 |
HAM621S - HAEMATOLOGY 2B - 1ST OPP - NOVEMBER 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAml BIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE AnDTECHnOLOGY
Faculty of Health, Natural
Resources and Applied
Sciences
School of Health Sciences
Department of Clinical
Health Sciences
13Jackson Kaujeua Street
Private Bag 13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T; +264 61 207 2970
F: +264 61 207 9970
E: dchs@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR of MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
LEVEL:6
COURSE:HAEMATOLOGY 2B
COURSECODE: HAM621S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2023
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY: QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
Ms Edwig Shingenge
Dr Elzabe Van Der Coif
INSTRUCTIONS :
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHMENTS
1. Cytochemistry answer table
This paper consists of 7 pages including this front page.
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTioN'A:iviOLTIPTfoioi'cE&sHORTANSWE.. RQUESTION[S30MARKSJ
QUESTIO1 N
[10)
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate answer or
phrase from the given possibilities. Write the appropriate letter next to the number of the
statement/ phrase.
1.1 Which organ is the primary site of haemopoiesis in a developing foetus:
(1)
A) liver
B) Bone Marrow
C) Spleen
D) All of the above
1.2 Which bone marrow pool holds the largest number of band cells and mature neutrophils? (l)
A) Miotic
B) Post miotic
C) Storage
D) Functional
1.3 Primary granules also known as azurophilic granules contain:
(1)
A) Myeloperoxidase
B) Lactoferrin
C) Iron
D) Collagenase
1.4 A neutrophil precursor with 10-18um in diameter, with round or oval nucleus, no nucleoli, (l)
prominent primary granules and a few secondary granules bests describes:
A) Blast
B) Band cells
C) Myelocyte
D) Metamyelocyte
1.5 Which of the following conditions do not result in a leukemoid reaction?
(1)
A) Severe infection
B) Chronic myeloid Leukaemia
C) Metastatic Cancer
D) Acute Haemolysis
Haematology 28 (HAM621S)
1st Opportunity November 2023
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.6 Identify the disorder associated with the following morphology:
(1)
A) Neiman Picks Disease
B) Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
C) Pleger Huet Syndrome
D) Gauscher's Disease
1.7 Mary suffers from hay-fever during spring, due to pollen allergies. Which of her leukocytes (1)
are likely to be increased?
A) Neutrophils
B) Monocytes
C) Eosinophils
D) Basophils
1.8 Identify the number of blasts in bone marrow necessary to diagnose acute myeloid (1)
leukaemia according to WHO criteria.
A) 30%
B) 10%
C) 15%
D) 20%
1.9 Identify the chromosomal abnormality associated with Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) (1)
M2?
A) t(8:21)
B) t(9:22)
C) t(lS:17)
D) t(l:19)
1.10 Which cytochemical stain is best for differentiating AML from Acute Lymphoblastic (1)
Leukaemia (ALL)?
A) Alpha-naphylacetate
B) Non-specific esterase
C) Periodic Acid Schiff
D) Myeloperoxidase
Haematology 2B (HAM621S)
1'1 Opportunity November 2023
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2
(20]
2.1 Identify the white cells that stem from the myeloid progenitor stem cells.
(4)
2.2 For each of the granulocytes identified in 2.1, state the percentages found in the peripheral (8)
blood and their main functions. You may tabulate your answers.
2.3 What is the difference in maturation between B cells and T cells?
(2)
2.4 For each of the following lymphocytes, suggest at least two specific antigenic cluster
{6)
differentiation {CD) markers.
A) B cells:
B) T Cells:
C) Natural Killers
QUESTION 3
(21]
3.1 Outline the World Health Organization {WHO) and French British American (FAB)
(6)
classification methods for haematological malignancies.
3.2 Haematological malignancies have the following general symptoms of which are tied to
{S)
physiological processes in these patients. Identify the physiological reasoning behind each
of the following symptoms.
3.2.1 Pallor & Lethargy:
3.2.2 Recurrent infections:
3.2.3 Ecchymoses or Petechiae:
3.2.4 Fever:
3.2.5 Bone Pain:
3.3 lmmunophenotyping is a very valuable method of diagnosis for haematological
malignancies. Answer the following questions regarding immunophenotyping.
3.3.1 Briefly explain what immunophenotyping is?
(2)
3.3.2 In which two ways is sample prepared for immunophenotyping analysis?
(2)
3.3.3 The most common method of immunophenotyping used is flow cytometry. Briefly
(6)
explain its principle.
Haematology 28 {HAM621S)
1st Opportunity November 2023
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 4
[20]
4.1 Complete the table provided in the answer book by identifying staining properties of the (12)
following cytochemical stains.
Stain
4.1.1 Myeloperoxidase
4.1.2 Sudan Black
4.1.3 Periodic Acid-
Schiff
4.1.4 Acid Phosphatase
Component Stained
Positive cells
Negative Cells
4.2 Identify and explain the four patterns in which metastatic cancers can infiltrate the bone (8)
marrow.
(29 MARKS)
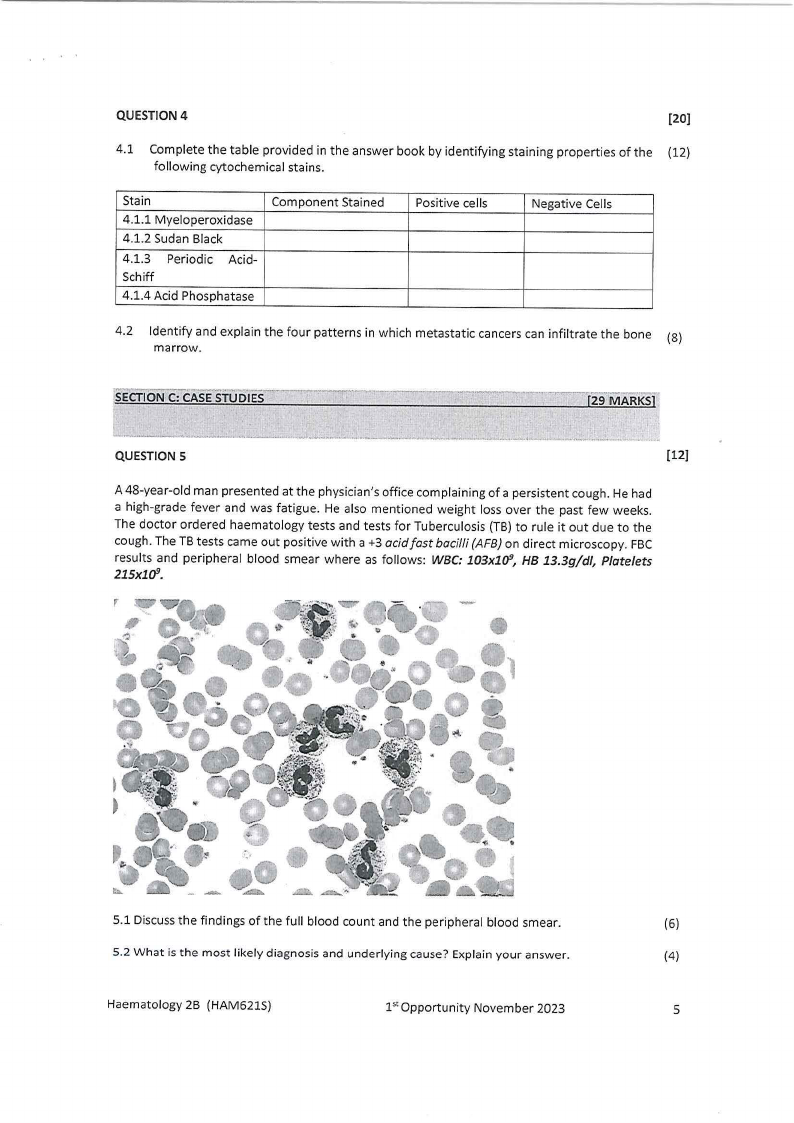
QUESTION 5
(12]
A 48-year-old man presented at the physician's office complaining of a persistent cough. He had
a high-grade fever and was fatigue. He also mentioned weight loss over the past few weeks.
The doctor ordered haematology tests and tests for Tuberculosis (TB) to rule it out due to the
cough. The TB tests came out positive with a +3 acid fast bacilli (AFB) on direct microscopy. FBC
results and peripheral blood smear where as follows: WBC: 103xla9, HB 13.3g/dl, Platelets
215xla9.
r
' - ~--.7....-.t\\'
....,lf·f:' ,·
5.1 Discussthe findings of the full blood count and the peripheral blood smear.
(6)
5.2 What is the most likely diagnosis and underlying cause? Explain your answer.
(4)
Haematology 2B (HAM621S)
istopportunity November 2023
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

5.3 Suggest further tests to confirm diagnosis.
(2)
QUESTION 6
[17]
A 15-year-old girl is admitted to the emergency room with complaints of abdominal pain for the
past three days. The ultrasound examination revealed a uniform, well-demarcated mass on the
left superolateral part of the uterus. On MRI examination, an encapsulated, well-demarcated
mass was observed at the same location. On peripheral blood smear examination 20% of cells
were blasts. On bone marrow aspiration, 85% of cells were large myeloid blasts with fine
chromatin and striking nucleoli. Overall, there was a 10% rate of maturation of granulocytic
cells. The laboratory findings were as follows:
WBC 125 x 1a9/L, HB 10. 7 g/L, and platelets: 107 x 1a9/L). Lactate dehydrogenase {LOH) level
was1144U/L
6.1 Explain the ultrasound and MRI findings.
(3)
6.2 Interpret laboratory results.
(4)
6.3 The Doctor made the diagnosis of AML FABsubtype M2. Discussthe rationale behind Dr's (4)
diagnosis.
6.4 Suggest at least four (4) CD markers that would be positive in this case.
(4)
6.5 What is the most common genetic mutation associated with this subtype?
(2)
END OF QUESTION PAPER [100 MARKS]
Haematology 28 (HAM621S)
1st Opportunity November 2023
6





