 |
GDC611S - GENDER COMMUNICATION - 2ND OPP - JULY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmI BI AunIVE RSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHn0L0GY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF COMMUNICATION
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BCMM
LEVEL: 6
COURSE CODE: GDC611S
COURSE NAME: GROUP DYNAMICS AND
COMMUNICATION
SESSION: JULY 2024
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY (PAPER1)
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION MEMORANDUM
EXAMINER(S) Dr. C PEEL,Mrs M MUBIANA and Ms E SHITAATALA
MODERATOR: Mrs. A TJIRAMANGA
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer TH-REEquestions. Note that Question 1 is worth 50
marks, is compulsory, and may not be substituted.
2. Read all the questions carefully before answering.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. Please ensure that your writing is legible, neat and
presentable.
THIS MEMORANDUM
CONSISTS OF _6_ PAGES (Including this front page)
xt~ No~-e:. c..,l\\.O\\,~e5\\<\\ 1~1
-;J\\Q,\\N'i'. ~" (h. . I CVA'eSl.
/
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

Question 2
25 marks
(a) During the course, you conducted a case study analysis of an organisation, its group
dynamics, human relations and management philosophy. Discus·sfrom your analysis how
you compared the influence in the organisation of Human Relations Theory (Elton Mayo),
Hierarchical Structure (Max Weber), and Scientific Management Theory {Henri Fayal)
15 marks
(b)Justify, with examples, the merits of Gossip Theory in any organisation ......10 marks
Answers:
(a}Candidates should recollect and review case studies they undertook and presented in
· class, in which they applied the above work management philosophies.
{b) According to Harari (2014), Gossip Theory is useful in maintaining strong teams
through sharing information about the world (global economic trends and
opportunities), about human needs, threats, achievements, and environmental
developments. Give examples.
Question 3
25 marks
Military teams provide us with an excellent model to make sure communication is clear.
They have developed rules, because miscommunication in the military can be fatal.
Provide four military team practices that other teams can learn from, and explain why
and how these practices should be emulated in an organisation familiar to you.
Answer:
o In the military, team members monitor each other's performance and help each
other out when they see a team member getting stuck. In an organisation, we
should not work in silos, or look on while others fail, but we should provide support
to those who need it. (The assumption is that all team members have the basic
competence required to be in the team).] marks for the military practice, andJ> /;----
marks for its application in other organisation contexts.
o All military team members give each other feedback during debriefing sessions to
improve performance. Likewise, it is important in all work environments to learn
1/ from mistakes or, even in the absence of error, to reflect on and discuss areas
where the team_~ould impr~ve, because there i: alwa~s r~om_for improve~en~.]
marks for the m1!,tarypractice, and]marks for its appl,cat1onmother organisation ·
contexts.
o Internal communication happens in a closed-loop fashion, i.e. both the sender and
receiver must acknowledge and ensure that everybody has received the correct
meaning of the message. Team members often err through miscommunication and
misunderstanding. It would be helpful in other organisations for communicators to
request confirmation from receivers that they have understood messages sent, and
3
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
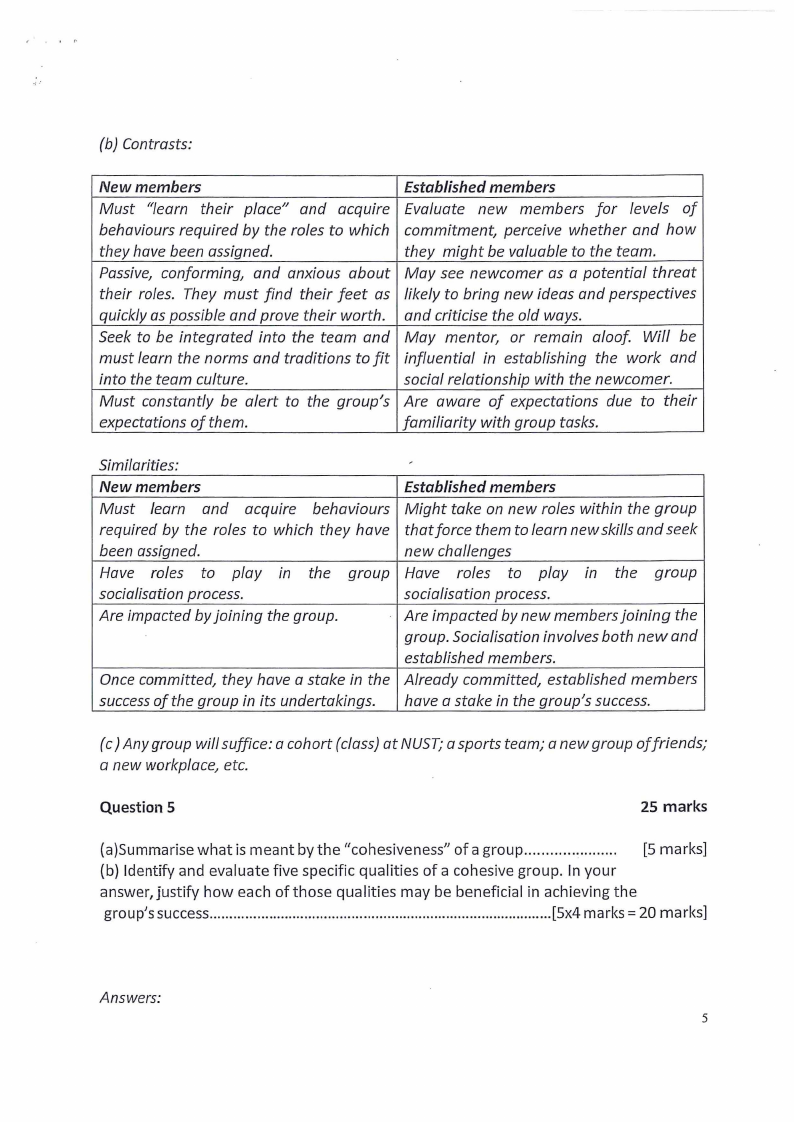
{b) Contrasts:
New members
Established members
Must "learn their place" and acquire Evaluate new members for levels of
behaviours required by the roles to which commitment, perceive whether and how
they have been assigned.
they might be valuable to the team.
Passive, conforming, and anxious about May see newcomer as a potential threat
their roles. They must find their feet as likely to bring new ideas and perspectives
quickly as possible and prove their worth. and criticise the old ways.
Seek to be integrated into the team and May mentor, or remain aloof. Wi/1 be
must learn the norms and traditions to fit influential in establishing the work and
into the team culture.
social relationship with the newcomer.
Must constantly be alert to the group's Are aware of expectations due to their
expectations of them.
familiarity with group tasks.
Similarities:
New members
Must learn and acquire behaviours
required by the roles to which they have
been assigned.
Have roles to play in the group
socialisation process.
Are impacted by joining the group.
Once committed, they have a stake in the
success of the group in its undertakings.
Established members
Might take on new roles within the group
that force them to learn new skills and seek
new challenges
Have roles to play in the group
socialisation process.
Are impacted by new members joining the
group. Socialisation involves both new and
established members.
Already committed, established members
have a stake in the group's success.
(c) Any group willsuffice: a cohort (class) at NUST;a sports team; a new group of friends;
a new workplace, etc.
Question 5
25 marks
(a)Summarise what is meant by the "cohesiveness" of a group...................... [5 marks]
(b) Identify and evaluate five specific qualities of a cohesive group. In your
answer, justify how each of those qualities may be beneficial in achieving the
group's success...................................................................................[.5..x.4 marks= 20 marks]
Answers:
5





