 |
GES512S - GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS 1 - 1ST OPP - NOV 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA un1VERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF ENGINEERINGAND THE BUILTENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENT OF LAND AND SPATIALSCIENCESS
QUALIFICATION:
DIPLOMA IN GEOMATICS, BACHELOR OF GEOMATICS, BACHELOR OF GEOINFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY, DIPLOMA IN LAND ADMINISTRATION, BACHELOR OF LAND ADMINISTRATION,
BACHELOR OF TOWN AND REGIONAL PLANNING, BACHELOR OF PROPERTY STUDIES, DIPLOMA IN
PROPERTY STUDIES, BACHELOR OF REGIONAL & RURAL DEVELOPMENT, BACHELOR OF NATURAL
RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION CODE:
06DGEO, 06DIPS, 06DPRS,
07BLAM, 07BNRS, 07BORR,
07BURP,08BOPS,08BPRS
COURSECODE: GES512S
07BGEI, 07BGEO
07BRAR, 07BTAR
LEVEL:5
COURSENAME: GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION SYSTEMS 1
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2024
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER
Ms Ivonne Makando
MODERATOR:
Mr Erich Naoseb
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF (5) PAGES
(Excluding this front page)
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Write clearly and neatly
2. Answer ALLthe questions.
3. Number the answers clearly.
1. Examination paper.
2. Examination script.
3. Calculator, ruler, pencils, eraser
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Geographic Information Systems 1
Question 1 State if the following statements are True or False.
GES512S
1.1. To locate spatial features on the Earth's surface, we can use either a geographic or a projected
coordinate system.
(1)
1.2. A Map projection is made up of a class and aspect.
(1)
1.3. lri the location selection method, the features of the layer being selected are not compared
spatially with the features of the second layer to see which ones meet the criteria, and features
meeting the criteria are selected.
(1)
1.4. The prime meridian and the equator serve as the baselines of the geographic coordinate system. (1)
1.5. A GIS operation that combines the geometries and attributes of the input layers to create the
output is known as erase.
(1)
1.6. Data processing is not regarded as one of the functions of an Information Systems.
(1)
1.7. The context-diagram is used to isolate the data objects and to define the relationship between
(1)
them.
1.8. A phenomenon that populates the study area is known as a geographic object.
(1)
1.9. In a raster data model, the cell size does not affect the spatial resolution.
(1)
1.10. Geospatial data describe both the locations and characteristics of spatial features.
(1)
[10]
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page 2 of 6
November 2024
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Geographic Information Systems 1
Question 2
GES512S
2.1 Define the following terms and provide one example of each:
a) Scale
(2)
b) A geographic information system (GIS)
(2)
c) Buffer
(2)
d) A datum
(2)
e) Geographical Features
(2)
2.2. Explain hardware and people as components of GIS.
(4)
2.3. Give one (1) example each of geographic features that can be represented by a Point, Line and
Polygon·on a map.
(3)
2.4. The library building of the Namibia University of Science and Technology (NUST) can be
considered a geographic phenomenon. Explain why it can be considered as such.
(3)
2.5. Explain how the vector data model differs from the raster data model in representing spatial
features and provide one suitable example of what each can represent.
(4)
2.6. Describe the three types of map projections by the projection or developable surface.
(6)
2.7. Briefly explain how a UTM zone is defined in terms of its central meridian, standard meridian,
and scale factor.
(5)
2.8. Define buffering and provide an application example.
(2)
2.9. Suppose you need a map showing 4G LTEcoverage in Namibia. You have downloaded a shapefile
from the Digital Namibia: Namibia-NSA website that shows 4G LTEcoverage in every region in
Namibia. What kind of operation will you use on the 4G LTEcoverage layer so that you can get
only the region you need? Motivate your answer.
(2)
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page 3 of 6
November 2024
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Geographic Information Systems 1
GES512S
[39)
Question 3
3.1. There are many ways to classify the analytical functions of a GIS, describe what you can achieve
using the below functions with clear examples:
a) Classification
(2)
b) Retrieval functions
(2)
c) Measurement
(2)
3.2. Name four methods of vector data creation.
(4)
3.3. Write a valid SQLexpression to select "Cities" with people between 1000 and 10,000
using a field called POP2000 from Citizens layer.
(3)
3.4. Identify and explain the two labels in Figure1.
(4)
A.
8.
A.__ _
Figure 1
3.5. Explain the concept of utilising counts and cell value within a raster data model.
(4)
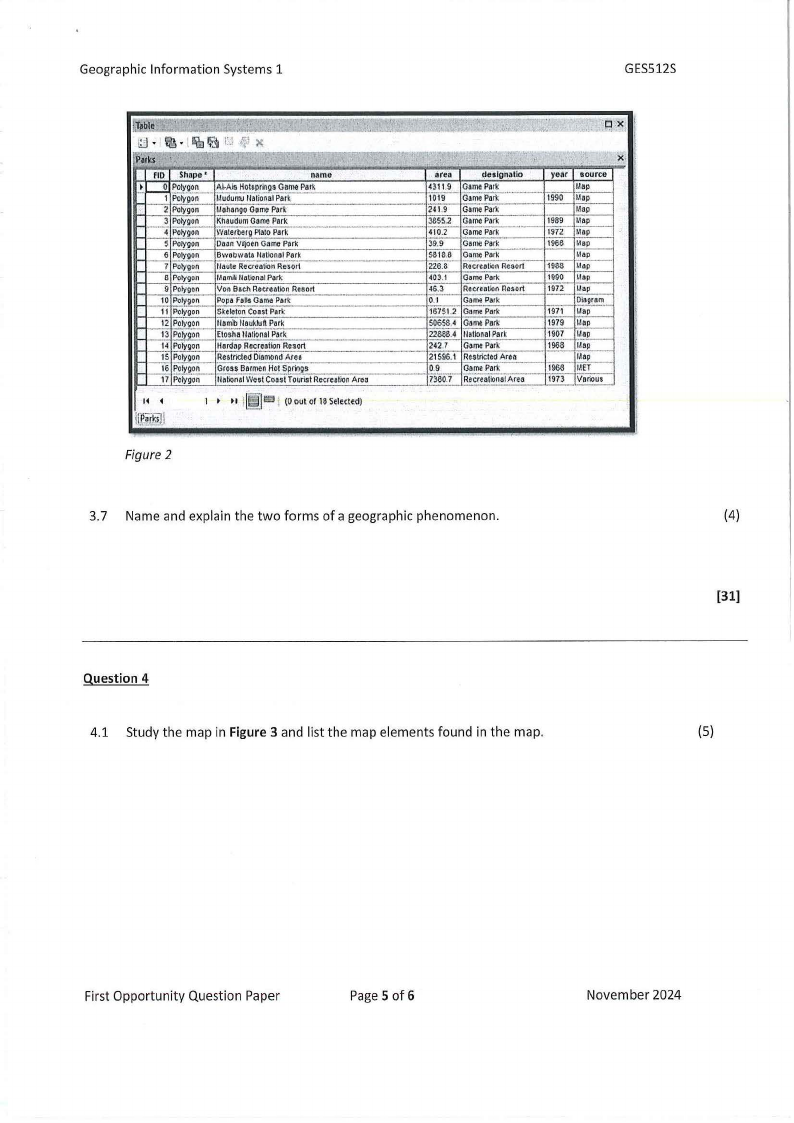
3.6. Describe the concepts of GISattribute tables based on Figure2.
(6)
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page 4 of 6
November 2024
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
Geographic Information Systems 1
GESS12S
, 'f1h.n
:~/~ 1-}ble
.,
i;j • ~-·l'Rii~i'J.f X
-Parks
''!
flD Shope•
name
f o Polygon Al-Als Hol,pring! GamePatk
1 Polygon l.ludu,w 11&1ionPaa1tk
-- 2 Polygon
3 Polygon
4 Polygon
l.lohangoGomePart
KhaudumGamePork
Wate,beroPlatoPark
---·
S Polygon
... 6 Polygon
7 Polygon
DeonVIJ<J&GnarnoPark
Bwabwala lla11ontP1Iotk
tlaute RecreationResort
8 Polygon l.lamlillatlonalPark
9 Polygon Von Baell RecreationResort
to Polygon PopaFall$GamePark
11 Polygon SkeletonCoos!Park
12 Polygon llamb llaukklft Park
13 Polygon EloshaUatlona1Park
-· ,-
,-,_.
14 Polygon
15 Polygon
,__,_16 folygon
17 Polygon
HordopRocreotlonResort
RestrictedDiamondArea
GrossBarmenHot Sprilgs
llationalWost CoastTouristRocrcoliooArca
1
!!£.~i@i
l~ln i (0 out of 18Sclettcd)
Figure 2
/~'-':
"' '-,:". :· ,;. ·"•·. "
·q..,.x' ,
..
><,11
area
deslon.•lio
GamePatk
1019 Galll'l Park
241.9 GamePark
l&SS.2 GamePatk
GamePMk
39.9 GomePart<
5818.8 GamePork
226.8 RecreallonResort
GomoPark
"6.3 RecteaoonResort
0:1
GomePark
16751,2 GomePark
50658.• GamePark
22888.4 lfollonalPark
242} GamePark
21596.1 Re$tricledArea
0.9
Gamt Park
7360.7 RecreallooaAl rea
year source
Ma~-
1990 I.lap
Map
I
1,
1989 Map
1972 I.lap
1968
1938
1990
Map
I,lap
Map
Map
Ii
I
f
1972 Map
1'1
1971 Dl,ilaagrpam·--
11
I
1979 Map
1907 (,lap
1008 Map
I.lap
1\\
1968 I.IET
1973 VDrlous
·-·
, ..
- ~-- .- -___
--,,--,
\\
3.7 Name and explain the two forms of a geographic phenomenon.
(4)
[31)
Question 4
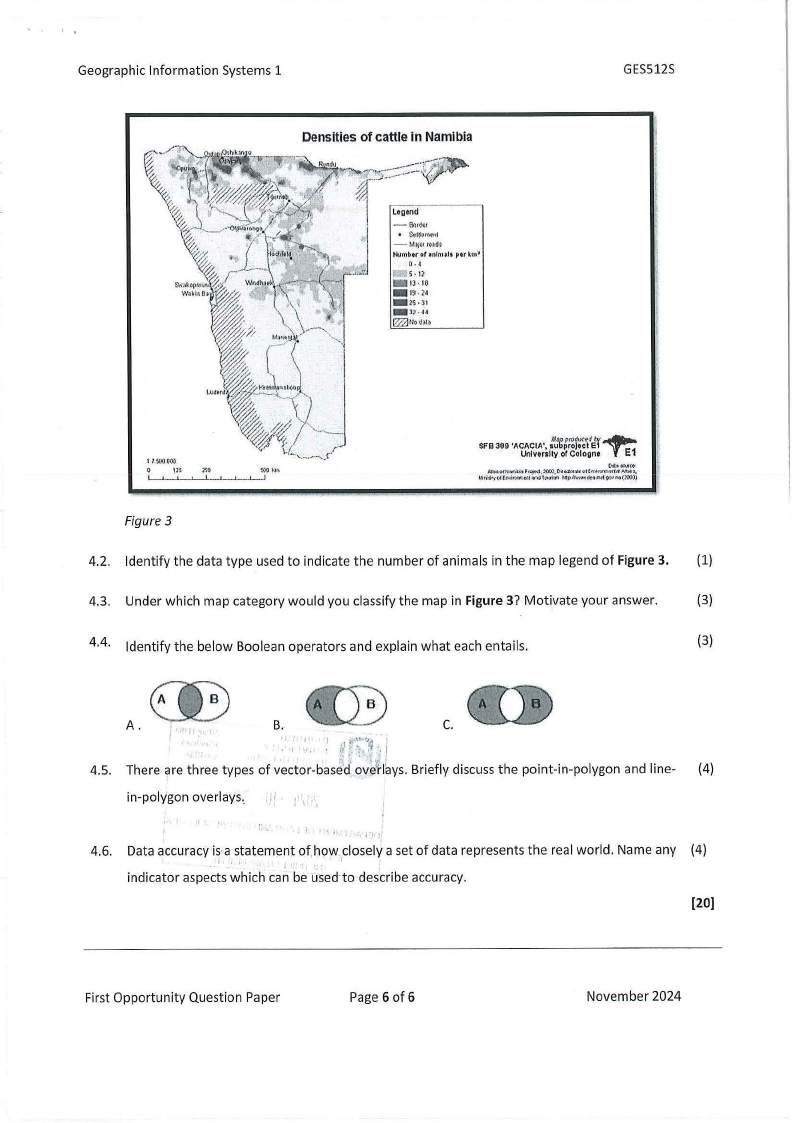
4.1 Study the map in Figure3 and list the map elements found in the map.
(S)
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page 5 of 6
November 2024
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
Geographic Information Systems 1
GES512S
[l,M:.t(),X(~
'-ll.uom~~11'1~,100J',Pft.iN'IOO!("',i,al"~tJ"f<'i,1JbfJ,
1,.tri"ll",y<,l(M\\l(<JttU ,.,Vlt'i.t)llfl. Hl:jl~~,:1r(
Ol)'Ir,.(:o).))
Figure 3
4.2. Identify the data type used to indicate the number of animals in the map legend of Figure3. (1)
4.3. Under which map category would you classify the map in Figure3? Motivate your answer.
(3)
4.4. Identify the below Boolean operators and explain what each entails.
(3)
00
A.
I 1'1.
B.
1
,.
I
.
:'It,,·/~,.··"•1j, ; I
0 C.
4.5. There are three types of vector-base·d q~e1'1aysB. riefly discuss the point-in-polygon and line- (4)
in-polygon overlays ..
: \\ 'i
4.6. Data accuracy is·astatement of.hc;:iwcloselya set of data represents the real world. Name any (4)
I•
. .i
indicator aspects which can be used·to describe accuracy.
[20)
First Opportunity Question Paper
Page 6 of 6
November 2024





