 |
CLC621S - CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 2B - 1ST OPP - NOVEMBER 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAm I BIA un IVERSITY
OFscience AnorecHnOLOGY
Facultyof Health, Natural
Resourcesand Applied
Sciences
School of Health Sciences
Department of Clinical
Health Sciences
13Jackson Kaujeua Street
Private Bag 13388
Windhoek
NAMIBIA
T: +264 612072970
F: +264 61 207 9970
E: dchs@nust.na
W: www.nust.na
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR of MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: 0SBMLS
LEVEL: 6
COURSE: CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 2B
COURSE CODE: CLC621S
DATE: NOVEMBER 2023
SESSION: 1
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
FIRST OPPORTUNITY: EXAMINATION QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER:
MODERATOR:
MRS. CARA MIA DUNAISKI
MRS. EDWIG SHINGENGE
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Answer all questions on the separate answer sheet.
2. Please write neatly and legibly.
3. Do not use the left side margin of the exam paper. This must be allowed for the
examiner.
4. No books, notes and other additional aids are allowed.
5. Mark all answers clearly with their respective question numbers.
PERMISSIBLE MATERIALS:
1. Non-Programmable Calculator
ATTACHMENTS:
1. Reference values
This question paper consists of 7 pages including this front page
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS
(30 MARKS]
QUESTION 1:
[10 MARKS]
Write short notes on the pre-analytical and analytical variables of the following laboratory
tests and their preferred specimens:
1.1 Faecalfat analysis.
(5)
1.2 Special considerations when measuring serum ammonia.
(5)
QUESTION 2:
[10 MARKS]
Review the following sets of results of patients that are presenting with symptoms
associated with hepatic disease. Answer the questions that follow:
Patient A
Patient B
Total Bilirubin: 230µmol/L
Total Bilirubin: 45µmol/L
Direct Bilirubin: lµmol/L
Direct Bilirubin: 22µmol/L
Total Protein: 63g/L
Total Protein: 55g/L
Albumin: 42g/L
Albumin: 30g/L
ALT: 5U/L
ALT: 800U/L
AST: 88U/L
AST: 390U/L
GGT:40U/L
GGT: 133U/L
ALP: 80U/L (Ref range:0-249U/L)
ALP: 66U/L (Ref range:40-130U/L)
2.1 Indicate which patient is more likely to be suffering from haemolytic disease of the (2)
new born. Motivate your answer.
2.2 Which patient is more likely to produce pale stools? Motivate your answer.
(2)
2.3 Indicate whether the following will be increased, normal, decreased or absent for (2)
each of patient A and B.
2.3.1 Urine urobilinogen
2.3.2 Urine bilirubin
2.4 Comment on the AST/ALT ratio of patient A.
(2)
2.5 Assuming that your laboratory performs ionised Ca2+ measurements only; would (2)
you correct your calcium measurement? Motivate your answer.
Clinical Chemistry 2B (CLC621S)
1st Opportunity- November 2023
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
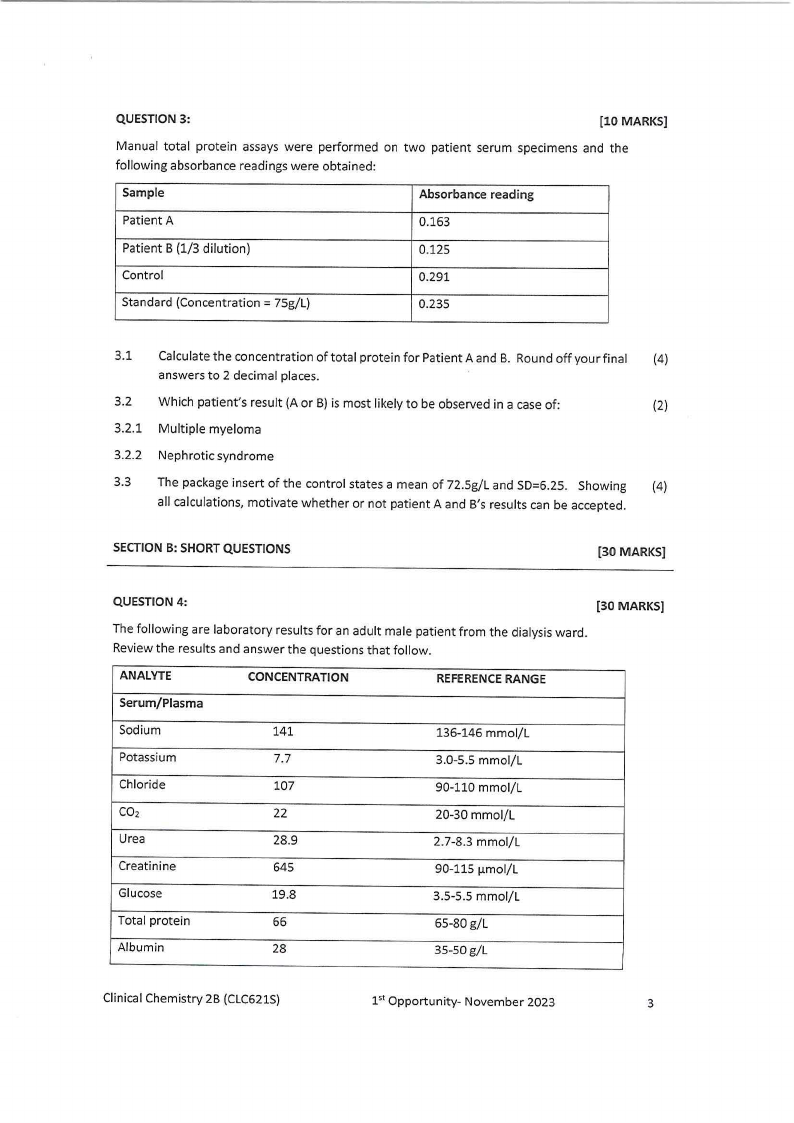
QUESTION 3:
[10 MARKS]
Manual total protein assays were performed on two patient serum specimens and the
following absorbance readings were obtained:
Sample
Absorbance reading
Patient A
0.163
Patient B (1/3 dilution)
0.125
Control
0.291
Standard (Concentration = 75g/L)
0.235
3.1 Calculate the concentration of total protein for Patient A and B. Round off your final (4)
answers to 2 decimal places.
3.2 Which patient's result (A or B) is most likely to be observed in a case of:
(2)
3.2.1 Multiple myeloma
3.2.2 Nephrotic syndrome
3.3 The package insert of the control states a mean of 72.5g/L and SD=6.25. Showing (4)
all calculations, motivate whether or not patient A and B's results can be accepted.
SECTION B: SHORT QUESTIONS
[30 MARKS]
QUESTION 4:
[30 MARKS]
The following are laboratory results for an adult male patient from the dialysis ward.
Review the results and answer the questions that follow.
ANALYTE
CONCENTRATION
REFERENCERANGE
Serum/Plasma
Sodium
Potassium
Chloride
CO2
Urea
Creatinine
Glucose
Total protein
Albumin
141
7.7
107
22
28.9
645
19.8
66
28
136-146 mmol/L
3.0-5.5 mmol/L
90-110 mmol/L
20-30 mmol/L
2.7-8.3 mmol/L
90-115 µmol/L
3.5-5.5 mmol/L
65-80 g/L
35-50 g/L
Clinical Chemistry 2B (CLC621S)
1'1 Opportunity- November 2023
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
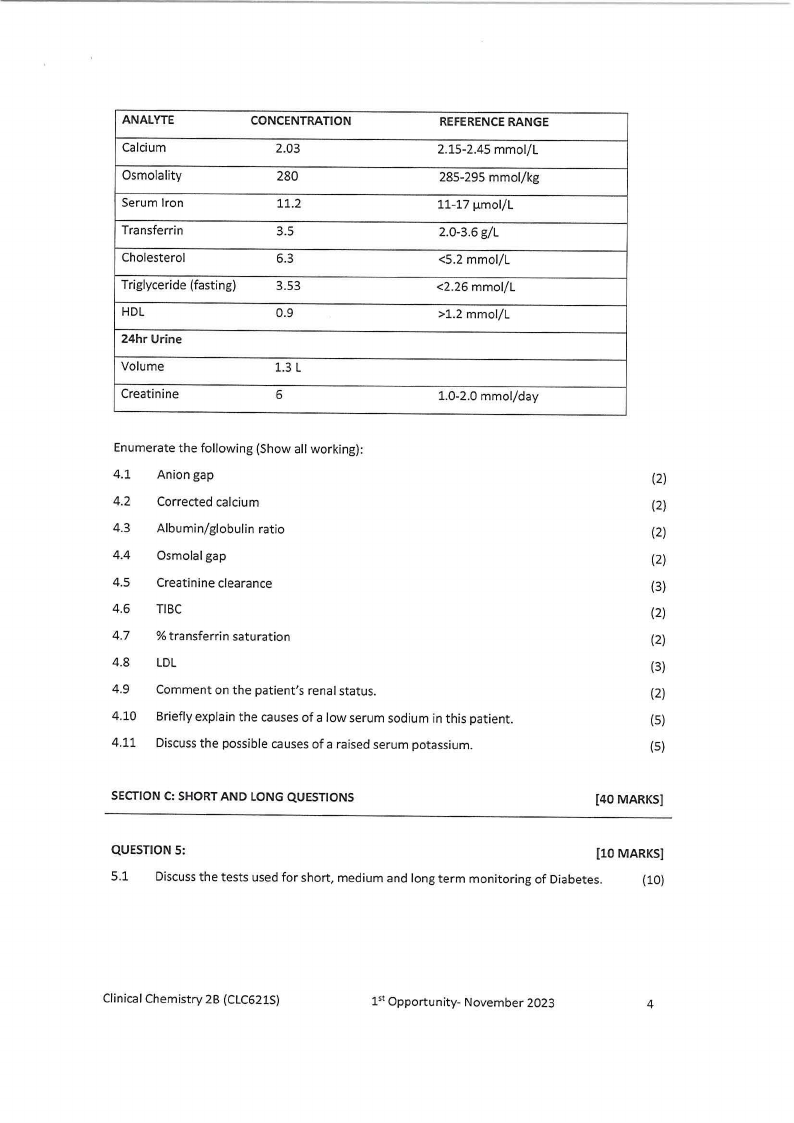
ANALYTE
CONCENTRATION
Calcium
2.03
Osmolality
280
Serum Iron
11.2
Transferrin
3.5
Cholesterol
6.3
Triglyceride (fasting)
3.53
HDL
0.9
24hr Urine
Volume
1.3 L
Creatinine
6
REFERENCE RANGE
2.15-2.45 mmol/L
285-295 mmol/kg
11-17 µmol/L
2.0-3.6 g/L
<5.2 mmol/L
<2.26 mmol/L
>1.2 mmol/L
1.0-2.0 mmol/day
Enumerate the following (Show all working):
4.1 Anion gap
(2)
4.2 Corrected calcium
(2)
4.3 Albumin/globulin ratio
(2)
4.4 Osmolal gap
(2)
4.5 Creatinine clearance
(3)
4.6 TIBC
(2)
4.7 % transferrin saturation
(2)
4.8 LDL
(3)
4.9 Comment on the patient's renal status.
(2)
4.10 Briefly explain the causes of a low serum sodium in this patient.
(5)
4.11 Discussthe possible causes of a raised serum potassium.
(5)
SECTION C: SHORT AND LONG QUESTIONS
[40 MARKS]
QUESTION 5:
[10 MARKS]
5.1 Discussthe tests used for short, medium and long term monitoring of Diabetes.
(10)
Clinical Chemistry 2B (CLC621S)
1st Opportunity- November 2023
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6: LONG QUESTION
[10 MARKS]
6.1 Blood gas samples are very delicate and are to be treated as 'urgent samples'.
(10)
Outline the special conditions considered during the pre-analytical and analytical
phase for arterial blood gas analysis.
QUESTION 7: LONG QUESTION
[10 MARKS]
7.1 Give a detailed description of how the body degrades haemoglobin and the fate of (10)
molecules produced during the catabolic process.
QUESTION 8: LONG QUESTION
[10 MARKS]
8.1 Using relevant examples describe the five methodologies where enzymes are used (10)
as reagents in the clinical chemistry laboratory.
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Clinical Chemistry 28 (CLC621S)
l't Opportunity- November 2023
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
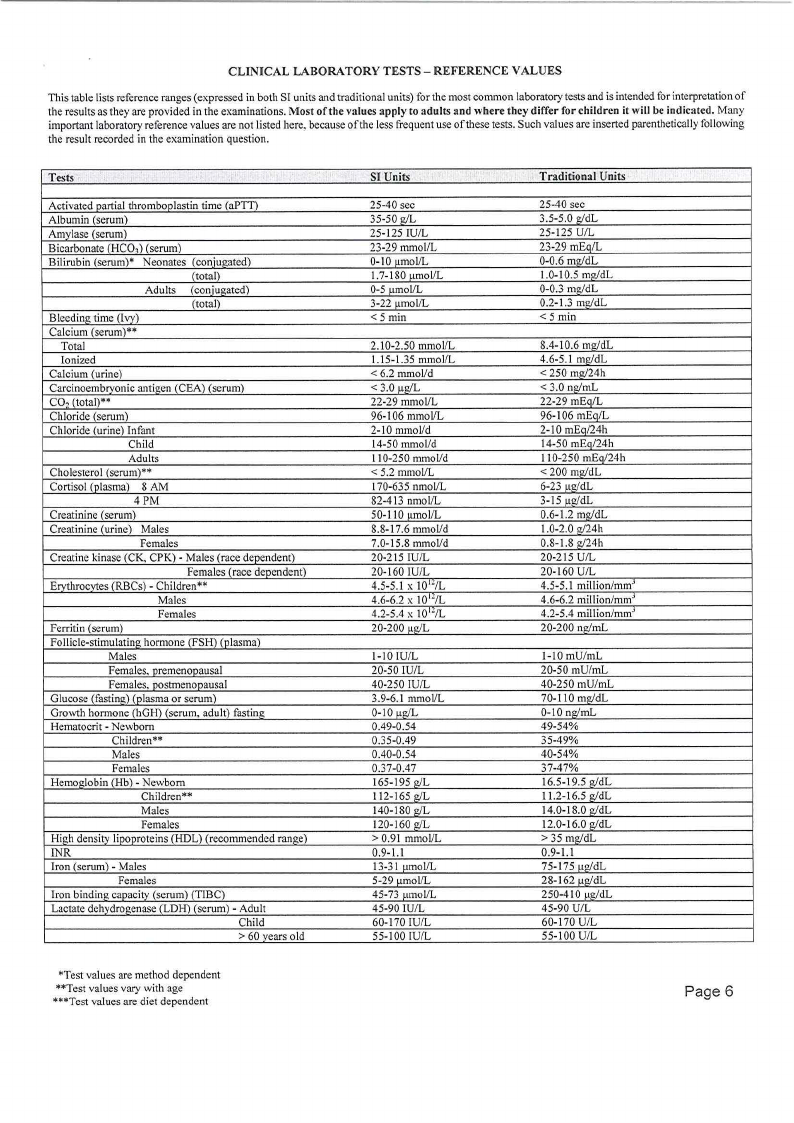
CLINICAL LABORATORY TESTS - REFERENCE VALUES
This table lists reference ranges (expressed in both SI units and traditional units) for the most common laboratory tests and is intended for interpretation of
the results as they are provided in the examinations. Most of the values apply to adults and where they differ for children it will be indicated. Many
important laboratory reference values are not listed here, because of the less frequent use of these tests. Such values are inserted parenthetically following
the result recorded in the examination question.
Tests
Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTI)
Albumin (serum)
Amylase (serum)
Bicarbonate (HCO,) (serum)
Bilirubin (serum)* Neonates (conjugated)
(total)
Adults (conjugated)
(total)
Bleeding time (Ivy)
Calcium (serum)**
Total
Ionized
Calcium (urine)
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) (serum)
CO2 (total)**
Chloride (serum)
Chloride (urine) Infant
Child
Adults
Cholesterol (serum)**
Cortisol (plasma) SAM
4PM
Creatinine (serum)
Creatinine (urine) Males
Females
Creatine kinase (CK. CPK) • Males (race dependent)
Females (race dependent)
Ervthrocvtes (RBCs) • Children**
Males
Females
Ferritin (serum)
Follicle-stimulating hom1one (FSH) (plasma)
Males
Females. premenopausal
Females. postrnenopausal
Glucose (fasting) (plasma or serum)
Growth hormone (hGH) (serum, adult) fasting
Hematocrit • Newborn
Children**
Males
Females
Hemoglobin (Hb) • Newborn
Children**
Males
Females
High density lipoproteins (HDL) (recommended ran11;e)
INR
Iron (serum)· Males
Females
Iron bindin11c:apacity (serum) (TIBC)
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) (serum) • Adult
Child
> 60 years old
..
SI Units
25-40 sec
35-50 l!/L
25-125 IU/L
23-29 mmol/L
0-10 umol/L
1.7-180 umol/L
0-5 umol/L
3-22 umol/L
< 5 min
2.10-2.50 mmol/L
1.15-1.35 mmol/L
<6.2 mmol/d
< 3.0 µg/L
22-29 mmol/L
96-106 mmol/L
2-10 mmol/d
14-50 mmol/d
110-250 mmol/d
< 5.2 mrnol/L
170-635 nmol/L
82-413 nmol/L
50-110 ~lmol/L
8.8-17.6 mmol/d
7.0-15.8 mmol/d
20-215 IU/L
20-160 IU/L
4.5-5.1 x 101·/L
4.6-6.2 x 1011/L
4.2-5.4 X 101"/L
20-200 ug/L
1-10 IU/L
20-50 IU/L
40-250 IU/L
3.9-6.1 mmol/L
0-10 u!'/L
0.49-0.54
0.35-0.49
0.40-0.54
0.37-0.47
165-195 l!/L
112-165 g/L
140-180 g/L
120-160 l!/L
> 0.91 mmol/L
0.9-1.1
13-31 umol/L
5-29 umol/L
45-73 umol/L
45-90 IU/L
60-170 IU/L
55-100 IU/L
Traditional Units
25-40 sec
3.5-5.0 g,fdL
25-125 U/L
23-29 rnEa/L
0-0.6 ml!/dL
1.0-10.5 m2/dL
0-0.3 m2/dL
0.2-1.3 mg/dL
<5 min
8.4-10.6 mvdL
4.6-5.1 m!!/dL
< 250 m!!/24h
< 3.0 nvmL
22-29 mEa/L
96-1 06 mEo/L
2-10 mEo/24h
14-50 mEo/24h
110-250 rnEa/24h
< 200 ml!/dL
6-23 uv'dL
3-15 ug/dL
0.6-1.2 m~dL
1.0-2.0 l!/24h
0.8-1.8 g,f24h
20-215 U/L
20-160 U/L
4.5-5.1 million/mm 3
4.6-6.2 million/mm'
4.2-5.4 million/mm 3
20-200 n!!/mL
1-10 mU/mL
20-50 mU/mL
40-250 mU/mL
70-110 mv'dL
0-10 ng/mL
49-54%
35-49%
40-54%
37-47%
16.5-19.5 l!/dL
11.2-16.5 g/dL
14.0-18.0 2/dL
12.0-16.0 !!/dL
>35 mg/dL
0.9-1.1
75-175 ll<:>ldL
28-162 110/dL
250-410 ug/dL
45-90 U/L
60-170 U/L
55-100 U/L
*Test values are method dependent
**Test values vary with age
***Test values are diet dependent
Page 6
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |
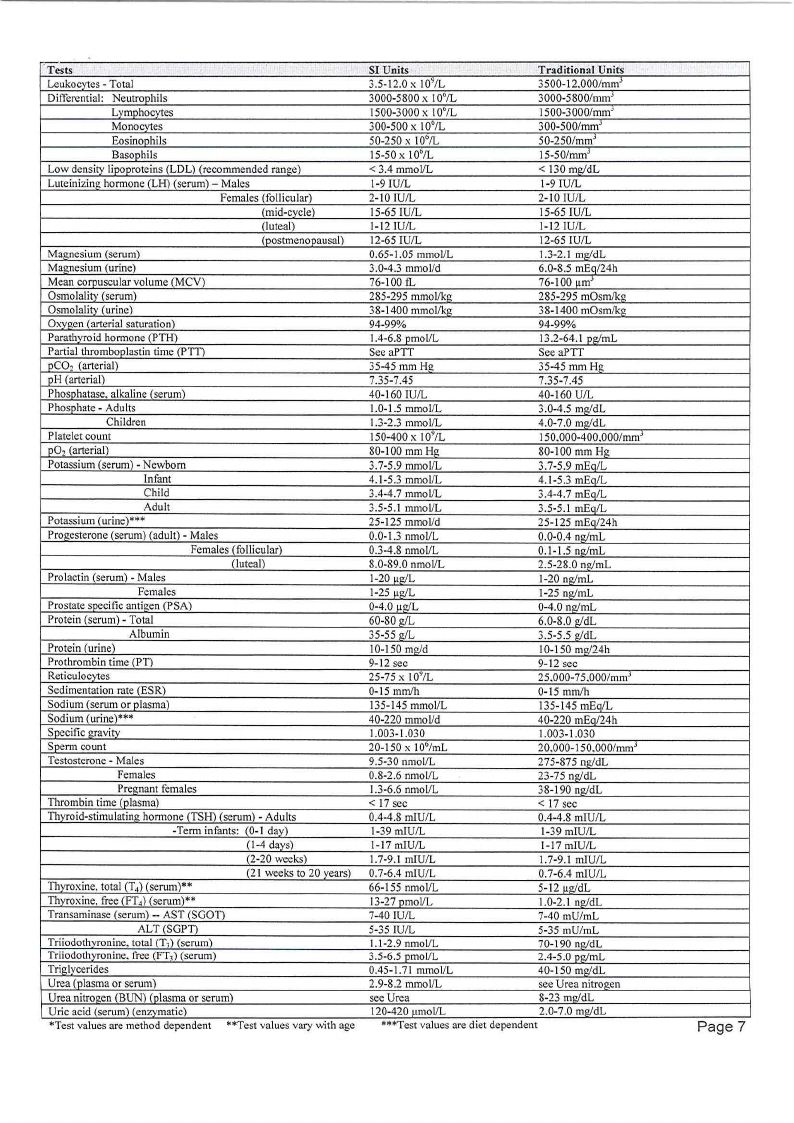
Tests
Leukocvtes - Total
Differential: Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
Monocvtes
Eosinophils
Basophils
Low density lipoproteins (LDL) (recommended range)
Luteinizin11h. ormone (LH) (serum) - Males
Females (follicular)
(mid-cycle)
(luteal)
(postmenopausal)
Magnesium (serum)
Magnesium (urine)
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV)
Osmolalitv (serum)
Osmolality (urine)
Oxy11.en(arterial saturation)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Partial thromboplastin time (PIT)
pCO, (arterial)
PH (arterial)
Phosphatase, alkaline (serum)
Phosphate - Adults
Children
Platelet count
pO, (arterial)
Potassium (serum) - Newborn
Infant
Child
Adult
Potassium (urine)***
Progesterone {serum) (adult) - Males
Females (follicular)
(luteal)
Prolactin (serum) - Males
Females
Prostate specific antigen (PSA)
Protein (serum) - Total
Albumin
Protein (urine)
Prothrombin time (PT)
Reticulocvtes
Sedimentation rate (ESR)
Sodium (serum or plasma)
Sodium {urine)***
Specific gravity
Sperm count
Testosterone - Males
Females
Pregnant females
Thrombin time (plasma)
Thyroid-stimulating horn1one (TSH) (serum) - Adults
-Term infants: (0-1 day)
(1-4 days)
(2-20 weeks)
(21 weeks to 20 years)
Thyroxine. total (T4) (serum)**
Thyroxine. free (FT4) (serum)**
Transaminase (serum)•· AST {SGOT)
ALT{SGPn
Triiodothvronine. total (T1) (serum)
Triiodothyronine. free (FT,) (serum)
Triglycerides
Urea (plasma or serum)
Urea nitrogen (BUN) {plasma or serum)
Uric acid (serum) (enzymatic)
*Test values are method dependent "*Test values vary with age
SI Units
3.5-12.0 x IO'/L
'
Traditional Units
3500-12.000/mm'
3000-5800 x 10°/L
3000-5 800/mm'
1500-3000 x 10°/L
1500-3000/mm'
300-500 x I0°/L
300-500/mm'
50-250 x I0°/L
50-250/mm'
15-50 x 10°/L
15-50/mm'
< 3.4 mmol/L
< 130 mg/dL
1-9 IU/L
1-9 IU/L
2-10 TU/L
2-10 IU/L
15-65 IU/L
15-65 IU/L
l-121U/L
1-12 IU/L
12-65 IU/L
12-65 IU/L
0.65-1.05 mmol/L
1.3-2.1 mg/dL
3.0-4.3 mmol/d
6.0-8.5 mEq/24h
76-100 tL
76-100 µm'
285-295 mmol/kg
285-295 mOsm/kg
38-1400 mmol/kg
38-1400 mOsm/kg
94-99%
94-99%
1.4-6.8 pmol/L
13.2-64.1 o!!/mL
See aPTT
See aPTT
35-45 mm Hg
35-45 mm Hg
7.35-7.45
7.35-7.45
40-160 TU/L
40-160 U/L
1.0-1.5 mmol/L
3.0-4.5 mg/dL
1.3-2.3 mmol/L
150-400 X I09/L
4.0-7.0 mg/dL
150.000-400.000/mm'
80-100 mm Hg
80-100 mm Hg
3.7-5.9 mmol/L
3.7-5.9 mEq/L
4.1-5.3 mmol/L
4. 1-5.3 mEq/L
3.4-4.7 mmol/L
3.4-4.7 mEq/L
3.5-5.1 mmol/L
3.5-5.1 mEq/L
25-125 mmol/d
25-125 mEq/24h
0.0-1.3 nmol/L
0.0-0.4 ng!mL
0.3-4.8 nmol/L
0.1-1.5 ng/mL
8.0-89.0 nmol/L
2.5-28.0 ng/mL
1-20 flg/L
1-20 ng/mL
1-25 µg/L
1-25 ng/mL
0-4.0 ug/L
0-4.0 ng/mL
60-80 g/L
6.0-8.0 g/dL
35-55 g/L
3.5-5.5 g/dL
10-150 mg/d
I0-150 mg/24h
9-12 sec
9-12 sec
25-75 x 10'/L
25.000- 75.0001mm'
0-15 mm/h
0-15 mm/h
135-145 mmol/L
135-145 mEq/L
40-220 mmol/d
40-220 mEq/24h
1.003-1.030
1.003-1.030
20-150 X )0°/mL
20.000-150.000/mm'
9.5-30 nmol/L
275-875 ng/dL
0.8-2.6 nmol/L
23-75 ng/dL
1.3-6.6 nmol/L
38-190 ng/dL
< 17 sec
< 17 sec
0.4-4.8 mlU/L
0.4-4.8 mIU/L
1-39 mIU/L
1-39 mIU/L
1-17 mIU/L
1-17 mlU/L
1.7-9.1 m.lU/L
1.7-9.1 mlU/L
0.7-6.4 m!U/L
0.7-6.4 mIU/L
66-155 nmol/L
5-12 ug/dL
13-27 pmol/L
1.0-2.1 ng/dL
7-40 IU/L
7-40 mU/mL
5-35 IU/L
5-35 mU/mL
1.1-2.9 nmol/L
70-190 ng/dL
3.5-6.5 pmol/L
2.4-5.0 og/mL
0.45-1.71 mmol/L
40-150 mg/dL
2.9-8.2 mmol/L
see Urea nitrogen
see Urea
8-23 mg/dL
120-420 (lmol/L
2.0-7.0 mg/dL
***Test values are dtet dependent
Page 7





