 |
CEY720S - CROP ECOPHYSIOLOGY - 1ST OPP - NOV 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE AnD TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,NATURAL RESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
DEPARTMENTOF AGRICULTUREAND NATURALRESOURCESSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOROF HORTICULTURE
QUALIFICATION CODE: 07BHOR
LEVEL: 7
COURSECODE: CEY7205
COURSENAME: CROPECOPHYSIOLOGY
DATE: NOVEMBER 2022
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRSTOPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER(S) Dr Norman Muzhinji
MODERATOR: Dr Brian Makeredza
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly .
. 3. Number the answers clearly.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. Examination question paper
2. Answering book
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 4 PAGES{Excluding this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A: Multiple choice questions (12 marks}
1. Which hormone is most involved in response to abiotic stresses?
A. Abscisic acid
B. Ethylene
C. Auxin
D. Gibberellic acid
2. Which amino acid accumulates under water stress condition in plants
A. Praline
B. Methionine
C. Valine
D. Leucine
3. In C3 and C4 plants, primary carboxylation takes place with the help of
A. PEPcarboxylse _andpyruvate carboxylase respectively
B. RuBPcarboxylase and PEPcarboxylase respectively
C. PEPcaboxylase and RuBPcarboxylase respectively
D. RuBP carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase respectively
4. Which enzyme plays major role in opening and closing of stomata?
A. Beta-amylase
B. Pyruvic kinase
C. RuDP
D. PEPcarboxylase
5. Why isn't lime {CaCO3} a very good amendment choice for the treatment of sodic soils in
Namibia?
A. Lime is scarce in Namibia, and it would cost too much
B. Lime containing Ca2+and wont dissolve in alkaline soil therefore not effective in the
reclamation of sodic soils
C. Many Namibian soils already contain high levels of lime
D. Sadie soils do not occur in Namibia
6. Which one is not a cause of water logging?
A. Rainfall
B. Floods
C. Roads
D. Sodium
7.The plant hormone that plays a role in closing of the stomata is;
A. Auxin
B. Abscisic acid
C. Gibberellin
1
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

D. Ethylene
E. Cytochrome
8. Plant grown in saline soils is primarily inhibited by
A. Poor water uptake due to osmotic stress
B. pH less than 8.5
C. Poor soil structure
D. Poor nutrient uptake
9. Transpiration is mostly affected by
A. Humidity
B. Temperature
C. Light
D. Wind
10.Which chemicals are involved in flooding injury in crops?
A. Acetic acid
B. Acetaldehyde
C. Alcohol
D. All of the above
11. An inadequate supply of water can compromise plants' ability to carry out
photosynthesis. How do desert plants prevent such water loss when they are subjected
to high heat?
A. By using CAM photosynthesis and by closing stomata! pores during the night
B. By using CAM photosynthesis and by opening stomata! pores during the night
C. By using CAM photosynthesis and by keeping stomata! pores closed at all times
D. By bypassing CAM photosynthesis and by keeping stomata! pores closed at night
12. Which type of plants are adapted to the arid conditions of Namibia
A. C4 plants
B. C3 plants
C. CAM plants
D. A and Care correct
2
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

Section B: Answer all questions (88 MARKS}
1. a. Describe any three (3) environmental factors that influence the geographical
distribution of plant species in Namibia, give examples.
(6)
b. From your answer in la, select any two (2) factors and describe how you can modify
them to suit the basic growing needs of a crop of your choice.
(4)
2. Write short notes on the following, giving examples
a. Abiotic Stress of plants
(2)
b. Genotype and environment interactions in plants.
(2)
c. Plant phenotypic Plasticity.
(2)
d. Dedifferentiation in plants.
(2)
e. Distinguish between acclimation and adaptation to abiotic stress of plants.
(6)
3. Plants have adapted to different environmental conditions. One of the most important
conditions they have adapted to is soil salinity and sodicity.
a. Describe at least five (5) factors that contribute to salinity in Namibian soils. (10)
b. Explain at least four (4) effects of salinity on growth and development of
horticultural crops.
(8)
c. Imagine you have been instructed to grow vegetables in saline soils. Describe at least
four (4) strategies that you would implement to successfully produce vegetables in
such kind of soils.
(4)
4. Water potential is represented by the following equation.
llJw=llJs+ llJp+ llJg+ llJm.
a. Explain what each component of the equation stands for?
(5)
b. Describe how transpiration and the cohesion-tension theory can explain the
movement of water from the roots through the leaves to the atmosphere.
(10)
c. Assume, you have just been appointed as a horticulturalist responsible for crop
production in Karasburg, a well-known drought prone area. You have been tasked
with selecting a crop that you can grow in drought conditions
Describe some of the morphological, physiological and biochemical mechanisms that
the crop will use for it to survive under drought conditions.
(9)
3
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
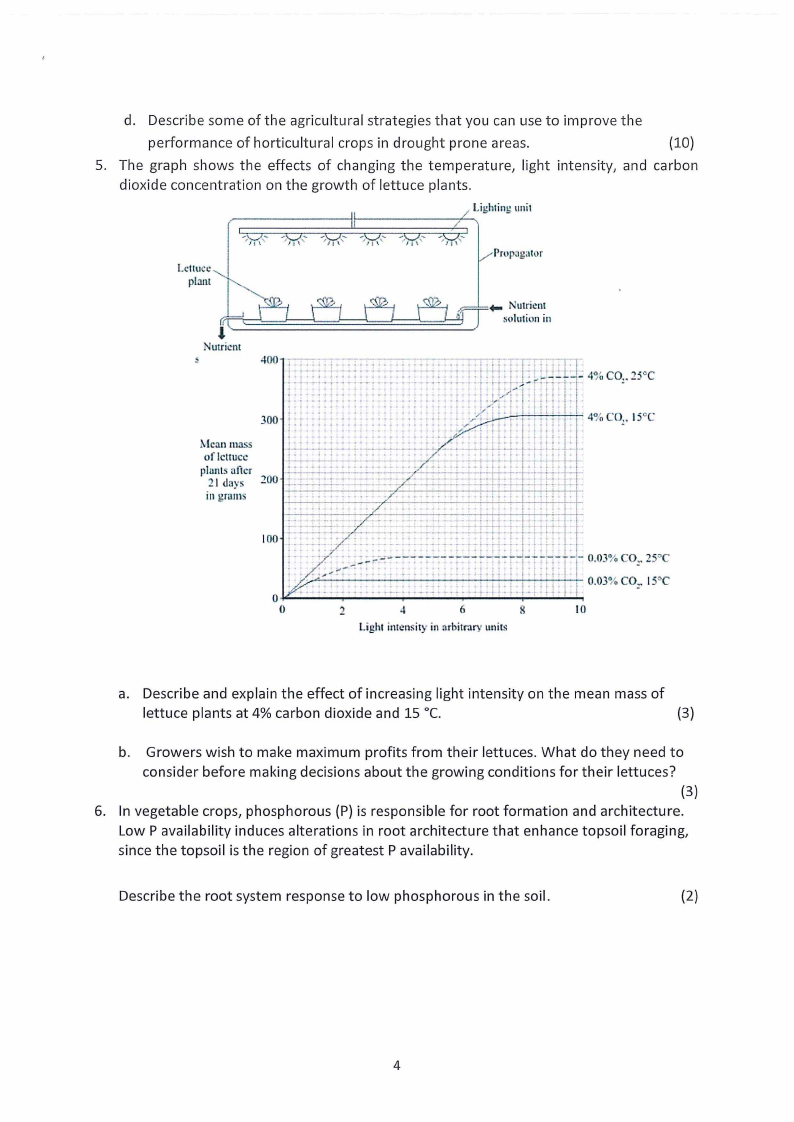
d. Describe some of the agricultural strategies that you can use to improve the
performance of horticultural crops in drought prone areas.
{10)
5. The graph shows the effects of changing the temperature, light intensity, and carbon
dioxide concentration on the growth of lettuce plants.
t-----------
/ Ligl11inguni1
Lcltucc
plant
~='
l
Nutrient
Propagalvr
==!:::_::====_r-,c=::0===~==~~~=+C- R=soN~luu·ttiroinenint
l\\ilcanmass
of lettuce
pluntsalkr
21 <lays
in grams
100 fl'G*::I~~(°qfr-F., W.re f'~tn
, . .( ~~---;-;-7:•·'... -~·ti_~ ·1•1 :I~·;!
0-·03 ,() 0
1 • ,;:.,,
•
•.
, , • , • L · 1, t 1 l ·1 , r 1
l,1,(:.~: .. : .... :... , ..:.:~:.... ,.(:(!:[. :i!U.j 0.03¾C0 1.l5°C
0 ......----...---
0
2
......-.------------.....------
......
4
6
S
10
l.ight intensity in nrbitr:ir,•units
a. Describe and explain the effect of increasing light intensity on the mean mass of
lettuce plants at 4% carbon dioxide and 15 °C.
{3)
b. Growers wish to make maximum profits from their lettuces. What do they need to
consider before making decisions about the growing conditions for their lettuces?
{3)
6. In vegetable crops, phosphorous (P) is responsible for root formation and architecture.
Low P availability induces alterations in root architecture that enhance topsoil foraging,
since the topsoil is the region of greatest P availability.
Describe the root system response to low phosphorous in the soil.
{2)
4
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |






