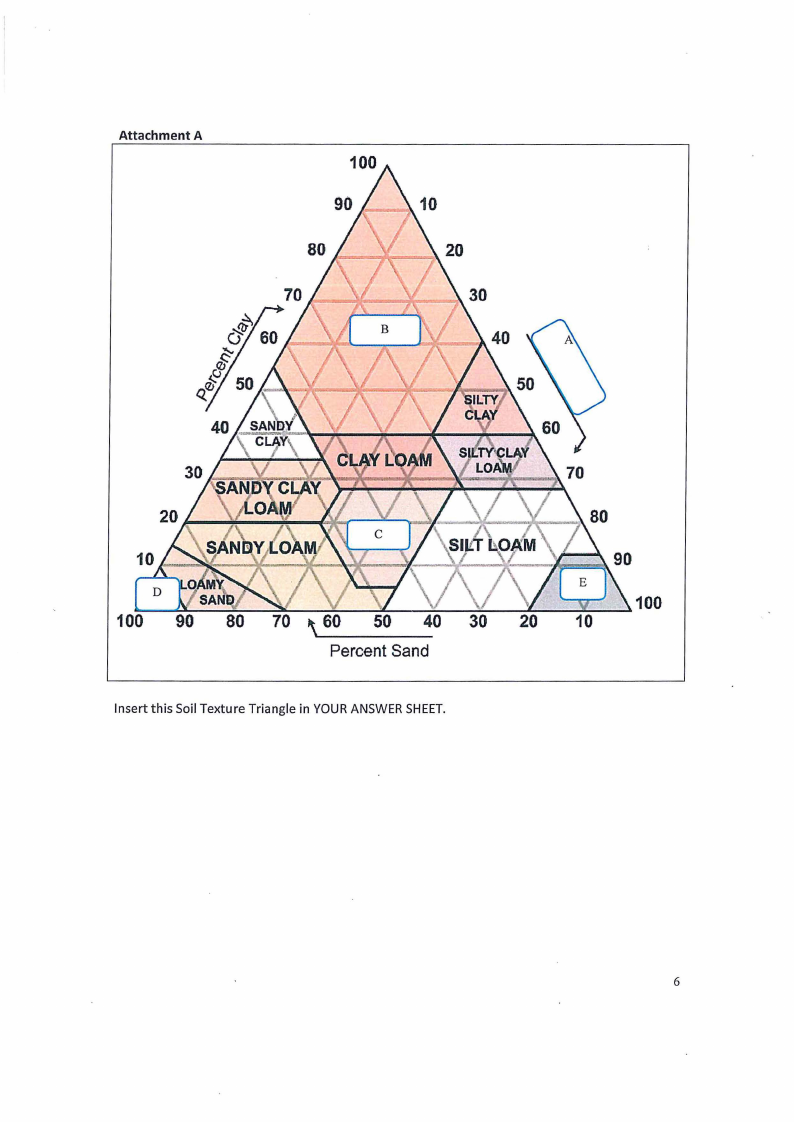
Attachment A
10
100 90 80 70 \\ 60
100
40 30 20 10
Percent Sand
Insert this Soil Texture Triangle in YOUR ANSWER SHEET.
6





