 |
IPP521S - INTRODUCTION TO PHONETICS AND PHONOLOGY - 2ND OPP - JANUARY 2024 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTY OF COMMERCE, HUMAN SCIENCESAND EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNICATION AND LANGUAGES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF ENGLISH AND LINGUISTICS
QUALIFICATION CODE: (07BENL)
LEVEL: 5
COURSE CODE: IPP521S
COURSE NAME: INTRODUCTIONTO PHONETICSAND
PHONOLOGY
SESSION: JANUARY2024
TIME:
3 HOURS
PAPER: THEORY
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER(S}
MODERATOR:
SECOND OPPORTUNITY/SUPPLEMENTARY EXAMINATION PAPER
Dr Sylvia N lthindi
Ms Ndeshipandula Haimbodi
Ms Anneli Nghikembua
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Follow all instructions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. Give essay type responses where necessary.
5. Use blue or black ink only.
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 4 PAGESINCLUDINGTHE COVERPAGE
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
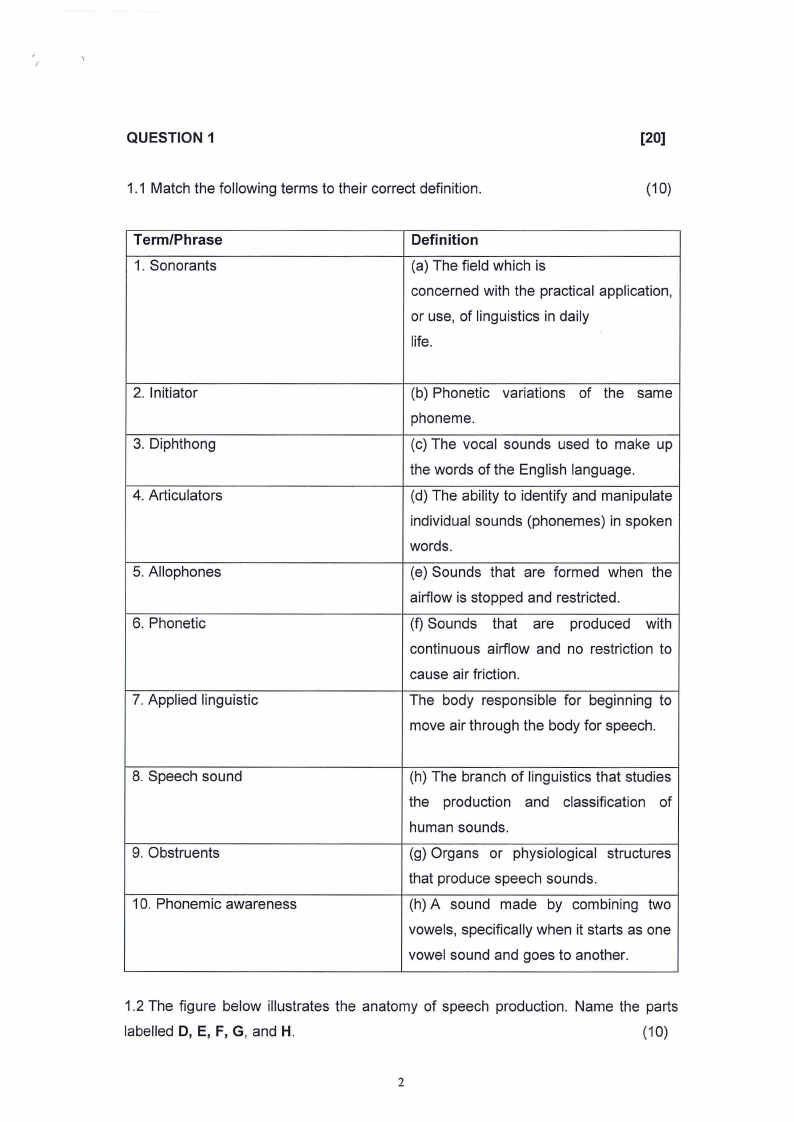
QUESTION 1
[20]
1.1 Match the following terms to their correct definition.
(10)
Term/Phrase
1. Sonorants
Definition
(a) The field which is
concerned with the practical application,
or use, of linguistics in daily
life.
2. Initiator
3. Diphthong
4. Articulators
5. Allophones
6. Phonetic
7. Applied linguistic
(b) Phonetic variations of the same
phoneme.
(c) The vocal sounds used to make up
the words of the English language.
(d) The ability to identify and manipulate
individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken
words.
(e) Sounds that are formed when the
airflow is stopped and restricted.
(f) Sounds that are produced with
continuous airflow and no restriction to
cause air friction.
The body responsible for beginning to
move air through the body for speech.
8. Speech sound
9. Obstruents
10. Phonemic awareness
(h) The branch of linguistics that studies
the production and classification of
human sounds.
(g) Organs or physiological structures
that produce speech sounds.
(h) A sound made by combining two
vowels, specifically when it starts as one
vowel sound and goes to another.
1.2 The figure below illustrates the anatomy of speech production. Name the parts
labelled D, E, F, G, and H.
(10)
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 2
[20]
2.1 With relevant examples clearly distinguish the following pairs of linguistic terms.
(a) The hard palate and alveolar ridge
(4)
(b) Monophthong and diphthong
(4)
(c) Assimilation and stopping
(4)
(d) Minimal pairs and allophones
(4)
(e) Nucleus and coda
(4)
Question 3
[20]
3.1 From the list of words below, identify the word that represents a minimal pair to the
following words.
(10)
Disk, three, bed, thing, hat, now, but, she, copy, seat, they, do
(a) Free
(b) Bat
(c) Fat
(d) Sit
(e) Day
(f) Know
(g) Sea
(h) Two
(i) Coffee
U) Think
3.2 Phonemes are produced differently according to the amount of air expelled from
the lungs. Provide the actual pronunciation for the phoneme /c/ in each of the following
words.
(8)
(a) Call
(b) Cell
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

(c) Choir
(d) Social
(e) Indict
(f) Climb
(g) Cello
(h) Chef
3.3 What can you deduce regarding the phoneme /c/ in 4.3 above?
(2)
QUESTION 4
[20]
4.1 Place the following sounds in the appropriate columns of the table below. Copy the
table in your answer book.
(10)
/ti, Im/, Id/, lg/, Ir/, /j/, /fl, lwl, /vi, /rif
Category
Obstruents
Sonorants
Sound
4.2 Explain how words are articulated in the following places of articulation. Give at
least three examples each.
(10)
(a) Bilabials
(b) Alveolorpalatal
QUESTION 5
[20]
Give a detailed description of the three air stream mechanisms used in speech
production. Your descriptions should include the initiators and organs involved in each
airstream.
(20)
THE END
4





