 |
GES512S - GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS 1 - 2ND OPP - JAN 2025 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT
DEPARTMENT OF LANDAND SPATIALSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION:
DIPLOMA IN GEOMATICS, BACHELOR OF GEOMATICS, BACHELOR OF GEOINFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY, DIPLOMA IN LAND ADMINISTRATION, BACHELOR OF LAND ADMINISTRATION,
BACHELOROF TOWN AND REGIONAL PLANNING, BACHELOROF PROPERTYSTUDIES,DIPLOMA IN
PROPERTYSTUDIES,BACHELOROF REGIONAL& RURAL DEVELOPMENT, BACHELOROF NATURAL
RESOURCEMANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION CODE:
06DGEO, 06DIPS, 06DPRS, 07BGEI, 07BGEO,
07BLAM, 07BNRS, 07BORR, 07BRAR, 07BTAR,
07BURP,08BOPS,08BPRS
COURSECODE: GES512S
LEVEL:5
COURSENAME: GEOGRAPHIC
INFORMATION SYSTEMS1
SESSION: JANUARY2025
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER
Ms Ivonne Makando
MODERATOR:
Mr Erich Naoseb
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF (4) PAGES
(Excluding this front page)
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Write clearly and neatly
2. Answer ALLthe questions.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examination paper.
2. Examination script.
3. SCalculator, ruler, pencils, eraser
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Geographic Information Systems 1
GES.5125
Question 1 State if the following statements are True or False.
1.1. The Raster Data Model relates to picture elements.
(1)
1.2. The Equivalent projection refers to equal area in map projection categories.
(1)
1.3. Map elements such as a legend, scale bar, and north arrow are legally required for all printed
maps.
(1)
1.4 The prime meridian and the equator serve as the baselines of the geographic coordinate
system.
(1)
1.5. A GISoperation that combines the geometries and attributes of the input layers to create the
output is known as erase.
(1)
1.6. A map cannot be printed from ArcMap without elements like a legend and north arrow.
(l)
1.7. Layers may contain features or surfaces.
(1)
1.8. A phenomenon that populates the study area is known as a geographic object.
1.9. Features have no shape and size.
1.10. GISstands for Geographical Institution System.
(1)
(1)
(1)
[10)
Question 2
2.1. What is the purpose of a Geographical Information System (GIS}? Provide an example of a
GIS.
(4)
2.2. A GIS (Geographic Information Systems) is a computer-based systems that provides four
capabilities relative to spatial data. Name the four capabilities.
(4)
2.3.
Discuss3 of the five questions a GIScan answer.
(6)
2.4. Discussbriefly Data as one component of GIS.
(3)
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page2 of 5
January 2025
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Geographic Information Systems 1
GES5l25
2.5.
Describe the difference between vector and raster data models in GIS. Provide examples of
when each might be used.
(6)
2.6. Why is 1:200,000 considered a smaller scale than 1:200 in cartography?
(2)
(25]
Question3
3.1.
Differentiate between a coordinate and a coordinate system.
(4)
3.2.
When is it necessary to use point geometry to model a geographic phenomenon?
(2)
3.3.
Based on Figure 1 below, which GIS concept is displayed? Explain the concept mentioned.
(3)
•18 ii
12.
1~.
"4 ~5
•17
12 Moparte
20 15
Terminalia
13 SSW.
18
10
14 Baobab
120 30
15 DeadVlei
30
5
16 ~ID~Sl)Q,
26
3
17 Acacia
60
9
18 Q~sn1i
10
2
Figure 1
3.4.
Briefly explain what a datum is.
(3)
3.5.
What is the relationship between a geoid and an ellipsoid?
(2)
3.6.
Which term describes a surface that can be laid flat without stretching or tearing? Name
three types of such a surface onto which the reference sphere is projected.
(4)
3.7.
Which term is used for map projections that preserve shape, area, distance and direction?
(2)
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 3 of 5
January 2025
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
Geographic Information Systems 1
GES512S
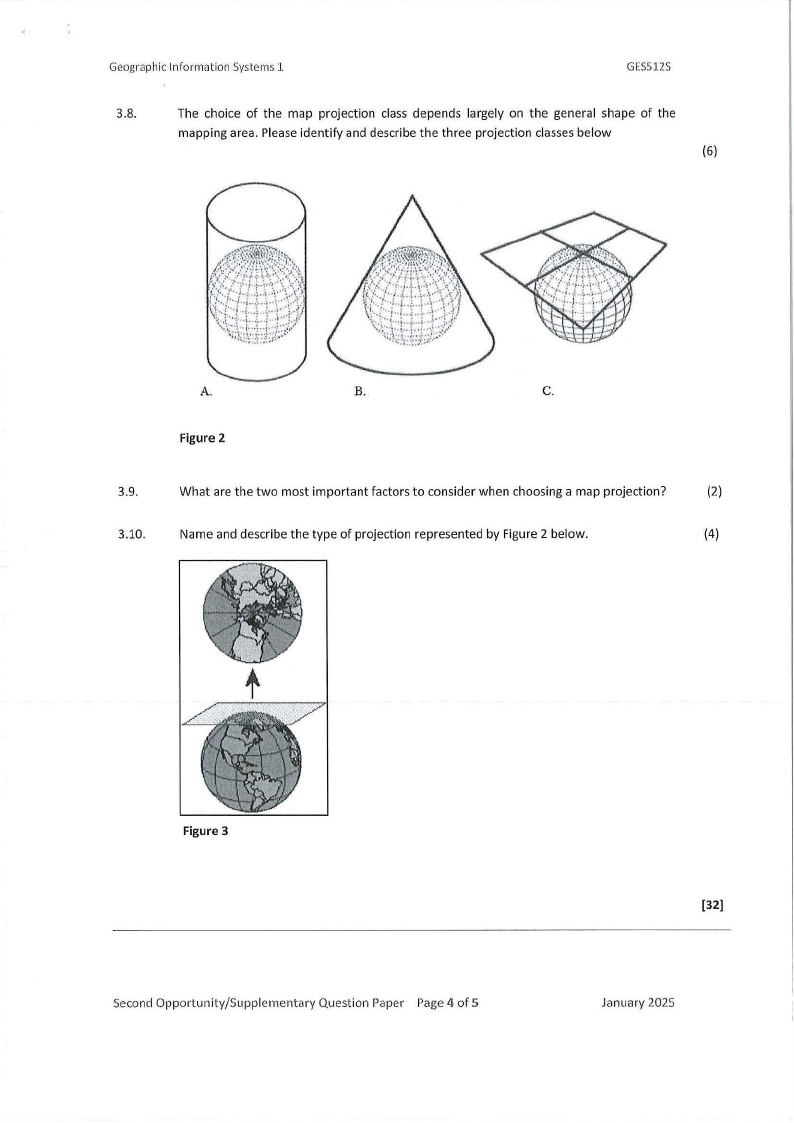
3.8.
The choice of the map projection class depends largely on the general shape of the
mapping area. Please identify and describe the three projection classes below
(6)
A.
B.
C.
Figure 2
3.9.
What are the two most important factors to consider when choosing a map projection?
(2)
3.10.
Name and describe the type of projection represented by Figure 2 below.
(4)
t
Figure 3
Second Opportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page 4 of 5
(32]
January 2025
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

Geographic Information Systems 1
GES512S
Question 4
4.1.
What does SQLstand for, and how is it used in GIS?
(2)
4.2.
What is geocoding in GIS,and why is it important
(3)
4.3.
What is the fundamental difference between raster and vector data models in GIS?
(2)
4.4.
Explain how pixel size influences the accuracy of a raster dataset.
{3)
4.5.
Provide two advantages and disadvantages of raster data, as well as two advantages and
disadvantages of vector data.
(4)
4.6.
In Geographical Information Systems {GIS) (ArcMap), entering data in attribute tables is
done in two common ways. Explain the two methods used to enter data in an attribute table.
(2)
4.7.
Name and explain two types of thematic maps.
4.8.
You are tasked to create a map that will show the farms the government of Namibia has
resettled landless people between 1990 and 2010. Name three basic principles of designing (3)
a map
[23]
.I: I
' ,'
SecondOpportunity/Supplementary Question Paper Page5 of 5
January 2025





