 |
BPM821S - BIOSYNTHETIC PATHWAYS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY - 2ND OPP - JAN 2023 |
 |
1 Page 1 |
▲back to top |

nAmlBIA unlVERSITY
OF SCIEn CE Ano TECHn OLOGY
FACULTYOF HEALTH,NATURAL RESOURCESAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
DEPARTMENT OF NATURALAND APPLIEDSCIENCES
QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF SCIENCEHONOURS
QUALIFICATION CODE:08BOSC
LEVEL: 8
COURSENAME: BIOSYNTHETIC PATHWAYS AND COURSECODE: BPM821S
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
SESSION:JANUARY 2023
DURATION: 3 HOURS
PAPER:THEORY
MARKS: 100
SUPPLEMENTARY/SECONDOPPORTUNITY QUESTION PAPER
EXAMINER
DR LAMECH MWAPAGHA
MODERATOR: DR EMMANUEL NEPOLO
INSTRUCTIONS
1. Answer ALL the questions.
2-. \\A(nte clearly and neatly.
3. Number the answers clearly.
4. All written work MUST be done in BLUEor BLACKink.
PERMISSIBLEMATERIALS
None
THIS QUESTION PAPERCONSISTSOF FIVE (5) PAGES
(Including this front page)
1
 |
2 Page 2 |
▲back to top |
QUESTION 1
[16]
a) The Tricarboxylic acid cycle is a source of biosynthetic precursors. Provide SIX (6)
metabolic precursors and from each give ONE (1) example of an amino acid they lead to. (6)
b) Briefly describe the following databases:
(6)
I. Genbank database;
II. SNPs database;
Ill. PrimerBank;
IV. UniProt database;
V. RefSeq database;
VI. PlasmoDB;
c) What are some of the strategies you could use in designing universal primers?
(4)
QUESTION 2
[16]
a) Describe THREE (3) specific tasks that are generally tackled by computational tools used
in integrating 'omics' data.
(3)
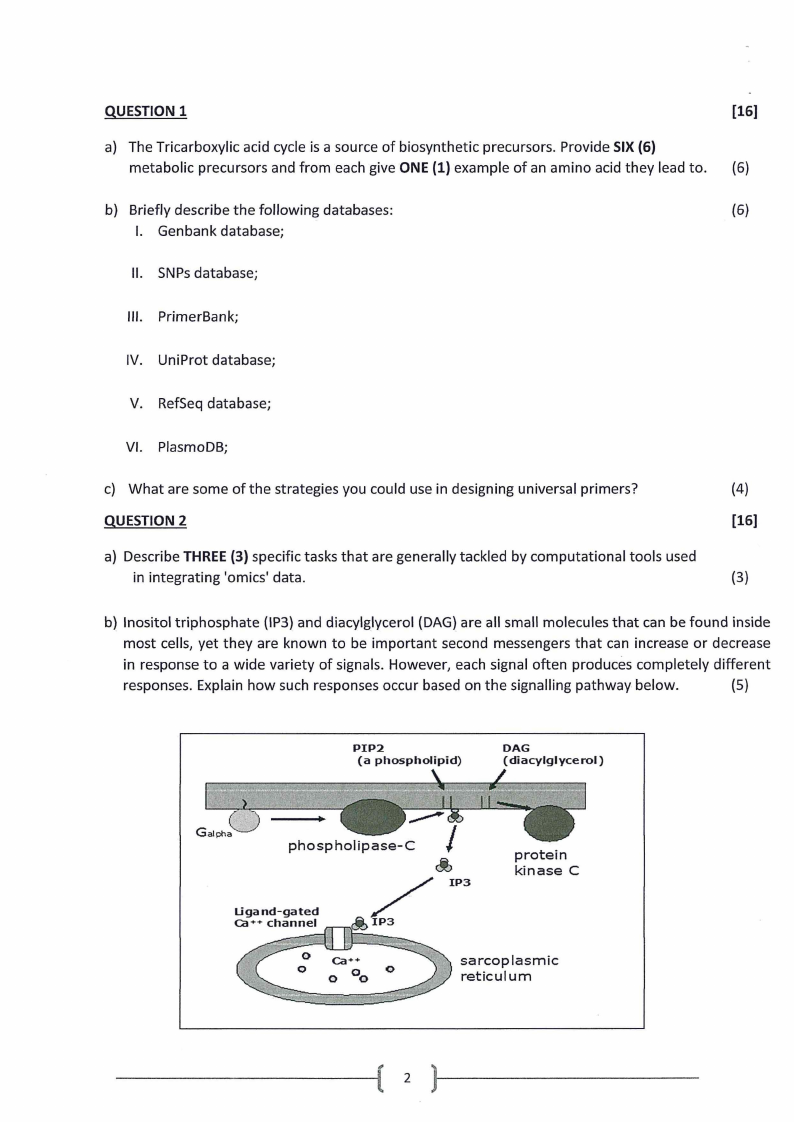
b) Inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) are all small molecules that can be found inside
most cells, yet they are known to be important second messengers that can increase or decrease
in response to a wide variety of signals. However, each signal often produces completely different
responses. Explain how such responses occur based on the signalling pathway below.
(5)
I)
PIP2
(a phospholipid)
\\
phospholipase-C
---:1~
I
<i>
/
IP3
DAG
(diacylglycerol)
protein
kinase C
~IP3
sarcoplasmic
reticulum
2
 |
3 Page 3 |
▲back to top |
c) Discuss signal transduction
(8)
QUESTION 3
[14)
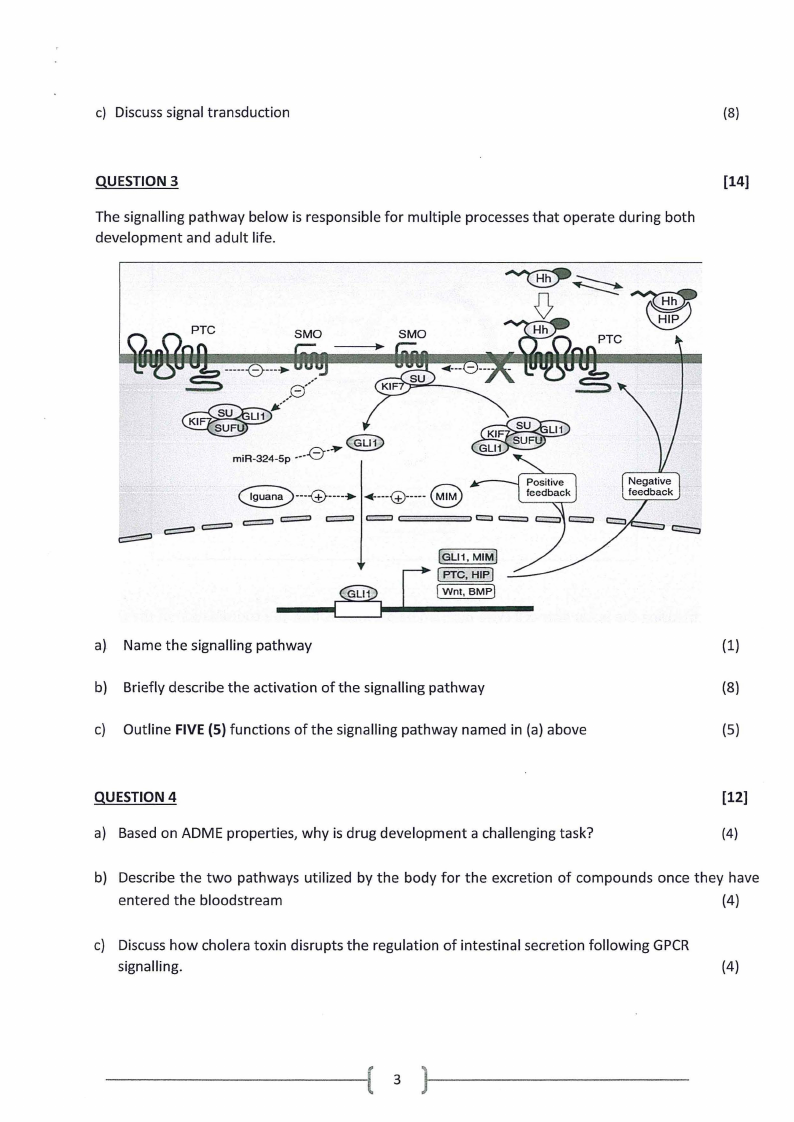
The signalling pathway below is responsible for multiple processes that operate during both
development and adult life.
SMO
_e··
---
_,... G
miR-324-Sp ---0
~----©----•
(§)
=
a:::::=' c::==> c:==> c::==> c==J c==> c:::::====>
----1 r (§u!)
[GL11, MIMI
[PTC,HIPj
[ Wnt, BMPJ
jll1 ----------
a) Name the signalling pathway
(1)
b) Briefly describe the activation of the signalling pathway
(8)
c) Outline FIVE (5) functions of the signalling pathway named in (a) above
(5)
QUESTION 4
[12)
a) Based on ADME properties, why is drug development a challenging task?
(4)
b) Describe the two pathways utilized by the body for the excretion of compounds once they have
entered the bloodstream
(4)
c) Discuss how cholera toxin disrupts the regulation of intestinal secretion following GPCR
signalling.
(4)
3
 |
4 Page 4 |
▲back to top |
QUESTIONS
[16)
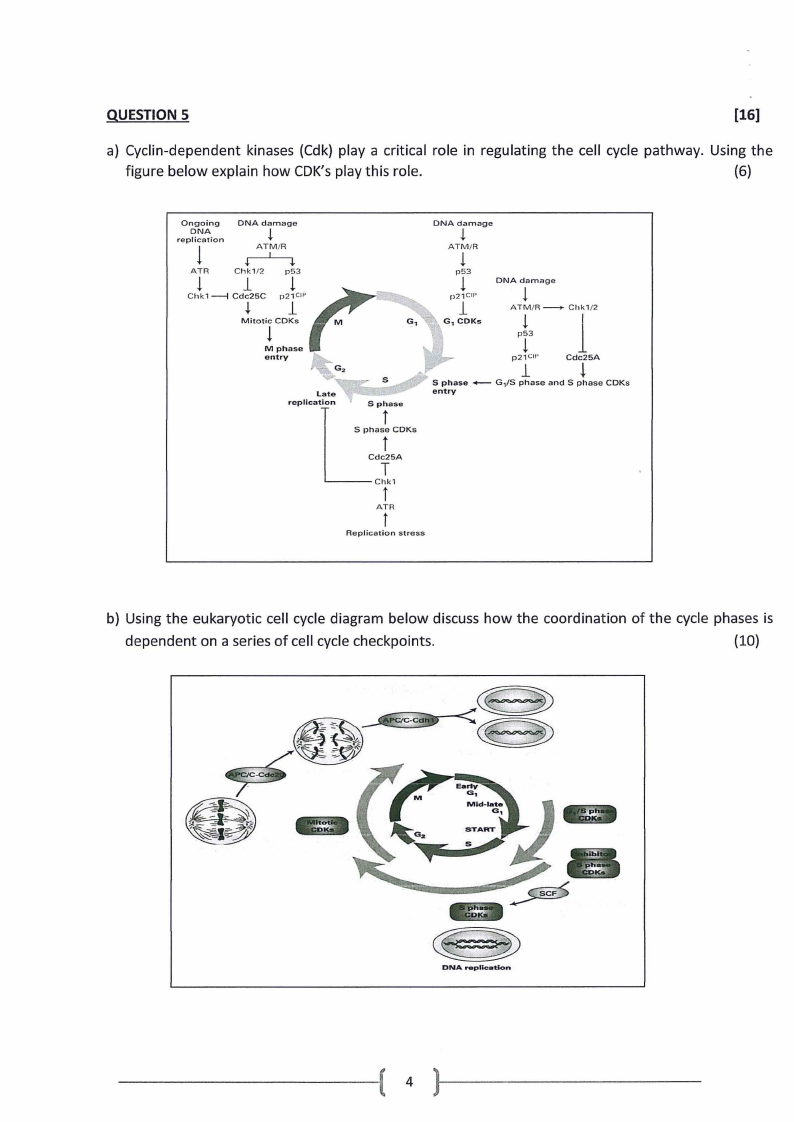
a) Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk) play a critical role in regulating the cell cycle pathway. Using the
figure below explain how CDK'splay this role.
(6)
Ongoing
DNA
replication
1
ATR
!
Chkl --l
DNA damage
DNA damage
!
!
ATM/R
ATM/R
.j, I l
!
Chkl/2
p53
p53
1
Cd125C
!
p2lCIP
Mitotic CDKs
M
!
M phase
entry
!
p21CIP
1
DNA damage
!
ATM/R--+-
!
p53
!
p21c1p
Chkl/2
1
Cdc25A
::r::~ Late
replicatL;°"'
phase 1 ! 5
-+-- G 1/S phase and S phase CDKs
entry
Cdc25A
T
Chkl
i
ATR
t
Replication stress
b) Using the eukaryotic cell cycle diagram below discuss how the coordination of the cycle phases is
dependent on a series of cell cycle checkpoints.
(10)
DNA repllcatJon
4
 |
5 Page 5 |
▲back to top |

QUESTION 6
[14)
a) State FOUR (4) characteristics of an ideal screening Biomarker
(4)
b) Give a detailed description of the TNM system of staging cancers
(10)
Based on:
T- Extent of the tumour (Size, in cm)
N- Extent of spread to the lymph nodes
M- Presence or absence of metastasis
QUESTION 7
[12)
a) Deduce why Hela cells being cancer cells are useful for research into anything other than
cancer?
(2)
b) Briefly describe the following hallmarks of cancer;
(10)
I. Enabling replicative immortality;
II. Evading Immune Destruction;
Ill. Tumour-promoting inflammation;
IV. Sustaining proliferative signalling;
V. Inducing angiogenesis;
THEEND
5
 |
6 Page 6 |
▲back to top |






