 |
ATE711S- ADVANCED TRANSPORT ECONOMICS- 1ST OPP- JUNE 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF MARKETING, LOGISTICS AND SPORT MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF TRANSPORT MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BTRA
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: ATE711S
COURSE NAME: ADVANCED TRANSPORT ECONOMICS
SESSION: JUNE 2024
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
Ms. Hilma Nuuyandja
MODERATOR Ms Tunomukumo Thikusho
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF ,2.PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
Multiple choice questions
[2x10 Marks]
1.
What factor does the concept of "price elasticity of demand" in transportation economics
primarily measure?
a) The extent to which transportation companies adjust prices in response to changes in
demand.
b) The sensitivity of demand for transportation services to changes in price.
c) The impact of government regulations on transportation pricing strategies.
d) The variability of transportation demand over time.
2.
Which of the following is an example of a "strategic consideration" when pricing
transportation services?
a) Setting prices based on short-term costs to maximise immediate profit.
b) Adjusting prices dynamically to reflect changes in market demand.
c) Offering discounts to loyal customers to increase brand loyalty.
d) Implementing price discrimination to capture surplus consumer value.
3.
Which of the following is NOT an example of an external cost of transportation?
a) Traffic congestion.
b) Vehicle emissions.
c) Vehicle maintenance costs.
d) Noise pollution.
4.
Road pricing aims to:
a) Minimise profit for transportation companies.
b) Maximise social benefits.
c) Increase environmental regulations.
d) Decrease competition in the transportation sector.
5.
Which of the following is an example of an internal cost of transportation?
a) Traffic congestion.
b) Vehicle emissions.
c) Fuel expenses.
d) Noise pollution.
6.
Deregulation in the transportation sector often leads to:
a) Increased competition.
b) Higher prices for consumers.
c) Reduced safety standards.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

d) More government intervention.
7.
Accessibility in transportation refers to:
a) The ease of reaching transportation hubs.
b) The cost of transportation services.
c) The speed of transportation vehicles.
d) The quality of transportation infrastructure.
8.
Which of the following is an example of a vertical equity measure to improve road
pricing?
a) Implementing toll discounts for frequent users.
b) Charging higher tolls during peak hours.
c) Providing subsidies to low-income drivers.
d) Introducing congestion charges in city centres.
9.
Road pricing impacts on equity primarily address issues related to:
a) The environmental impact of transportation.
b) The distribution of costs and benefits among different groups of road users.
c) The efficiency of transportation networks.
d) The safety of road infrastructure.
10. Accessibility in transport economics is primarily concerned with:
a) The physical condition of transportation infrastructure
b) The efficiency of transportation systems in moving goods
c) The ease of reaching desired destinations or services
d) The cost of operating transportation networks
Sub-total: 20 Marks
QUESTION 2
True or False questions:
[2x10 Marks]
1. One way to address negative externalities in transport is to impose a tax or fee on the users
of the transport system, equal to the external cost they impose on others.
2. Maximising social benefits is often the primary objective of optimally pricing transportation
services.
3. Variable costs refer to the costs that remain unchanged as the movement and level of
traffic change.
4. Roadway pricing aims to manage congestion by offering discounts during peak hours.
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
5. Economic impact analyses of transportation investments primarily focus on financial
returns.
6. Roadway pricing is primarily aimed at generating additional revenue for transportation
infrastructure.
7. Measures to improve horizontal equity in road pricing aim to ensure fairness in the
distribution of transportation costs among users.
8. How different people value their travel time includes the socio-economic status of an
individual.
9. A congestion cost arises when an additional vehicle reduces the speed of the other vehicles
of the flow and hence increases their travel time.
10. Transportation demand refers to the desire and ability of individuals and firms to move
goods and people.
Sub-total: 20 Marks
QUESTION 3
3.1 Why is road congestion seen as an external cost/negative externality in transport?
(10 marks)
3.2 Analyse the effectiveness of road pricing in reducing traffic congestion and improving traffic
flow in urban areas.
(10 marks)
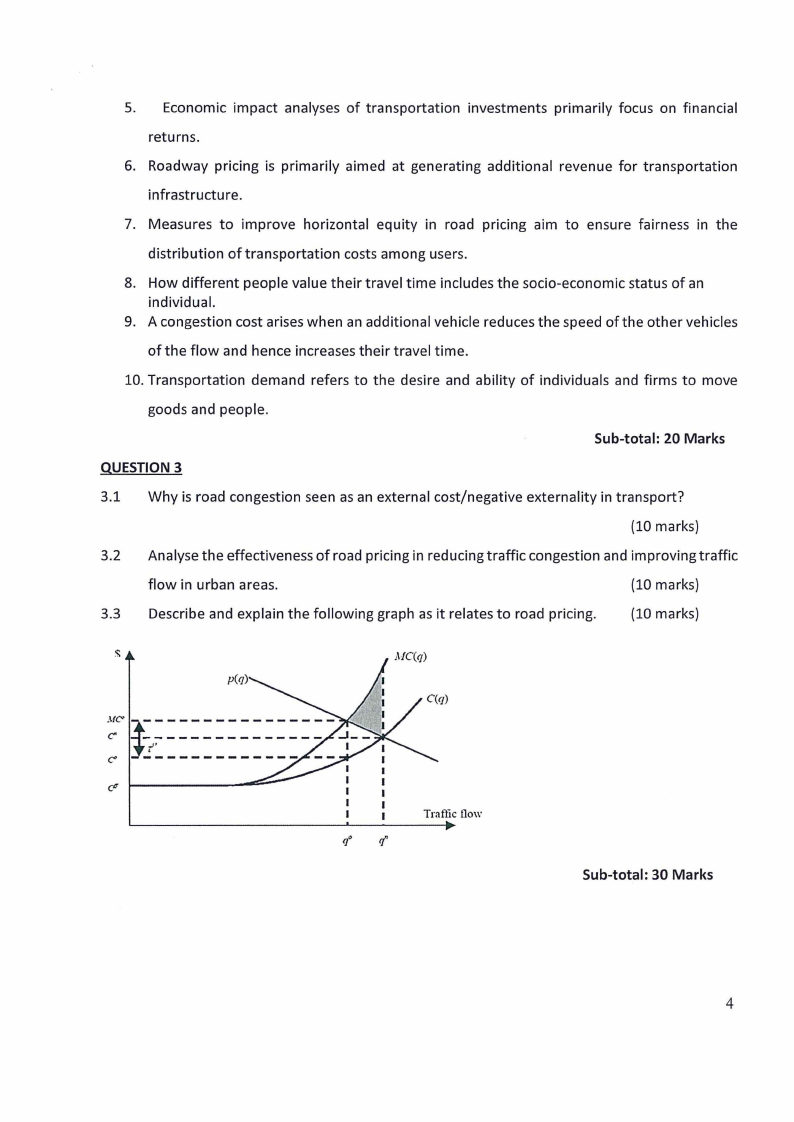
3.3 Describe and explain the following graph as it relates to road pricing.
(10 marks)
p(q)
.\\IC' 1---------
C"
--r--'-' -----
C"
----------
c6
'I
I
I
tf
Traffic !low
Sub-total: 30 Marks
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 4
4.1 Discuss the economic benefits of transportation infrastructure development in Namibia,
and explore how transportation investments contribute to enhancing Namibia's
competitiveness and economic resilience in the global market.
(10 marks)
4.2 Evaluate the effects of deregulation on competition and consumer welfare in the transport
industry.
(10 marks)
4.3 Discuss how transportation influences location choice for businesses and residents.
(10 marks)
Sub-total: 30 Marks
Grand Total: 100 Marks
5





