 |
MMB711S - MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 3 - 2ND OPP - JULY 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nArnlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH, APPLIED SCIENCESAND NATURAL RESOURCES
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORYSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 08BMLS
LEVEL: 7
COURSE CODE: MMB711S
COURSE NAME: MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY 3
SESSION:
JULY 2022
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION:
3 HOURS
MARKS:
109
SUPPLEMENTARY/ SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Ms. V Tjijenda
Dr Markus Schuppler
MODERATOR: Prof RT Mavenyengwa
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS
None
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 8 PAGES (Including this front page}
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
SECTION A {15)
QUESTION 1
[10]
Identify the disease/infection that is associated with the following:
1.1
Ring form trophozoites found on the blood smear of a patient who has
a history of travelling to Ohangwena region for a holiday.
(2)
1.2
Hallucination and paralysis seen in a patient who was bitten by a wild
rabid dog while on an adventure.
(2)
1.3
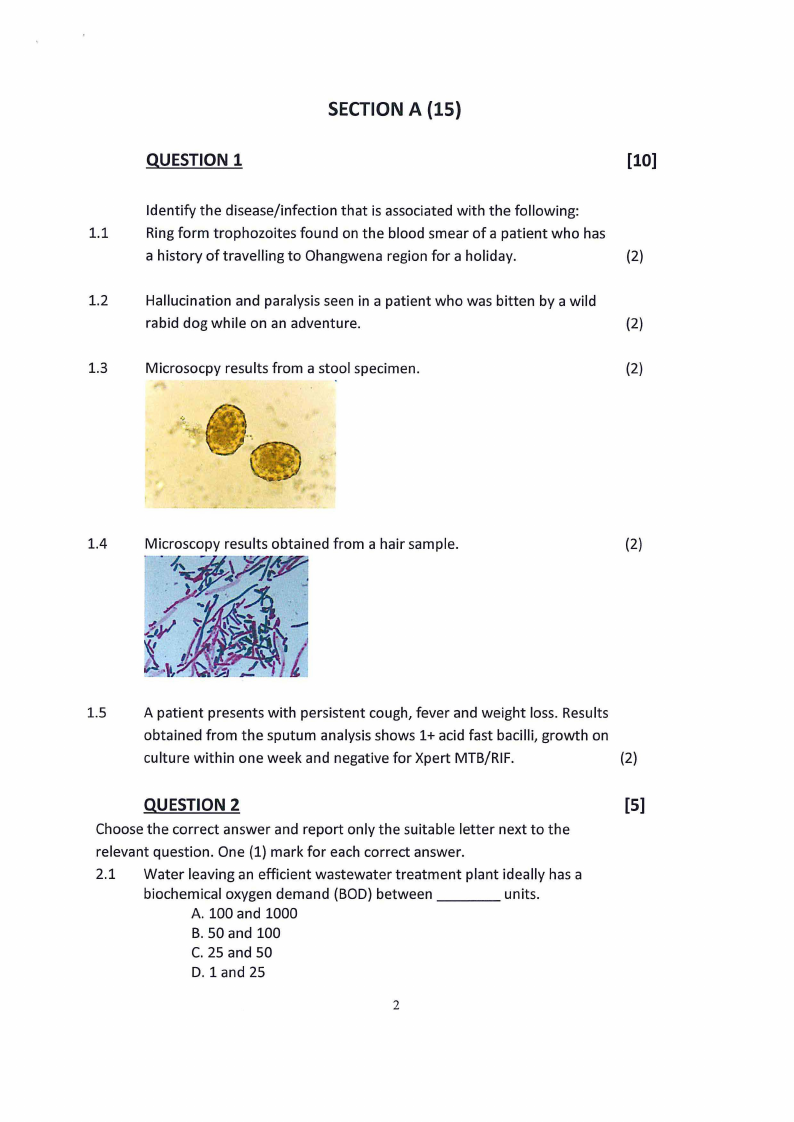
Microsocpy results from a stool specimen.
(2)
1.4
Microscopy results obtained from a hair sample.
(2)
\\~
: . ',. .,.,, 1·.
.-r:_~~~' -t.,.~
~.;.,r .,...,~Loi
.
\\6,
1.5
A patient presents with persistent cough, fever and weight loss. Results
obtained from the sputum analysis shows 1+ acid fast bacilli, growth on
culture within one week and negative for Xpert MTB/RIF.
(2)
QUESTION 2
[S]
Choose the correct answer and report only the suitable letter next to the
relevant question. One (1) mark for each correct answer.
2.1 Water leaving an efficient wastewater treatment plant ideally has a
biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) between ____
units.
A. 100 and 1000
B. 50 and 100
C. 25 and 50
D. 1 and 25
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

2.2 Microbes are used in secondary wastewater treatment to:
A. remove heavy metals
B. remove organic matter
C. remove chemical pollutants
D. remove pathogenic organisms
2.3 Which bacteria are truly waterborne bacterial pathogens?
A. Vibrio cholera
B. Campylobacter jejuni
C. Staphylococcus aureus
D. Clostridium perfringens
2.4 Why are "indicator organisms" used in drinking water analysis?
A. It is impractical to screen drinking water for every pathogen
B. Not all waterborne bacterial pathogens grow on agar plates
C. "Indicator organisms" signal definite presence of pathogens
D. "Indicator organisms" are normal flora
2.5 Which enzyme is specific for fecal coliforms and used for their identification
as "indicator organisms" in drinking water analysis?
A. ~-Glucosidase
B. ~-Glucuronidase
C. ~-Galactosidase
D. ~-Amylase
SECTION B (79)
QUESTION 3
[20]
3.1
Differentiate between the two forms of Hansen disease.
(5)
3.2
Give the definition for the acronym DOT in TB treatment.
(1)
3.4
Explain the five (5) essential elements reinforced by the DOT strategy. (5)
3.3
Define poly-drug resistant TB.
(2)
3.4
Interpret the following Line Probe Assay results with a specific mention
of the antibiotics.
(7)
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

--- -
QUESTION 4
[19]
4.1
4.1.1
4.1.2
4.1.3
A 40-year-old man living in the Karoo presented with influenza like
Symptoms such as coughing, chills, low grade fever, minimal chest
pains and weight loss. He was hospitalized and a CSFsample sent
to the laboratory. His history indicated that he worked with pigeons
and took part in pigeon racings.
Name the pathogen that the physicians suspected is the causative agent. (2)
Why is it important that the causative agent be identified and that the
patient is treated immediately?
(2)
Describe how you would process the sample in the laboratory to isolate
the etiological agent involved and expected results. Using the following
headings:
4.1.3.1
Microscopy
(2)
4.1.3.2
Culture
(2)
4.1.3.3 S
erology
(2)
4.2
Differentiate between P. vivax, P. malaria and P.falciparum under
The following:
(9)
4.2.1 Red blood cell size
4.2.2 Inclusion bodies
4.2.3 Number of merozoites in schizont
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 5
[20]
5.1
Differentiate between antigenic drift and antigenic shift.
(2)
5.2
Mention four similarities between measles and rubella viruses.
(4)
5.3
Enzyme linked Im mun no Sorbent Assays (ELISA)have been used in
diagnostic laboratories and provide the added advantage to improve
turnaround time. You are recruited by the Executive Director of the
Ministry of Health and Social Services to serve on a task force group
on "COVID-19 Diagnostics" tasked with the responsibility to develop an
ELISArapid test for COVID-19. Identify the preferred assay and
summarize the principle of the test assay your team will develop
(4)
5.4
What is the mode of action of Oxford/AstraZeneca vaccine.
(4)
5.5
5.5.1
5.5.2
Study the case study below.
In September 2004, a 15-year-old girl picked up a bat that she found in
a church located in Wisconsin. She sustained a small bite on her left index
finger, and having treated it with hydrogen peroxide, her mother decided
not to seek medical attention. Thirty-seven days after the bite Giese
developed neurological symptoms. She was admitted to the hospital
with tremors and trouble walking. Her condition continued to deteriorate,
and she was referred to a local hospital in Wisconsin.
Provide the disease.
(1)
Discuss the pathogenesis of the disease in 5.5.1
(5)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6
[20]
6.1 A 40-year-old male from North America is presenting with a cough, weight
loss, chest pain and fever. Examination of tissue from culture grown from the patient's
tissues yield mold-like structures as shown below.
Answer the following questions regarding the pathogen:
6.1.1 Identify the causative pathogen
(2)
6.1.2 Explain how you would culture the pathogen.
(3)
6.1.3 Discuss the pathogenesis of the disease caused by the organism.
(4)
6.2 A yeast is isolated from the oral cavity of an HIV patient diagnosed with
oral thrush.
6.2.1 Identify the presumptive causative agent.
(2)
6.2.2 Describe the organisms' expected results for the following:
(6)
(a) Gram stain
(b) Cultural morphology
(c) Chromogenic agar
6.3 Discuss the principle of Chromogenic agar
(3)
6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

SECTION C (15)
QUESTION 7
[15]
7.1
7.1.1
7.1.2
7.1.3
7.1.4
7.1.5
For the below statement provided, decide whether the statement is
True or False. Write only the number and "True" for a true statement
and "False" for a false statement. One mark for each correct answer.
(5)
The heat-labile diarrhea-type enterotoxins are pre-formed by Bacillus
cereus during growth of the bacteria in food.
The heat-stable emetic-type enterotoxin Cereulide of B. cereus acts as an
ionophore.
The majority of botulism cases are in infants.
Parents can help to prevent infant botulism in babies by avoiding to feed
honey to the baby.
Botulinum neurotoxins (BoNTs) prevent the release of SNAREproteins from
the nerve end by the degradation of acetylcholine.
7.2 Answer the following questions regarding pathogenic E. coli.
(5)
One mark for each correct answer.
7.2.1 What is the difference between Enteropathogenic E.coli (EPEC)and
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC)?
7.2.2 What is the function of the toxin?
7.2.3 What life-threatening complication might be caused by the production of
Shiga-like toxin (Stx) in the host?
7.2.4 What important pathogenicity factor or system is encoded by the "Locus of Enterocyte
Effacement" (LEE)pathogenicity island that is also present in EHECstrains?
7.2.5 What type of food is most often responsible for EHECinfections?
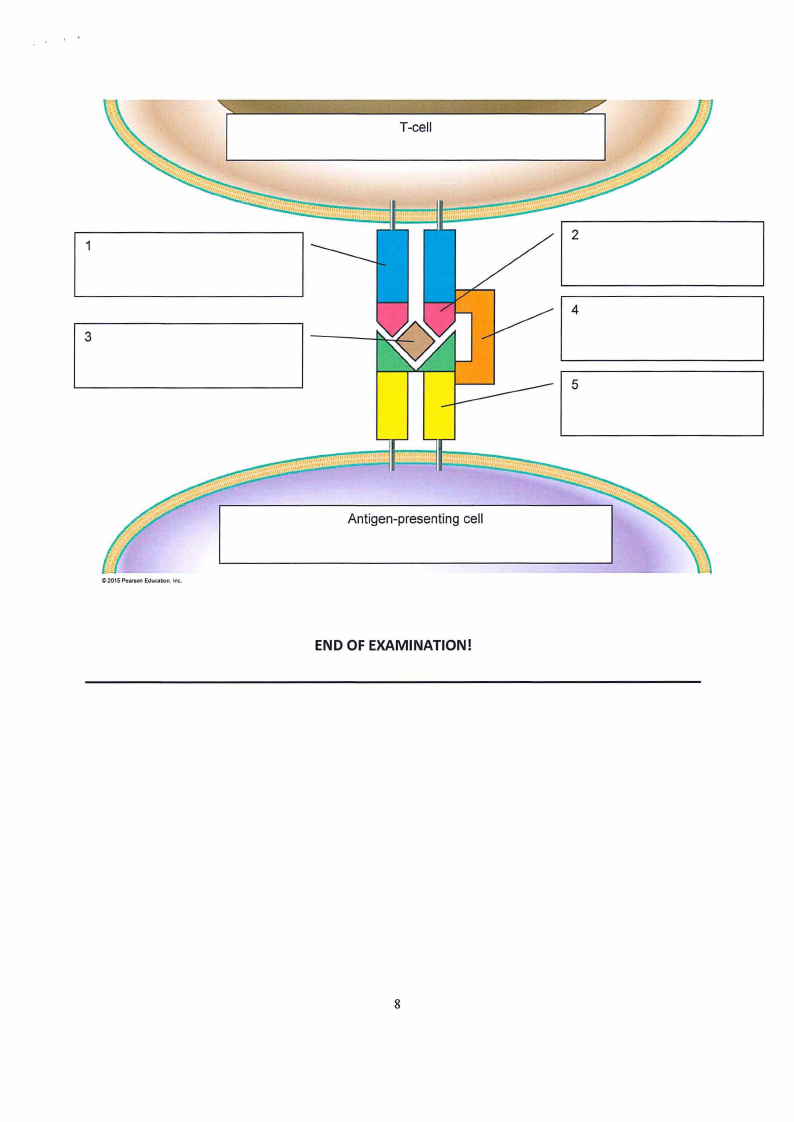
7.3 Please label the below image showing the action of superantigens accordingly. (5)
(See image on next page)
7
 |
8 Page 8 |
▲back to top |
:o2015PearsonEducalioo,lr,c.
Antigen-presenting cell
END OF EXAMINATION!
8





