 |
PPM712S- PRODUCT PRICING MANAGEMENT- 1ST OPP- JUNE 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

n Am I BI A u n IVER s I TY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF MARKETING, LOGISTICS AND SPORT MANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MARKETING
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07MARB
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: PPM712S
COURSE NAME: PRODUCT PRICING MANAGEMENT
SESSION: JUNE 2024
PAPER: THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER(S)
MR. C. KAZONDOVI
DR. E. SIMATAA
MODERATOR:
MS. L. PRINZONSKY
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. Use the table provided on page [5] to answer Questions 5 and
Question 6: Detach and insert into your answer booklet.
5. Write as legible as possible, and as precise as possible.
6. Read each question carefully.
7. Use a non-programmable calculator (STRICTLYNO USEOF
CELLPHONE/MOBILE CALCULATOR).
8. Round of your answers to two (2) Decimal places.
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 5 PAGES (Including this front page)
-----;(
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
Question 1
[10 marks]
Discuss five (5) factors that influence how Price plays a Role in the Distribution/Place Strategy of
the Marketing Mix, with examples from any company of your choice.
(10 marks
Question 2
[20 marks]
Denu Stationers has calculated that it has fixed costs that consist of its lease, depreciation of its
assets, executive salaries, and property taxes. Those fixed costs add up to N$60,000. Their
product is a pencil. Their variable costs associated with producing the pencil are raw material,
factory labour, and sales commissions. Variable costs have been calculated to be N$0.80 per unit.
The pencil is priced at N$2.00 each.
2.1) What is the Contribution Margin? Also, what is the meaning of this Margin?
2.2) Calculate and Prepare the break-even chart for Denu Stationers?
2.3) What is the meaning of the break-even analysis for Denu Stationers?
(5 marks)
(10 marks)
(5 marks)
Question 3
[20 marks]
Pricing objectives can be divided into three (3) main categories. Discuss below categories with
specific examples.
a.) Profit-oriented pricing objectives
b.) Sales-oriented objectives
c.) Status-quo objectives
(7 marks)
(7 marks)
(6 marks)
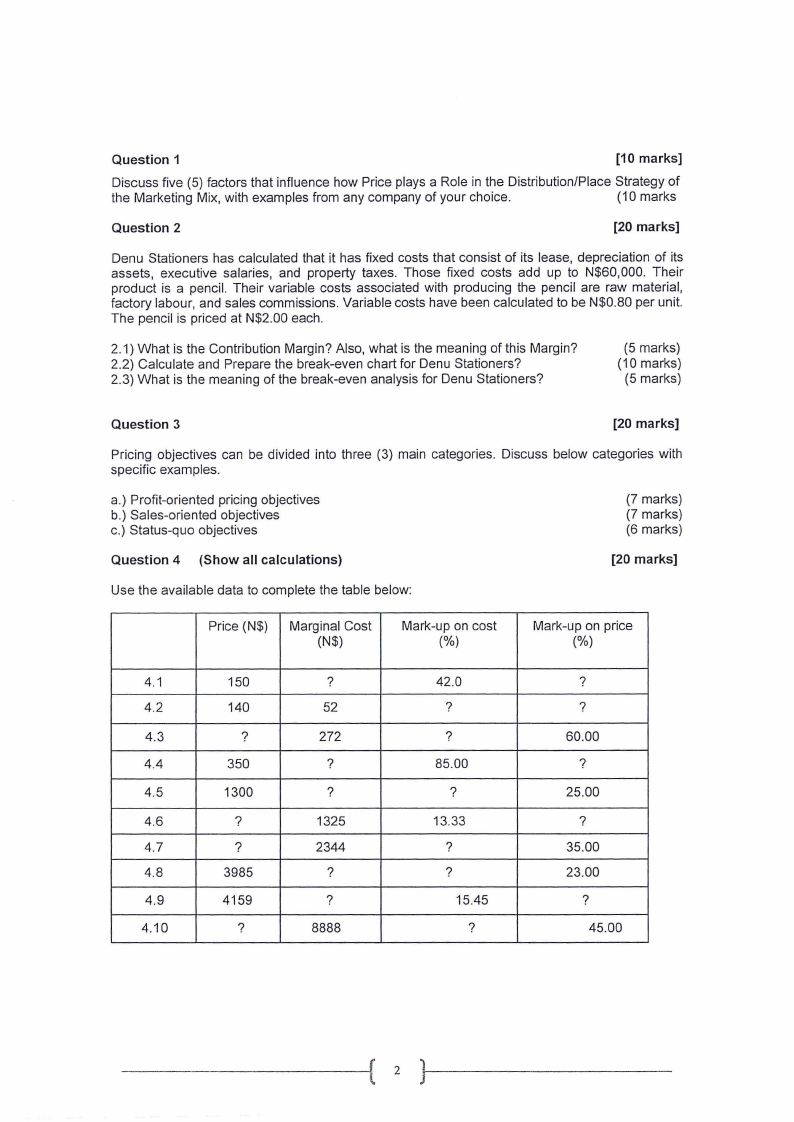
Question 4 (Show all calculations)
[20 marks]
Use the available data to complete the table below:
Price (N$) Marginal Cost
(N$)
Mark-up on cost
(%)
Mark-up on price
(%)
4.1
150
?
4.2
140
52
4.3
?
272
4.4
350
?
4.5
1300
?
4.6
?
4.7
?
4.8
3985
1325
2344
?
4.9
4159
?
4.10
?
8888
42.0
?
?
85.00
?
13.33
?
?
15.45
?
?
?
60.00
?
25.00
?
35.00
23.00
?
45.00
2 ),--------------
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

Question 5
(15 marks]
Multiple choice questions
Use the table provided on [page 5] to answer these questions, detach and insert it into your
answer booklet. 1.5 mark will be awarded for each correct answer.
5.1. If demand changes greatly with a small change in price, we say the demand is ___ _
a. Inelastic.
b. variable.
c. elastic.
d. value-based.
e. fixed.
5.2. A company sets not a single price, but rather a ____
that covers different items in its
line that change over time as products move through their life cycles.
a. pricing by-product.
b. pricing structure.
c. pricing loop.
d. pricing cycle.
e. pricing bundle.
5.3. Why should a product's price be set in line with the marketing strategy?
a. It is easier to explain to the sales staff.
b. To avoid confusion in the customers mind and in the market place.
c. Profits can be assessed before a product is launched.
d. Price lists can be printed at the same time as brochures.
e. Sales people can advise on a price that is likely to sell well.
5.4. Competitor price increases are more likely to be followed when they are due to:
a. falling sales.
b. increased advertising.
c. supplier bankruptcies.
d. price wars.
e. rising costs.
5.5. Value to the customer, explicability, price quality relationships and marketing strategy are
some of the factors that need to be considered when adopting the _____
approach to
pricing.
a. cost-oriented.
b. marginal cost.
c. market-oriented.
d. competitor-oriented.
e. market-skimming.
5.6. Which of the following strategies best describes the attempt on the part of sellers to
sell below cost with the intention of punishing a competitor or gaining higher
long-run profits by putting competitors out of business?
a. price-fixing strategy.
b. deceptive pricing strategy.
c. price discrimination strategy.
d. predatory pricing strategy.
e. none of the above.
3;
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

5.7. The type of promotional pricing that uses a few products with very low prices to
attract customers into the store in the hope that they will then buy regularly priced
items is called:
a. loss leaders.
b. cash rebates.
c. special-event pricing.
d. low-value pricing.
e. penetration pricing.
5.8. Mitch owns a restaurant. The monthly payment on the land he purchased for his restaurant,
the mortgage on his small office building, and his business license are all examples of __
costs.
a. marginal.
b. variable.
c. demand.
d. promotional.
e. fixed.
5.9. During sporting events at Vrede Rede Primary School in Swakopmund, Steven Urangi runs
a food stand. The costs associated with the purchase of hot dogs, mustard, relish, ketchup,
chips, sodas, paper napkins, and cups are all examples of __ costs.
a. marginal.
b. variable.
c. fixed.
d. promotional.
e. liquidity.
5.10. Which of the following factors does NOT directly affect the elasticity of demand?
a. the other uses of a product.
b. the inputs needed to manufacture the product.
c. the availability of substitute goods.
d. the price relative to a consumer's purchasing power.
e. a product's durability.
Question 6
[15 marks]
True or False Questions
Use the table provided on [page 6) to answer these questions. Detach and insert it into your
answer booklet. 1.5 mark will be awarded for each correct answer.
6.1 Under oligopolistic competition the market consists of a few sellers who are highly sensitive
to each other's pricing and market strategies
6.2 When initiating price changes the company must anticipate possible reactions from both
buyers and competitors.
6.3 Monopoly or lack of regulation means one can always set prices at will.
6.4 Price discrimination is the practice of charging different mark-ups for the same product.
6.5 In setting the price of a product by its perceived value, the company decides on the value of
the product.
6.6 Pricing is considered to be the key within the capitalist system of the free market economy.
f
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
6.7 Pricing objectives are used to designate the role of price in the organisation's marketing
and strategic plans.
6.8 Selection of advertising media is determined by the target audience to be reached which may
. necessitate the use of price in the advertisement.
6.9 Value= Perceived Costs/Price
6.10 Price must be recognised as a statement of cost and not as a statement of value.
GRAND TOTAL= 100 MARKS (THE END)
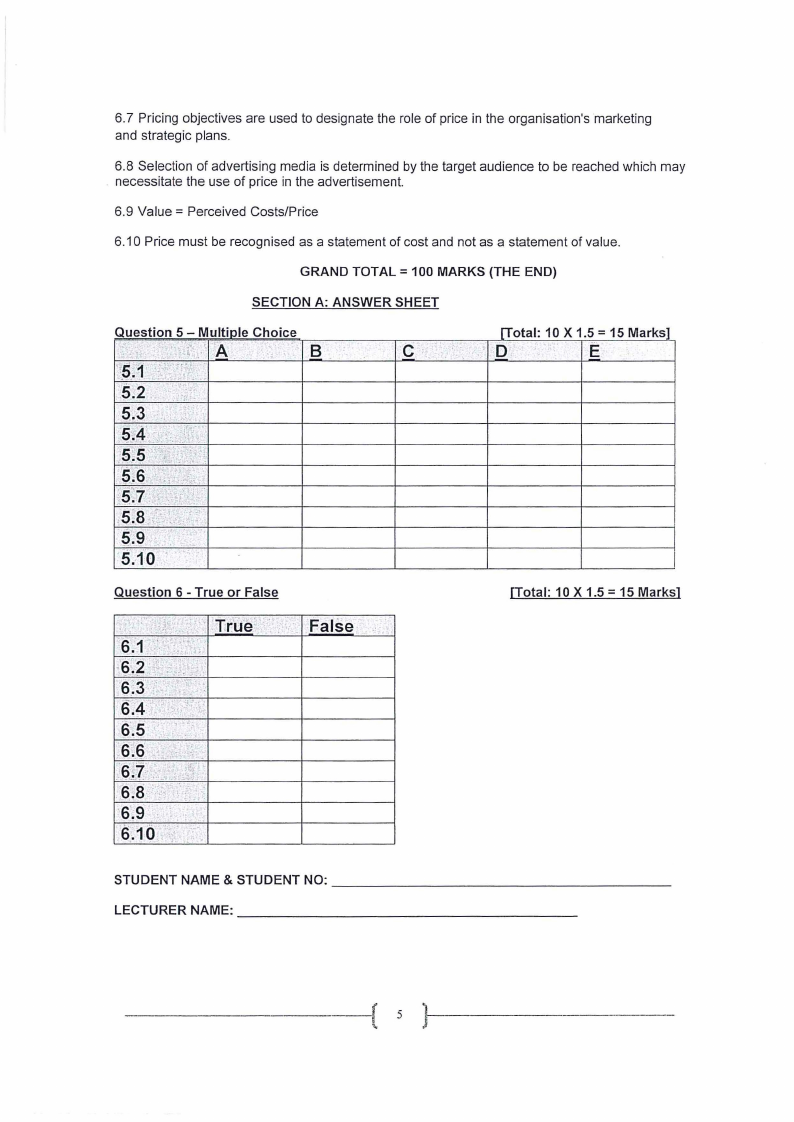
SECTION A: ANSWER SHEET
Question 5 - Multiple Choice
[Total: 10 X 1.5 = 15 Marks]
C.
D
E
l£s-··1.·· •..;.; .
••
• ' : .,
•• >
5.-10 .
Question 6 - True or False
False-
[Total: 10 X 1.5 = 15 Marks]
6.5
6..10.··r_:.·
STUDENT NAME & STUDENT NO: _________________
LECTURER NAME: _________________
_
_
5





