 |
HAM711S - HAEMATOLOGY 3 -1ST OPP - JUNE 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmI BI AunIVER s ITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnOLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF HEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF MEDICAL LABORATORYSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE:08BMLS
LEVEL: 7
COURSECODE: HAM711S
COURSENAME: HAEMATOLOGY 3
SESSION:
JUNE 2022
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
EXAMINER(S)
MODERATOR:
First Opportunity Examination
Dr Maurice Nyambuya
Dr Aaron Maramba
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Pen
2. Calculator
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 7 PAGES(Including this front page)
Page I of7
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A {60 MARKS)
QUESTION 1
Answer all the following multiple questions and select the best suitable answer.
[15]
1.1 The typical immunophenotype of CLL/ SLLtumour cells includes:
(1)
a) Bright expression of surface lg and B- cell markers, along with positivity for CDS
and CD23
b) Dim expression of surface lg and B- cell markers, along with positivity for CDSand
CD23
c) CD10, CD20 and CDS positivity
d) Cyclin Dl, CD20 and CDSpositivity
1.2 Which of the following imparts a poor prognosis for patients with CLL/SLL?
(1)
a) CD38 negativity
b) ZAP- 70 negativity
c) Presence of deletion 13q
d) Presence of trisomy 12
1.3 A 60-year-old man presented with weight loss and fatigue. Examination of complete
blood counts showed anaemia and leucocytosis, peripheral smear shows >55% of the (l)
cells having the morphology (in picture). Which of the following is the correct statement
regarding this condition?
a) On immunophenotyping the cells strongly express surface lgM and lgD.
b) CD 5 and CD 23 are positive in 100 % cases
c) ZAP 70 and CD 38 are always negative
d) All are true
1.4 A distinct feature seen in hairy cell leukaemia but not in hairy cell variant leukaemia is: (1)
a) Splenomegaly
b) Circulating neoplastic lymphocytes in the peripheral blood
c) Pancytopenia
d) Prominent nucleoli
Page 2 of7
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.5 Tartrate resistant alkaline phosphatase (TRAP)positivity is seen in all of the
(1)
conditions except
a) Gaucher disease
b) Hodgkins lymphoma
c) Osteoporosis
d) Osteoclastoma
1.6 The following cell was seen on the bone marrow biopsy of a patient who presented with (1)
lymphadenopathy, night sweats and who had recently had Epstein Barr virus infection.
What is the cell called?
.
..... .t~-~---
~-
·~,."-
•• ¥
·_ r:l .~;t.. .
"-~.
,·
·'t .
a) Megakaryocyte
b) Burkit's lymphoma cell
c) Reed-Sternberg cell
d) Lacunar cell
1.7 What disorder is characterised by the above cell?
(1)
a) Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
b) Hodgkin's lymphoma
c) Burkitt's lymphoma
d) Acute myeloid leukaemia
1.8 A definition of the dense tubular system of the platelet would be
a) A system which is important to allow entry of substances not platelet.
(1)
b) A storage site for calcium
c) A storage site for von Willebrand factor, fibrinogen and immunoglobulin
d) Microtubules which support the plasma membrane
1.9 In the maturation of the megakaryocyte.
a) The cell becomes polyploidy
(1)
b) The nucleus matures before the cytoplasm
c) The process takes 7 days
d) All of the above
1.10 What is needed to initiate fibrinolysis?
a) Tissue plasminogen activator must bind to fibrinogen
(1)
b) Thrombin must bind to fibrin and cleave peptide bonds to form fibrin degradation
Page 3 of7
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

products
c) Tissue plasminogen activator must bid to fibrin and convert plasminogen to plasmin
d) Degradation products D and E increase in circulation
1.11 A definition of haemostasis
(1)
a) The process of maintaining body temperature
b) The regulation of kidney function
c) A balanced process which maintains blood flow and prevents blood loss
d) A balanced process which stimulates clot formation
1.12 Hodgkin's lymphoma is associated with the Epstein Barr virus. Which of the following (1)
would be a characteristic of malignant cell affected by the virus?
a) Chromosome 14 abnormalities
b) CD15 and CD30 positivity using immunohistochemistry
c) Numerous Hodgkin's mononuclear cells
d) LMP1 positivity using immunohistochemistry
1.13 Primary haemostasis involves the following;
(1)
a) Factor VII, Tissue factor and Calcium
b) Thrombin, Fibrinogen and Pro-thrombin
c) Platelets, Endothelial cells and vessel wall
d) Endothelial cells, Factor XII and Fibrin
1.14 How do endothelia cell prevent abnormal clotting?
(1)
a) The secretion of Tissue factor
b) The expression of adhesion molecules on the surface of the cells
c) The exposure of collagen and the secretion of plasminogen activator
d) A negative charge and the secretion of nitric oxide
1.15 What is the action of Aspirin on the platelets?
(1)
a) Inhibits the action of cyclo-oxygenase
b) Interferes with platelet aggregation by preventing shape changes
c) Inhibits the release of alpha granule contents
d) Stimulates fibrinolysis
QUESTION 2
[20]
2.1 Immature B-cell neoplasms are broadly categorised as otherwise not specified or with
(12)
recurrent genetic abnormalities. List any three (3) categories that fall into the "with
recurrent genetic abnormalities" group discuss the cytogenetic abnormality.
Page 4 of7
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

2.2 There are 4 major tests used to reflect abnormal serum proteins, especially in
(4)
diagnosing plasma cell neoplasms. Name and briefly describe the rationale behind any
two (2) tests.
2.3 Patients suffering from acute leukaemia usually suffer from infection, fatigue, shortness (4)
of breath, bruising and bleeding. Explain why they suffer from these symptoms
QUESTION 3
[25]
3.1 By means of a table, highlight the difference between Multiple myeloma and
(lS)
Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia.
3.2 Define primary and secondary haemostasis and briefly discuss the function of each.
(4)
3.3 Describe the pathogenesis of thrombasthaenia (Glanzmans Disease).
(6)
SECTION B (40 MARKS)
QUESTION 4
[15]
A SO-year-old male presented with recurrent spontaneous and trauma-induced hemarthroses
in both the ankles and knees, episodes of gastrointestinal and soft tissue bleeding, and bleeding
with dental procedures. Coagulation tests were ordered and his results were as follows.
Test
APTT
INR
Factor VIII
% von Willebrand antigen
Ristocetin cofactor
Von Willebrand multi mer test
Patients results
61.2 s
1.04
50%
16%
<12
PlasmavWFmultimers barely
detectable, but a distribution
normal range of multimer sizes
appearsto be present.
Reference range
24-30 s
0.9-1.1
55-180%
50-200%
50%-200%
Normal size and
distribution
4.1 What is this patient's most likely diagnosis? Explain your answer
(8)
4.2 Outline the pathophysiology of the other major subtypes of this condition.
(4)
4.3 Briefly discuss the treatment options for these subtypes.
(3)
Page 5 of7
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
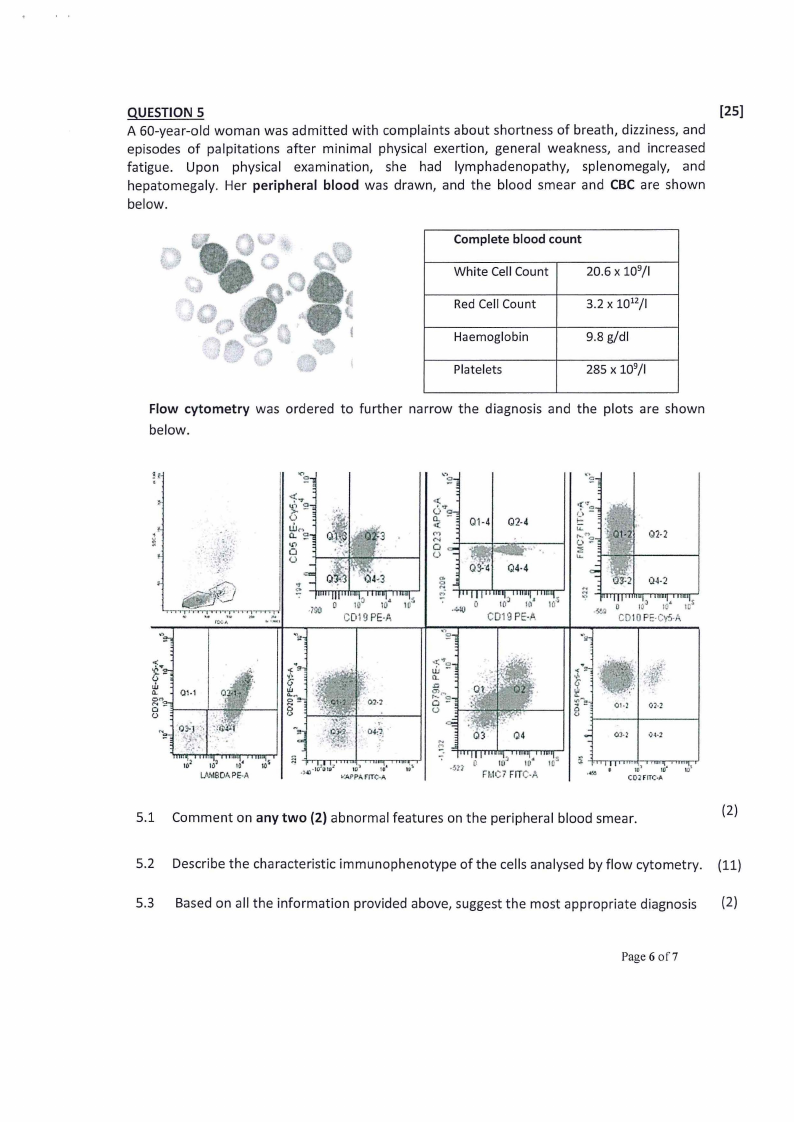
QUESTION 5
[25]
A 60-year-old woman was admitted with complaints about shortness of breath, dizziness, and
episodes of palpitations after minimal physical exertion, general weakness, and increased
fatigue. Upon physical examination, she had lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, and
hepatomegaly. Her peripheral blood was drawn, and the blood smear and CBC are shown
below.
Complete blood count
White Cell Count
20.6 X 109/1
Red Cell Count
3.2 X 1012/1
Haemoglobin
9.8 g/dl
Platelets
285 X 109/1
Flow cytometry was ordered to further narrow the diagnosis and the plots are shown
below.
Q2-2
dfi)
"T"T.....,. rrrr.rr.;rn-r,-'l
fC<:11
-ISO O 10~ 10•
CD19PE-ft.
-~ 0 CD19PE-
N
N
"
-¾~
~,,
0
IQa IO' 10s
CDIOPE-CyS-
-.. ~. 1t·
02·2
10" 104
LAMBDAPE-A
-~n
0
IOJ 10'
FMC7FITC-A
105
C; ....
04-2
.,. ,.. ,.,
CDHITC•A
5.1 Comment on any two (2) abnormal features on the peripheral blood smear.
(2)
5.2 Describe the characteristic immunophenotype of the cells analysed by flow cytometry. (11)
5.3 Based on all the information provided above, suggest the most appropriate diagnosis (2)
Page 6 of7
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

5.4 Which karyotype is associated with this malignancy?
(2)
5.5 Describe how the abnormality in 5.4 drives the pathogenesis of this disorder.
(8)
Total [100 marks]
Page 7 of7





