|
ATE711S - ADVANCE TRANSPORT ECONOMICS - 2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF COMMERCE,HUMAN SCIENCEAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF MARKETING AND LOGISTICS
QUALIFICATION:BACHELOROF TRANSPORTMANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 07BTRA
LEVEL: 7
COURSECODE: ATE711S
COURSENAME: ADVANCE TRANSPORT ECONOMICS
SESSION:JULY 2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/ SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Dr. Smart Dumba
Mr. Mukela Mabakeng
Ms. Hilma Nuuyandja
MODERATOR: Mr Sem Tangeni Kalumbu
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 3 PAGES(Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 1
[lxlO Marks]
Answer the following five questions either 'True' or 'False'.
a) Travelers with low values of time will likely choose to take the tolled route. FALSE
b) Providing improved travel time and travel time reliability is generally among the largest
societal benefits from transportation infrastructure projects. TRUE
c) Only if transport is evaluated in terms of access can strategies that reduce the need for
travel, such as telework and more efficient land use, be considered as solutions to
transport problems. TRUE
d) Marginal costs will start to fall before average costs start to fall. TRUE
e) Fuel costs, accident costs, congestion costs and climate change costs are all examples of
external costs FALSE
f) Transport economics is a field of study aimed at minimising social welfare FALSE
g) Social welfare is maximised where the Marginal Social Cost curve meets the Marginal
Social Benefit curve TRUE
h) Transport economics feeds into transport policy and vice versa TRUE
i) Equipment, buildings and land which are fixed cost, but can be sold and their value partly
recovered are sunk costs. TRUE
j) Transport is a public utility in the sense that it is vital to the overall public interest. TRUE
Sub-total:
[10 Marks]
QUESTION 2
2.1 Explain the following terms as they apply to transport economics
a) Marginal Social Costs, (MSB)
(3 marks)
b) Marginal Social Benefit, (MSB)
(3 marks)
c) Marginal Private Costs, (MPC)
(3 marks)
d) Utility
(3 marks)
2.2 Why is road congestion seen as an external cost/negative externality in transport?
(10 marks)
2.3 Describe and explain the following graph as it relates to road pricing? (12 marks)
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
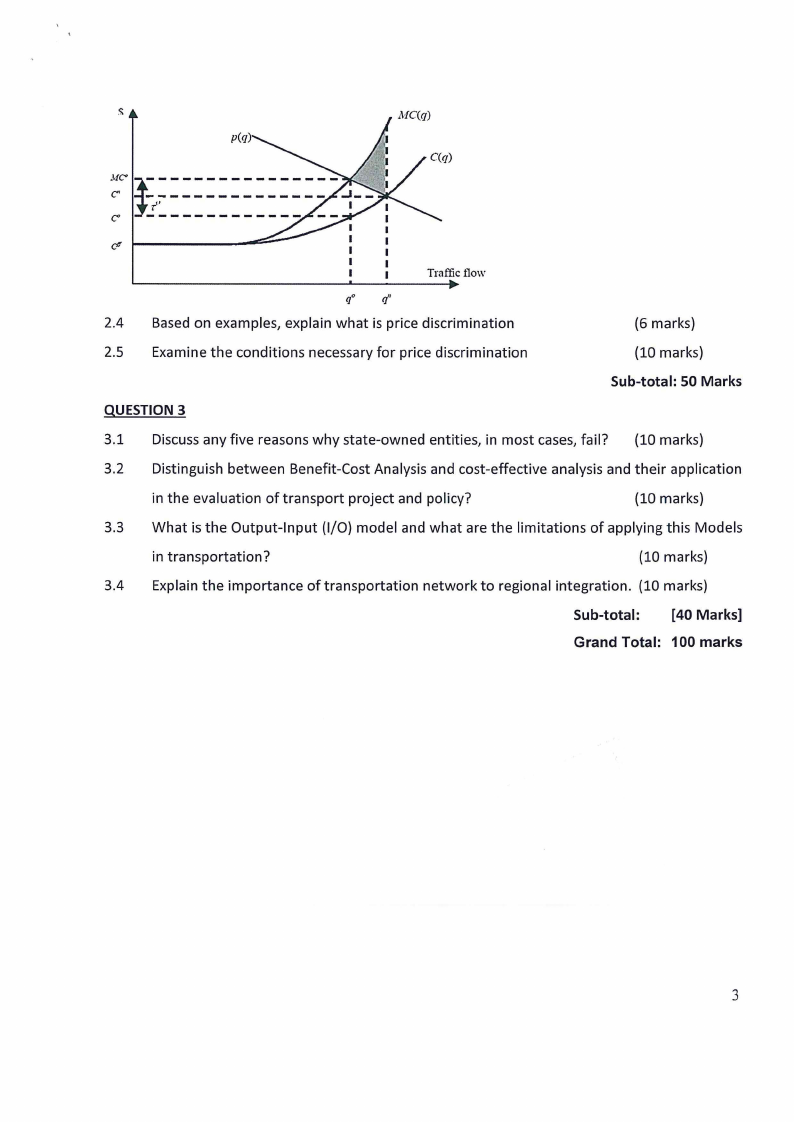
p(q)
MC° i----------
C"
--r--'-'-----
C°
----------
1
I
I
I
Traffic flow
<I'
2.4 Based on examples, explain what is price discrimination
(6 marks)
2.5 Examine the conditions necessary for price discrimination
(10 marks)
Sub-total: 50 Marks
QUESTION 3
3.1 Discuss any five reasons why state-owned entities, in most cases, fail? (10 marks)
3.2 Distinguish between Benefit-Cost Analysis and cost-effective analysis and their application
in the evaluation of transport project and policy?
(10 marks)
3.3 What is the Output-Input (1/0) model and what are the limitations of applying this Models
in transportation?
(10 marks)
3.4 Explain the importance of transportation network to regional integration. (10 marks)
Sub-total: [40 Marks]
Grand Total: 100 marks
3
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |