 |
ICA511S - INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY - 1ST OPP - JUNE 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
n Am I BI A u n IVER s I TY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,NATURALRESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
SCHOOLOF AGRICULTUREAND NATURALRESOURCESSCIENCES
DEPARTMENTOF AGRICULTURALSCIENCEAND AGRIBUSINESS
QUALIFICATIONS:BACHELOROF SCIENCEIN AGRICULTURE
BACHELOROF SCIENCEIN HORTICULTURE
QUALIFICATIONSCODE: 07BAGA LEVEL:7
07BHOR
COURSECODE: ICASllS
COURSENAME: INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
DATE: JUNE 2024
PAPER:1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
MS. PAULINA NDINELAGO NAUPU
MRS. LUCIA TUYENI-KELAO KAFIDI
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer all the questions.
2. Write neatly and clearly.
3. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
4. All written work MUST be done in blue or black ink.
5. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Calculator
2. Examination paper
3. Examination script
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 4 PAGES
(ExcludingThis Front Page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
Define the following terms
1.1 Atoms
{2}
1.2 Element
{2}
1.3 Matter
{1}
1.4 Molecules
{1}
1.5 Compound
{1}
1.6 Homogenous mixture
{1}
[8]
QUESTION 2
2.1 What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change?
{4}
2.2 What is an ionic bond and what charges does it form?
{3}
2.3 What is the relationship between molarity and molality?
{3}
[10]
QUESTION 3
3.1 Imagine that a chemist wants to measure out 0.214 ml of benzene, but lacks the
equipment to accurately measure such a small volume. The chemist, however, is
equipped with an analytical balance capable of measuring up to ±0.000lg. Looking at a
reference table, the chemist learns the density of benzene (p=0.8765g/ml ). How many
grams of benzene should the chemist use?
{4}
3.2 A rock has a mass of 20.5 g and a volume of 15.05 cm3. What is its density?
{4}
3.3 A rock has a density of 18.3 g/cm 3• If you have a rock bar with a volume of
43.9 cm3, what is its mass?
{4}
[12]
1
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 4
4.1 What is the molarity of a solution that contains 0.25 moles of glucose dissolved
ml of water?
{4}
in 500
4.2 How many milliliters of a 1.5 M solution of hydrochloric acid are needed to prepare
500ml of a 0.25 M solution?
{4}
4.3 How many ml of 2.0M H2SO4are needed to make 400ml of 0.11M H2SO4_
{4}
4.4 24.6 ml of a 0.S0M monoprotic acid solution was titrated with a 0.18M NaOH solution
What is the volume of NaOH that should be added to the solution in order to reach the
equivalence point?
{4}
4.5 Suppose you want to prepare 250 ml of 0.100 M CuSO4solution by diluting a 1.00 M
CuSO4stock solution. What volume of CuSO4do you need?
{3}
4.6 What is the mass of 0.30 moles Mg(NO3)2
{4}
[23]
QUESTION 5
5.1 Calculate the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 23.4 g of sodium sulfate
{Na2SO4)in enough water to form 125 ml of solution.
{9}
5.2 A 25.00 ml sample of a hydrochloric acid solution of unknown concentration was titrated
with 0.100 M sodium hydroxide solution. It took 37.55 ml of the sodium hydroxide
solution to reach the endpoint.
Using this equation, HCI+ NaOH NaCl+ H2O, what is the molarity of the hydrochloric
acid solution?
{9}
[18]
QUESTION 6
6.1 If a compound has an empirical formula of CH2and a molar mass of 84 g/mol, what is its
molecular formula
{5}
6.2 A compound has an empirical formula of C2Hsand a molar mass of 58 g/mol. What is its
molecular formula?
{5}
[10]
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 7
Balance the following chemical equations
7.1 C + 502 CS2+ CO
7.2
7.3
7.4 FeCb + NaOH Fe(OH}3+ NaCl
[2]
[2]
[2]
[2]
[8]
QUESTION 8
3.2 moles of N2 reacts with 5.4 moles H2 in the following chemical reaction:
N2 + 3H2 2NH3
8.1 What is the limiting reactant
8.2 How many moles of ammonia are formed
8.3 How much of the excess reactant in moles is left over?
{S}
{2}
{4}
[11]
Total Marks:
100
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
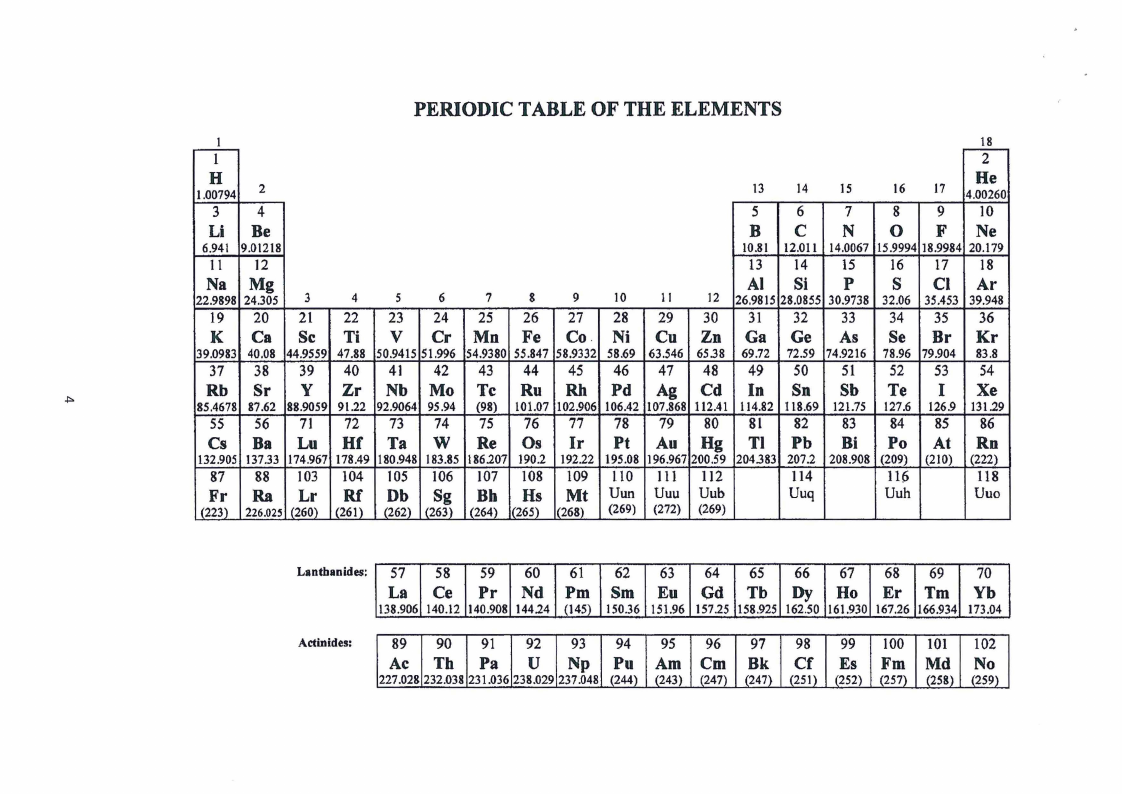
PERIODICTABLEOF THE ELEMENTS
18
l
2
H
1.00794 2
13
14
15
He
16
17 4.00260
34
56
7
8 9 10
Li Be
B C N 0 F Ne
6.941 9.01218
10.81 12.01 l 14.0067 15.9994 18.9984 20.179
11 12
Na Mg
22.9898 24.305 3
4
s6
13 14 15 16 17 18
Al Si p s Cl Ar
7
8
9
10
II
12 26.9815 28.0855 30.9738 32.06 35.453 39.948
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
39.0983 40.08 44.9559 47.88 50.9415 51.996 54.9380 55.847 58.9332 58.69 63.546 6538 69.72 72.59 74.9216 78.96 79.904 83.8
37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54
Rb Sr y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
.i:,.
85.4678 87.62 88.9059 91.22 92.9064 95.94 (98) 101.07 102.906 106.42 107.868 112.41 114.82 118.69 121.75 127.6 126.9 131.29
55 56 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85
Cs Ba Lu Hf Ta w Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At
132.905 137.33 174.967 178.49 180.948 183.85 186207 190.2 192.22 195.08 196.967 200.59 204.383 207.2 208.908 (209) (210)
86
Rn
(222)
87 88 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112
114
116
118
Fr Ra Lr Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Uun Uuu Uub
Uuq
(223) 226.025 (260) (261) (262) (263) (264) '265) (268) (269) (272) (269)
Uuh
Uuo
Lanthanides: 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70
La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb
138.906 140.12 140.908 144.24 (145) 150.36 151.96 157.25 158.925 162.50 161.930 167.26 166.934 173.04
Actinides:
89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102
Ac Tb Pa u Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No
227.028 232.038 231.036 238.029 237.048 {244) (243) (247) (247) (251) (252) (257) (258) (259)





