 |
PNM710S - Pyrometallurgy on Non-Ferrous Metals- 2nd OPP - JUN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

n Am I BI A u n IVER s ITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF ENGINEERINGAND SPATIALSCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL, MINING AND PROCESS ENGINEERING
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING IN METALLURGY
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMET
LEVEL: 8
COURSE CODE: PNM710S
COURSE NAME: PYROMETALLURGY OF NON-
FERROUS METALS
SESSION: JUNE 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S)
SUPPLEMENTARYQUESTION PAPER
Prof. Godfrey Dzinomwa
MODERATOR:
Prof. Sofya Mitropolskaya
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all questions.
2. Read all the questions carefully before answering.
3. Marks for each questions are indicated at the end of each question.
4. Please ensure that your writing is legible, neat and presentable.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examination paper.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Question 1
(a) Explain the properties required for an effective furnace refractory (5 marks)
(c) An oil-fired furnace is used to reheat metal 'x' stock from ambient to the working
temperature before further treatment. Given the data below,
0
Operating temperature: 1350 C
0
Exit flue gas temperature after preheater: 750 C
0
Ambient temperature: 40 C
Specific gravity of fuel oil: 0.89
Average fuel oil consumption: 400 liters/ hr= 400 x 0.89 =356 kg/hr
Calorific value of oil 10000 kCal/kg
Weight of stock: 6000 kg/hr
0
Specific heat of billet: 0.12 kCal/kg/ C
(Hint: Heat efficiency=
-------------H-e-at output (in billet stock)
xlOO )
Heat input (from Fuel Oil used to reheat the stock)
Calculate
(i) the heat content of metal 'x' as it comes out of the furnace (5 marks)
(ii) the heat input into the furnace (5 marks)
(iii)the efficiency of the furnace (5 marks)
(b) Ideally, all heat added to the furnaces for smelting or other heating purposes should be
used to heat the load or stock. In practice, however, a lot of heat is lost in several ways,
resulting in typical thermal efficiencies below 50%. Discuss five (5) ways by which heat
losses occur in the furnace (5 marks).
Question 2
1. Given the following Ellingham diagram below,
(i) Explain the significance of Ellingham diagrams in Pyrometallurgy (5 marks).
(ii) What is the free energy change at a temperature of 800°C for the reaction
Ni(s) + O2(g, 1 atm) = NiO(s) (5 marks)
(iii) Determine the Oxygen pressure in equilibrium with Ni and NiO at the temperature of
800°C (5 marks).
(iii) Explain in terms of the C/CO line in the Ellingham diagram why metals such as Al were
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
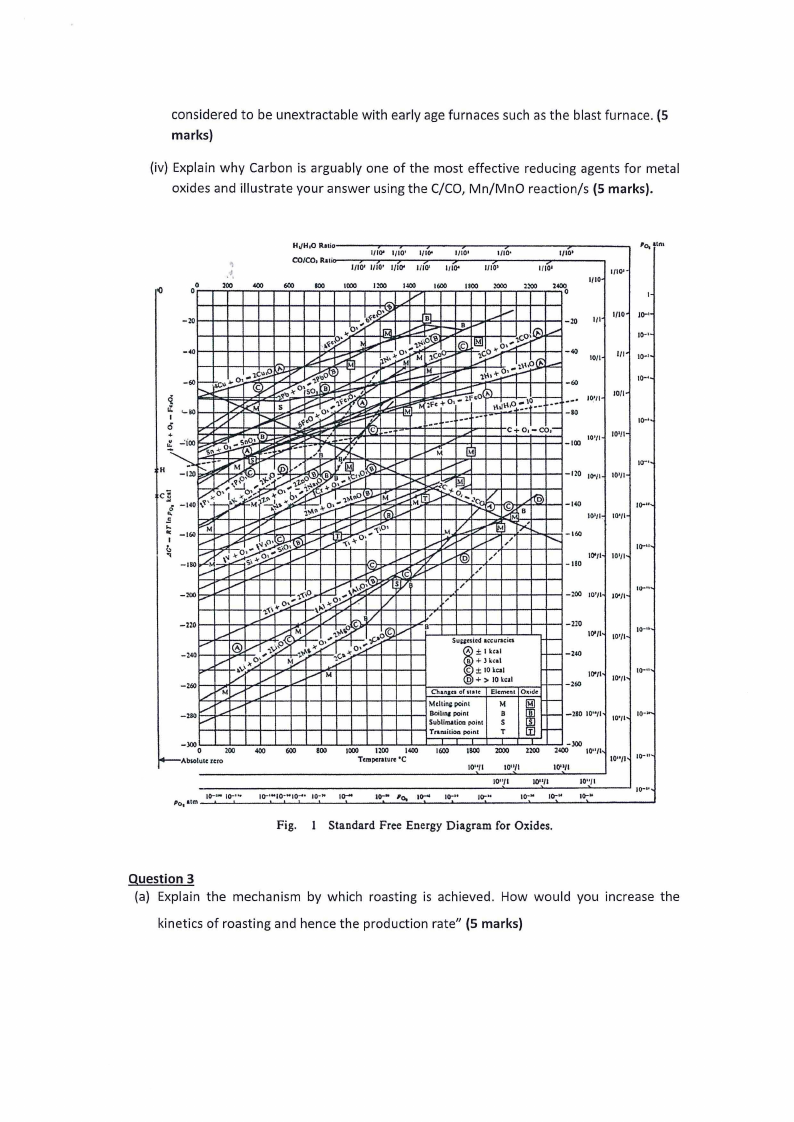
considered to be unextractable with early age furnaces such as the blast furnace. (5
marks)
(iv) Explain why Carbon is arguably one of the most effective reducing agents for metal
oxides and illustrate your answer using the C/CO, Mn/MnO reaction/s (5 marks).
.,,
lOO 400
HJH,O R11i
CO/COJRlli
1/10' 1/10'
J/10' 1110• 1/10'
1/10'
J/101
1110•
1/10'
1/10·
1/10'
1110•
600
IOO 1000 l:!00 1-IOO 1600 IIOO lOOO l!OO
1/101
1/10
-20
1/1 1/10 JO-•
10-•
-40
10/1 1/1 10·1
-ro
-·· 10,1,1 10/1
-80
10-•
101/I
-100
10•11
10-•
120 10'/I I0'/1
-"o
10--"
10'/I 10•11
,-....-.1.60
10-''
10'/I 10'/I
-110
tu-••
-200 JO'JI J0'/1
-2soV- V
V
l--4--1--4-1--4--1--4-l--4--1--4-l--+--+--lrransi1ioa.
M
Boihn, point
8
Sublimationpoinr s
point
T
-JOO'-_._ ......__._._...__.__._._...__.__._._..._
......~-'--~~-----...,.._
0
200 400
600
100 1000 1200 I400 1600 1800 2000
...,_Abs.olu1c uro
Tenipcnturc •c
Po, atm _.,__.._ __
_..___.._.,___.._
_ __,._ __ 10.-_•__,'l-o-_...._ 10'"4_' _J_0_-.0__
1011/l
1..0..-_• ___
-220
10'/I
10'/I
10-u
,-- -240
,...._
10'/I 10'/I 10-"
-260
I@ ---
-210 10"/I
10'11 10-
2200
-lOO
2400
1011/1
10'' /I
10"/I
10-11
10''/I
10"/I
10·"
10-._•_...__1~0----"-- 10-•
Fig.
Standard Free Energy Diagram for Oxides.
Question 3
(a) Explain the mechanism by which roasting is achieved. How would you increase the
kinetics of roasting and hence the production rate" (5 marks)
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

(b) In one roasting unit, 2000 kg of an ore concentrate of the composition given
below is roasted using excess air.
Ni3S2
FeS2
SiO2
H2O
25%
37%
30%
8%
The roasting unit is heated by oil of composition 85% C and 15% H, the amount of oil is
6.5% of the weight of the ore.
The gases from combustion and roasting mix together and are carried through as flue
gases. Sis converted to SO2. The roasted product consists of NiO, Fe2O3and SiO2and
the roasting reactions are given as;
Ni3S2+ 7/202 = 3NiO + 2SO2
2FeS2+ 11/202 = Fe2O3+ 4SO2
Calculate:
a) Weight of roasted product (10 marks)
b) Volume of the fuel oil used given that its density is 0.89 g/cm 3(5 marks)
c) Volume of SO2in m3 (5 marks)
{Note: Atomic weights are Ni= 59, Fe= 56, S =32, 0 =16, H =1}
Question 4
(a) Discuss the factors that you would consider in order to set up an Aluminium smelter in a
given location. What measures could be taken for Namibia to be a favourable destination
for such an investment (5 marks).
(b) As Group Metallurgist of Smelters, you find that the electrostatic precipitator and the rest
of the off-gas treatment plant of Smelter D (Ni-S) has not been operating for a month and
the Smelter D Manager seems to be accepting the position, mainly because of reduced
electricity bill due to the offline units. Explain to the Manager the disadvantages posed to
the Company by this situation (5 marks)
(c) Coal amounting to 2500kg is to be used to dry some mineral concentrate. The
composition by weight of the coal is given as;
C- 85%
H-5%
N-2%
S-3%
0-5%
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Using stoichiometric balances, calculate the volume of air required for complete
combustion of the coal to produce flue gases (mixture of 502, CO2, H20 and N2)
according to the reactions below (10 marks);
C + 02 = CO2
H2 + ½02 = H20
5 + 02 = 502
(i) If 5% excess air is blown, what is the total volume of air blown? (5 marks)
----------------------------- ---End--------------------------------------





