 |
CMB521S-CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY-JAN 2020 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |
NAMIBIA UNIVERSITY
OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION : MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES
QUALIFICATION CODE: O8BMLS
LEVEL: 5
COURSE CODE: CMB521S
COURSE NAME: CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
SESSION:
JANUARY 2020
PAPER:
THEORY
DURATION:
3 HOURS
MARKS:
100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECOND OPPORTUNITY EXAMINATION PAPER
EXAMINER(S)
Ms EDWIG HAUWANGA
MODERATOR:
Ms VANESSA TJJJENDA
INSTRUCTIONS
Answer ALL the questions.
Write clearly and neatly.
Number the answers clearly.
Graph paper included
THIS QUESTION PAPER CONSISTS OF 7 PAGES (Including this front page)
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |

SECTION A (45 MARKS)
QUESTION 1
[15]
Evaluate the statements in each numbered section and select the most appropriate
answer or phrase from the given possibilities. Write the appropriate letter next to the
number of the statement/phrase.
1.1 The endoplasmic reticulum works closely with which of the following organelle to
carry out its function?
A)
Vacuole
B)
Lysosome
C)
Nucleolus
D)
Gogli Apparatus
1.2 Which of the following is not true about mitotic spindle but rather speaks of
(1)
contractile ring:
A)
Physically splits the cell in two
B)
Made of microtubles
C)
Duplicates chromosome
D)
Splits the nucleus in two
1.3 Identify the enzyme responsible for relaxing the DNA helix during replication
(1)
A)
Helicase
B)
Primase
C)
Ligase
D)
Topoisomerase
1.4 Identify the histone protein that pulls the nucleosomes together to complete the (1)
chromosomal structure
A)
H1
B)
H2A
C)
H2B
D)
H3
1.5
Functional sections of DNA molecule that code for a protein are defined as....
(1)
A)
Codon
B)
Exons
C)
Intron
D)
Promotor
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |

1.6 A macrophage is responsible for:
(1)
A) — Exocytosis
B) Vesicular Transport
C) Phagocytosis
D) —_Pinocytosis
1.7 Vesicular transport is between the endomembrane system, which of the following (1)
organelles form part of this system.
A) — Endoplasmic Reticulum
B) Gogli Apparatus
C) Plasma membrane
D) Lysosome
1.8 Identify the protein that is responsible for the identification of target organelles (1)
during vesicular transport?
A)
Rab proteins
B)
SNARE
C)
COPI coated proteins
D)
Clarithin coated proteins
1.9 Communication often involves converting signals that carry information from one (1)
form to another, this is known as.....
A)
Paracrine signalling
B)
Transduction signalling
C)
Endocrine signalling
D)
Neuronal signalling
1.10 The following molecules are all transported by active transport except...
(1)
A) Glucose
B) Amino acids
C) Potassium
D) Carbon Dioxide
1.11 Identify the cell adhesion molecule that form desmosomes
(1)
A)
Selectin
B)
Immunoglobulin
C)
Cadherin
D)
Integrin
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |

1.12 Label the following DNA structure according to the letters
1.12.1 A-
1.12.2 B-
1.12.3 C-
1.12.4 D-
QUESTION 2
[10]
Define the following terms:
1.1
Chromosome
1.2
Gene
(2)
1.3
Genome
(2)
1.4
Genetic code
(2)
1.5
Codon
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 3
[21]
3.1 Match the following statements in column B with the appropriate phases in column A,
on phase can represent more than one statement. Write the number representing the (10)
statement with the matching phase next to it.
Column A
3.1.1 Nucleus divides into two
3.1.2 Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and decondense
3.1.3 Chromosome becomes visible as they begin condensing
3.1.4 Mitotic spindle breaks down
3.1.5 Nuclear membrane starts disappearing
3.1.6 Chromatids split in two
3.1.7 Chromatid attach to spindle fibres
3.1.8 Chromatids pulled to opposite sides
3.1.9 Division of cytoplasm starts
3.1.10 Spindle fibres start to appear
B
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
3.2 Identify four scientist that played a significant role in the study of cells and state the
roles they each played.
(8)
3.3 What does the cell theory state?
(3)
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |
SECTION B (24 MARKS)
QUESTION 4
[14]
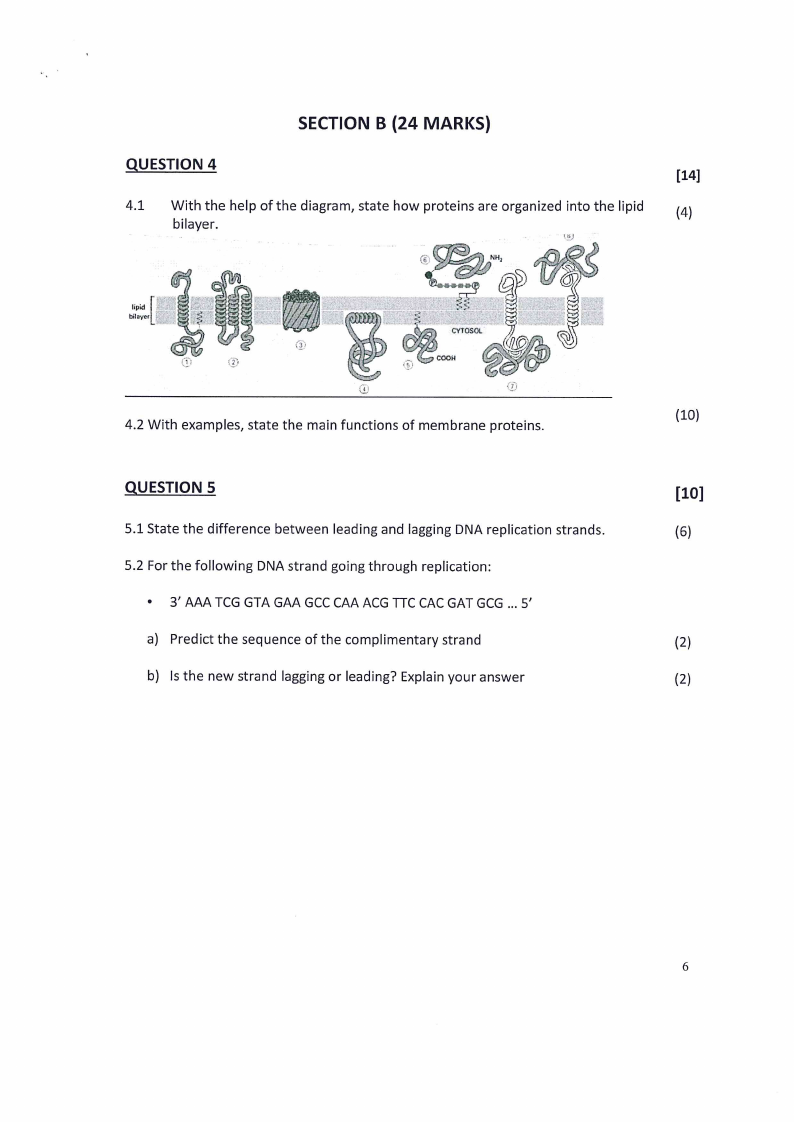
4.1 With the help of the diagram, state how proteins are organized into the lipid
(4)
bilayer.
pid |
bilayer]
RB
o Ris$
4.2 With examples, state the main functions of membrane proteins.
(10)
QUESTION 5
[10]
5.1 State the difference between leading and lagging DNA replication strands.
(6)
5.2 For the following DNA strand going through replication:
° 3’ AAATCG GTA GAA GCC CAA ACG TTC CAC GAT GCG... 5’
a) Predict the sequence of the complimentary strand
(2)
b) Is the new strand lagging or leading? Explain your answer
(2)
 |
7 Page 7 |
▲back to top |

SECTION C (31 MARKS)
QUESTION 6
[16]
6.1 Explain how the G-protein coupled receptor fulfils its role in cell signalling.
(8)
6.2 Explain the functions of the following proteins in translation:
(8)
6.2.1 Initiation factor 1 (IF1)
6.2.2 Initiation Factor 2 (IF2)
6.2.3 Initiation Factor 3 (IF3)
6.2.4 Elongation Factor Temperature stable (EFTs)
6.2.5 Elongation Factor Temperature unstable (EFTu)
6.2.6 Elongation Factor G (EFe)
6.2.7 Release Factor
6.2.8 Peptidyl Transferase
QUESTION 7
[15]
7.1 Explain the mechanisms a cell has in place to regulate cell division to ensure minimum
errors during the different phases.
THE END!





