 |
LAE621S- LABOUR ECONOMICS- 1ST OPP- NOV 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BI A un IVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
· FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCE AND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, ACCOUNTING AND FINANCE
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ECONOMICS
QUALIFICATION CODE:
07BECO
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: LAE612S
COURSE NAME: LABOUR ECONOMICS
SESSION: NOVEMBER 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) MR. PINEHAS NANGULA
MODERATOR: MRS LAVINIA HOFNI
INSTRUCTIONS
I. Answer ALL the questions
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
I. Scientific calculator
2. Pen and Pencil
3. Ruler
THIS. QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF _5_ PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION ONE
[20 MARKS]
Multiple choice questions
1. Which of the following is NOTa unique characteristic of the labour market?
a) The worker is not a product but a person.
b) The employer buys the services of the worker, but the employer does not buy the worker.
c) The equilibrium wage in the labour market could be influenced by factors like inflation and
the worker's standard of living.
d) The worker's personality characteristics can always be determined fully before employment
starts.
2. Which of the following is NOTan assumption of a perfectly competitive labour market?
a) Workers have full information on jobs available and wage rates.
b) Employers have full information on wage rates paid by other employers.
c) Workers and employers are entirely rational.
d) Workers are immobile and will only work in the same region in their entire lives.
3. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding a budget line?
I. The budget line is downward sloping.
II. An increase of non-labour income shifts the budget line upwards.
Ill. The absolute value of the slope of the budget line is equal to the wage rate.
a) Only [I] is correct.
b) Only [Ill] is correct.
c) Only [I] and [Ill] are correct.
d) All three statements are correct.
4. Assumingleisure is an inferior good, then an increase in non-labour income will result in the
hours of work to
·
a) decrease.
b) increase.
c) stay the same.
d) either decrease or increase.
5. The added worker effect would tend to cause the labour supply to ____
boom.
a) decrease
b) remain the same
c) increase, decrease or remain the same
d) drop to zero with 100%certainty
during economic
6. The demand for labour is a derived demand because it is derived from
a) the quantity of the product supplied to the market.
b) the number of people willing to work at a particular wage.
c) the price of labour, which is the wage.
d) the demand for the product or service for which the labour is used.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

7. Usethe information in the following table to calculate the employment elasticity of economic
growth of a hypothetical country between 2015 and 2016.
Year
Real GDP
Number of employed
2015
1 000 000
500 000
2016
1 100 000
600 000
a) Employment elasticity of economic growth = 0. 50
b) Employment elasticity of economic growth = 1.00
c) Employment elasticity of economic growth = 1.50
d) Employment elasticity of economic growth = 2.00
e) Employment elasticity of economic growth = 2.50
8. Which of the following does NOTexplain the law of diminishing marginal product of labour?
a) Hiring more employees means that each has less capital with which to work.
b) The best employees will always be hired first.
c) It is more difficult to manage a firm as both the size of the labour and capital increases.
d) Hiring more employees means that they will subdivide tasks and therefore become more
efficient.
9. The value of the marginal product of labour is equal to the product of:
a) the marginal product of labour and marginal cost of production.
b) the marginal product of labour and price.
c) the average product of labour and the average cost of production.
d) the average product of labour and price.
10. Which of the following statements is INCORRECrTegarding the long-run demand for labour
when the wage decreases?
a) Substitution effect: capital is replaced by labour to expand production.
b) Scale effect: the employer increases production by using more labour.
c) Scale effect: the employer increases production by using less capital.
d) Total effect: the employer uses more labour as a result of a wage decrease.
QUESTION TWO
[25 MARKS]
a) Explain the main differences between the labour market and the goods market. [10 marks]
b) In a farming industry, labour supply is Es = 3w - 10 and labour demand is Ed = 190 -
2w, where E is the level of employment and w is the hourly wage.
i. What are the market wage and employment if the labour market is competitive?
[2 marks]
ii. What is the unemployment rate at the current market wage?
[1 mark]
iii. Suppose the government sets a minimum hourly wage ofN$55.00, how many workers
would lose their jobs?
[4 marks]
iv. How many additional workers would want a job at the minimum wage?
[4 marks]
v. What is the unemployment rate at minimum wage
[4 marks]
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION THREE
[25MARKS]
Ms Martha has seven hours available per day to allocate between Leisure and work. She has
N$250.00 non - labour income and her wage rate per hour is N$25.00.
a) Contract budget constraint equation
[5 marks]
b) Draw a budget line and make sure to include intercepts
[5 marks]
c) Calculate the slope of the budget line
[5 marks]
= d) If Ms Martha's utility function is U(Y, L) 10-v'YL, use the information provided above
and utility function to calculate the highest level utility that you can get.
[IO marks]
QUESTION FOUR
a)
Labour hours
0
I
2
3
4
5
6
Total Product
0
40
134
246
340
400
440
[30 MARKS]
Per unit price
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
Use the information in the table above to draw the demand curve for labour in the short-run.
[5 marks]
b) Fill the table below for a hypothetical firm operating as a discriminating monopsonist
[5 marks]
Wage (W)
Employment (E)
Total costs
Marginal cost (MC)
800
0
1000
1
1200
2
1400
3
1600
4
1800
5
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
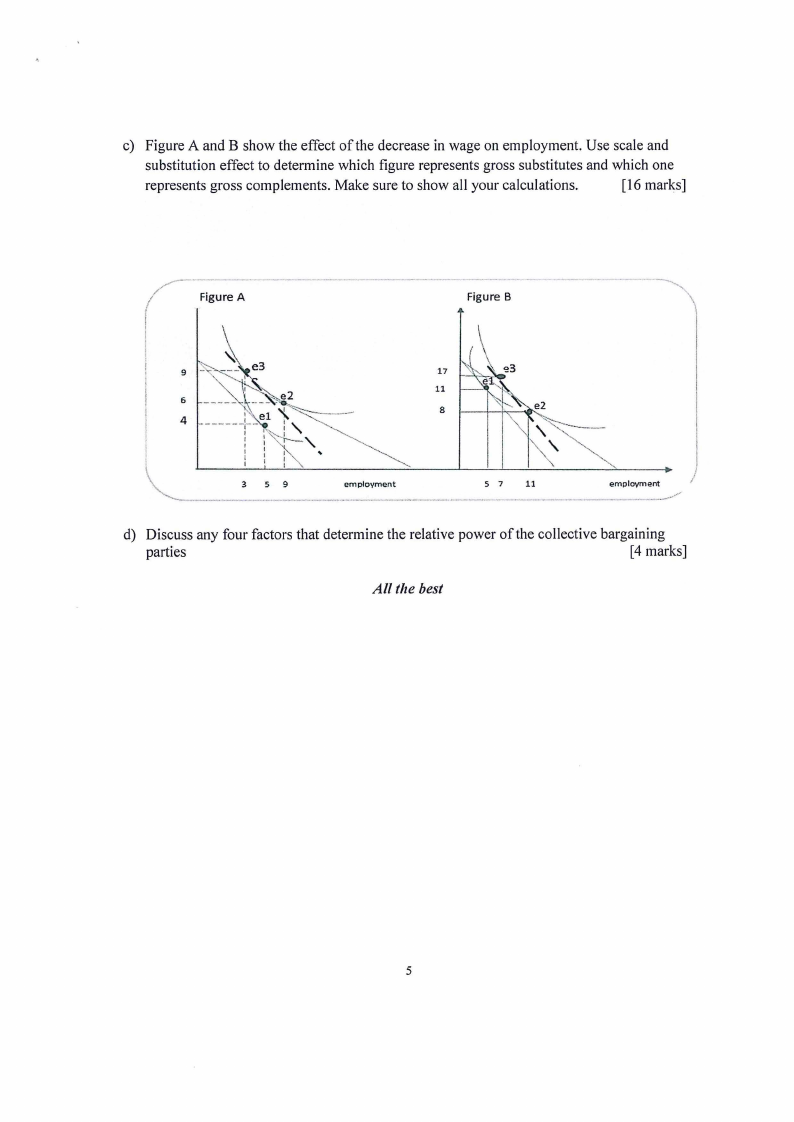
c) Figure A and B show the effect of the decrease in wage on employment. Use scale and
substitution effect to determine which figure represents gross substitutes and which one
represents gross complements. Make sure to show all your calculations.
[16 marks]
Figure A
Figure B
17
11
8
3 59
employment
57
11
employment
I
d) Discuss any four factors that determine the relative power of the collective bargaining
parties
[4 marks]
All the best
5





