 |
BPP521S - BASIC PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - 1ST OPP - NOV 2022 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
nAmlBIA UnlVERSITY
OF SCIEnCE Ano TECHnDLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,APPLIEDSCIENCESAND NATURALRESOURCES
DEPARTMENTOF HEALTHSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION : BACHELOROF SCIENCEIN HEALTHINFORMATION SYSTEMMANAGEMENT
QUALIFICATIONCODE: 07BHIS
COURSENAME: BASIC
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
SESSION:NOVEMBER 2022
LEVEL: 5
COURSECODE: BPP521S
PAPER:THEORY
DURATION: 3 HOURS
MARKS: 100
EXAMINER:
FIRSTOPPORTUNITYEXAMINATION QUESTIONPAPER
Dr Roswitha Mahalie
MODERATOR: Dr Elizabeth Van Der Coif
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2. Write clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. Write all answers in the answer booklet provided.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
1. SCIENTIFICCALCULATOR.
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF 6 PAGES{Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTIONA
QUESTION 1
[15 MARKS]
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate answer or
phrase from the given possibilities. Each question carries 1- mark.
(15)
1.1 Small ulcers that occur singly or in groups on the inside of the cheek, lip or underneath the
tongue are called:
A. Mumps
B. Aphthae
C. Vincent Disease
D. Aphthous stomatitis
1.2 A patient with a moon face, cervical fat pad, central obesity, thin extremities, weight gain, thin
skin, striae, hypertension, and hyperglycemia, has which disease
A. Addison's Disease
B. Cushing Syndrome
C. Conn Syndrome
D. Diabetes lnsipidus
1.3 The death unwanted cells resulting from activation of intracellular signalling cascades is
referred to as:
A. Anaplasia
B. Apoptosis
C. Chloasma
D. Melasma
1.4 Detached intravascular solid, liquid, or gaseous mass that is carried in the circulation to a site
distant from its point of origin where it often causes tissue dysfunction is referred to as:
A. Thrombosis
B. Embolism
C. Infarction
D. Oedema
1.5 An overall weight loss and generalized weakness in the body is also referred to as?
A. Hypolipidemia
B. Cachexia
C. Intracellular accumulation
D. adipose tissue disorder
1.6 An overactive thyroid gland is referred to as:
A. Graves disease.
B. Cretinism.
C. Myxoedemma.
D. Diabetes lnsipidus.
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.7 A replacement of a mature
A. Dysplasia
B. Hyperplasia
C. Hypertrophy
D. Metaplasia
cell type by a different
mature cell type, is called:
1.8 An active process resulting from arteriolar dilation and increased blood flow to an organ is
called:
A. Viremia
B. Osmosis
C. Hyperemia
D. Haemostasis
1.9 Inflammation of the testis caused by trauma or the reflux of sterile urine up the vas
deferens is called:
A. Cryptorchidism
B. Epididymitis
C. Epididymosis
D. Fournier gangrene
1.10 Increased amount and duration of menstrual flow, is called:
A. Oligomenorrhea
B. Menorrhagia
C. Metrorrhagia
D. Polymenorrhagia
1.11 Which of the following
A. Referred pain
B. Acute pain
C. Transient pain
D. Phantom pain
is known as a short episode of pain:
1.12 Ringing, buzzing or whistling noise heard in the ear resulting when the acoustic never
transmits nerve impulses to the brain in the absence of vibrations from external sources is
called
A. Hearing Loss
B. Tinnitus
C. Tinalgia
D. Otitis Media
1.13 _____
occurs when the placenta is implanted over the cervical os is called:
A. Abruptio placentae
B. Placenta absentia
C. Placenta previa
D. Placentarhagia
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.14 The cardinal signs of inflammation
A. Loss of function (functio laesa)
B. Redness (rubor)
C. Necrosis (dead cells)
D. Pain (dolor)
include all except:
1.15 The farsightedness associated with aging:
A. Myopia
B. Presbyopia
C. Astigmatism
D. Nystagmus
QUESTION 2
[10 MARKS]
Assess the following statements and decide whether they are True or False. Each question earns 1
mark.
2.1 Cranial nerves take impulses to and from the brain while spinal nerves take impulses to and
from the spinal cord.
2.2 When the cause of the disease is unknown it is called idiopathic.
2.3 The aetiology of oedema includes adipose tissue disorder, increased hydrostatic pressure
and hypoproteinemia.
2.4 The lower respiratory tract consists of the pharynx, trachea, the bronchial tree, and the
lungs.
2.5 Chemotaxis is the unidirectional attraction of leukocytes from vascular channels towards
the site of inflammation within the tissue space.
2.6 The pineal gland produces calcitonin.
2.7 Vasopressin causes milk ejection and contraction ofthe uterus in labour.
2.8 Saccular aneurysm appears only on one part or side of a vessel where the weakness is
found in the blood vessel.
2.9 Lesions in cerebrum lead to difficulty recognizing written words is referred to as alexia.
2.10 Frostbite is not an example of chemical injury.
QUESTION 3
[15 MARKS]
3.1 Match the appropriate answer from Column A with a meaning in Column B by inserting
the appropriate, e.g., 3.1.1 A. Each question earns 1 mark.
(10)
Nr
3.1.1
Item A
Bruit
3.1.2
Fomites
Item B
A. Involved in the development of
diseases based on the basic
reactions of cells and tissues to
abnormal stimuli.
B. A build-up of fatty deposits on the
walls of the coronary arteries.
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |
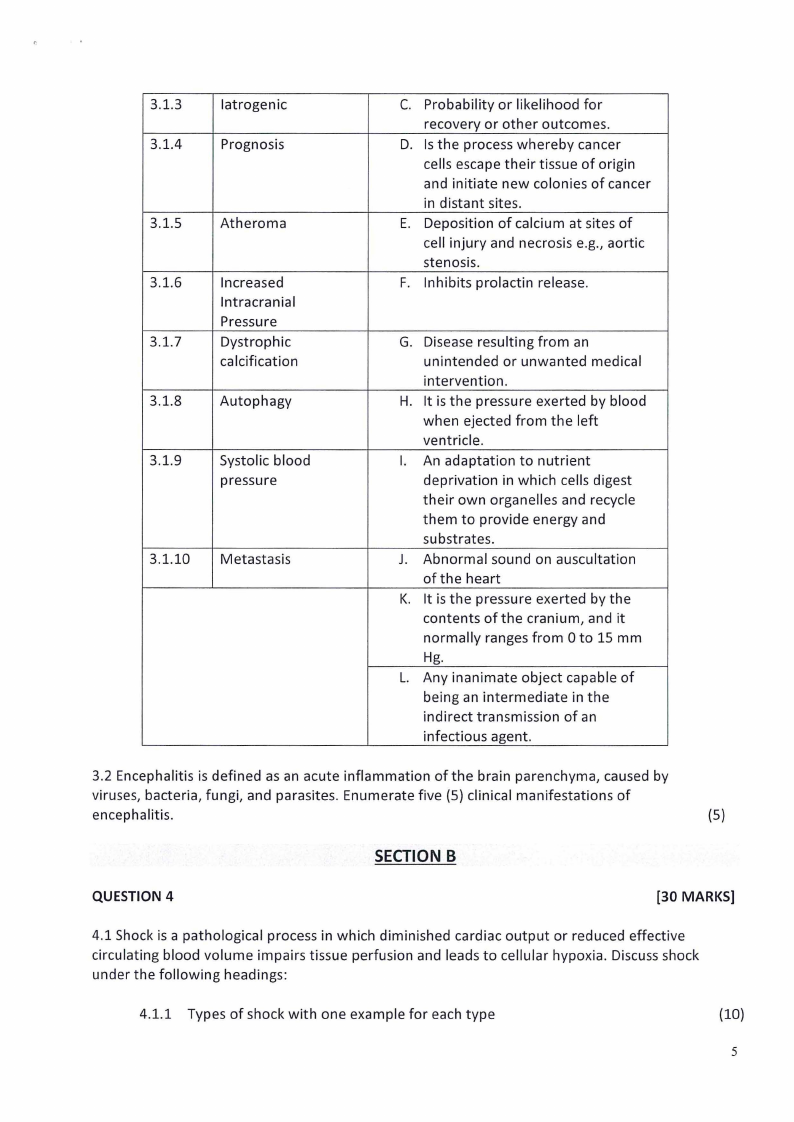
3.1.3
3.1.4
Iatrogenic
Prognosis
3.1.5
Atheroma
3.1.6
3.1.7
3.1.8
Increased
lntracranial
Pressure
Dystrophic
calcification
Autophagy
3.1.9
Systolic blood
pressure
3.1.10 Metastasis
C. Probability or likelihood for
recovery or other outcomes.
D. Is the process whereby cancer
cells escape their tissue of origin
and initiate new colonies of cancer
in distant sites.
E. Deposition of calcium at sites of
cell injury and necrosis e.g., aortic
stenosis.
F. Inhibits prolactin release.
G. Disease resulting from an
unintended or unwanted medical
intervention.
H. It is the pressure exerted by blood
when ejected from the left
ventricle.
I. An adaptation to nutrient
deprivation in which cells digest
their own organelles and recycle
them to provide energy and
substrates.
J. Abnormal sound on auscultation
of the heart
K. It is the pressure exerted by the
contents of the cranium, and it
normally ranges from Oto 15 mm
Hg.
L. Any inanimate object capable of
being an intermediate in the
indirect transmission of an
infectious agent.
3.2 Encephalitis is defined as an acute inflammation of the brain parenchyma, caused by
viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Enumerate five (5) clinical manifestations of
encephalitis.
(5)
SECTION B
QUESTION 4
[30 MARKS]
4.1 Shock is a pathological process in which diminished cardiac output or reduced effective
circulating blood volume impairs tissue perfusion and leads to cellular hypoxia. Discuss shock
under the following headings:
4.1.1 Types of shock with one example for each type
(10)
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |

4.1.2 Stages of shock
(6)
4.2 Briefly define the following concepts:
(7)
4.2.1 Extravasation:
(1)
4.2.2 Glasgow Coma Scale
(2)
4.2.3 Keloid
(2)
4.2.4 Cardiac Tamponade
(2)
4.3 One of the disease-causing microorganisms is bacteria. Describe the characteristics of
bacteria and provide an example of each type.
(7)
QUESTION 5
SECTION C
[30 MARKS]
5.1 Fractures is a break in the rigid structure and continuity of a bone as a result of direct, indirect
trauma, underlying disease or repeated stress on a bone. Describe the phases of fracture
healing and the bone activity that takes place during the healing process.
(15)
5.2 Ms. Bevel, a 45-year-old mother of 4 children, obtained burn wounds when their
corrugated house caught fire whilst they were all asleep. The whole family was rescued
from the house, but she had burns on her upper/mid/low back, buttocks, left arm and
both legs. Her 10-year-old daughter Britney had burn wounds on her left arm, foot and
both legs. It was determined by the paramedics that Ms. Bevel had full-thickness burns
and her daughter second degree burns.
5.2.1 Using the rules-of-nines, calculate the approximate area of full-thickness burns on
her on her left arm, upper/mid/low back, buttocks and both legs.
(5)
5.2.2 What measurement assessment will you use to determine the percentage area
burnt in Britney?
(1)
5.2.3 Use the measurement identified in 5.2.2 and calculate the percentage burn wounds
of Britney.
(6)
5.2.4 State the reasons why full-thickness burns are considered more serious than
second-degree burns.
(3)
All the best!!!!
6





